JWT
What is JWT (JSON Web Token) ?
JWT (JSON Web Token) is a compact, secure way to transmit data as a JSON object, commonly used for authentication and authorization.
While anyone can decode a JWT, only the server with the secret key can verify its validity, ensuring secure and efficient communication.
Example...
Think of a locker key at a gym. Anyone can see the locker number, but only the correct key can unlock and verify access to that locker.
How JWT Works ?
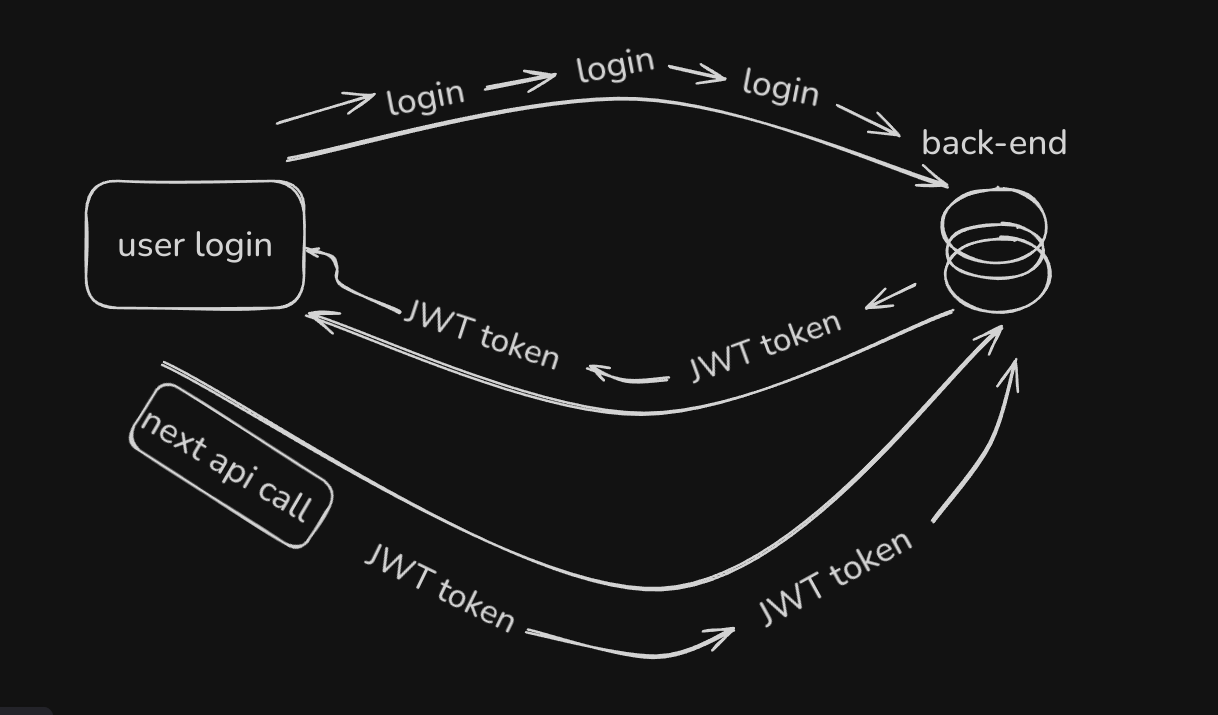
1. User Login:
- User provides valid credentials (e.g., email and password).
- Server validates the credentials and generates a JWT containing user information.
2. Token Sent to Client:
- The server sends the JWT to the client (usually stored in localStorage, cookies, or memory).
3. Client Sends JWT:
- The client includes the JWT in the Authorization header of API requests.
4. Server Verifies Token:
- The server verifies the token's signature using a secret key.
- If valid, the user is granted access; otherwise, access is denied.
A JWT (JSON Web Token) is essentially a string composed of three parts, separated by dots (.)
- Header: Contains metadata, like the type of token (JWT) and the signing algorithm (e.g., HS256).
- Payload: Contains the data (claims) being transmitted, such as user information or token expiration.
- Signature: A cryptographic hash generated using the header, payload, and a secret key to verify the token's integrity.

Use Cases of JWT
1. User Authentication.
2. Authorization.
3. Stateless Authentication:
- JWT is stateless. The server does not need to store session data; all the necessary information is inside the token.
4. Secure API Communication:
- Used in REST APIs to validate requests from users.
Implementation of JWT
1. install jsonwebtoken
npm install jsonwebtoken
2. Generate a JWT (Sign a Token)
import jwt from jsonwebtoken
const user = { id: 1, username: "mannu" };
const secretKey = "aabra_ka_dabara"; // here you add your secrete key or fetch from the environment file.
const token = jwt.sign(user, secretKey, { expiresIn: '1h' });
res.setHeader( "Authorization", `Bearer ${token} ) .
console.log("Generated Token:", token);
1. Import the library:
- It uses jsonwebtoken to work with JWTs.
2. Create user data:
- The user object has some basic details, like ID and username.
3. Set a secret key:
- The secretKey is like a password used to lock (sign) the token securely.
4. Generate the token:
- The jwt.sign function creates a token containing the user info. It also sets an expiry time of 1 hour (expiresIn: '1h').
5. Add Token to Response Header:
- The token is added to the Authorization header with the prefix Bearer, a convention used to indicate the token belongs to a specific user.
Verify JWT with test api.
import jwt from "jsonwebtoken";
server.get("/test", (req, res) => {
const token = req.headers.authorization;
if (!token) {
return res.status(401).json({
success: false,
message: "Authorization failed",
});
}
const tokenValue = token.split(" ")[1];
try {
const decoded = jwt.verify(tokenValue, "secrete_token");
return res.json({
success: true,
message: "Token is valid",
});
} catch (err) {
return res.status(401).json({
success: false,
message: "Token is invalid",
});
}
});
1. JWT Import:
- The jsonwebtoken library is imported to handle JWT operations.
2. Defining the /test Endpoint:
- A GET endpoint listens for requests at /test.
3. Checking for Token:
- The
Authorizationheader is checked. - If it's missing, the server responds with a 401
Unauthorizedand a failure message.
4. Extracting the Token Value:
- The token is typically sent as
Bearertoken. - The code
extractstokenby splitting the Authorization header on the space.
5. Verifying the Token:
- The
jwt.verify()function checks the token against the secret key ("secrete_token"). - If valid, a success
response is returned. - If invalid, an error is caught, and the server
responds with 401Unauthorizedand an invalid token message.