Introduction to Backend (ExpressJS)
Backend development
Backend development refers to the server-side part of web development. It involves creating and maintaining the server, application, and database that together make up the core of a web application. While users interact with the frontend (what they see and use), the backend is responsible for ensuring everything works behind the scenes.
Need of backend 👉
- Managing database operations.
- Handling business logic.
- Role-based authentication.
- Serving responses to the client side.
Managing Database Operations: The backend manages how data is stored, retrieved, updated, and deleted in the database. It ensures data is organized and accessible for the application to use.
Handling Business Logic: Backend processes and applies rules to data. It performs calculations, makes decisions based on rules (like pricing or discounts), and ensures data is accurate and valid.
Role-based authentication : The backend controls who can access what in the application. It verifies user identities, assigns roles (like admin or user), and allows different levels of access based on those roles.
Serving responses to the client side: The backend responds to requests from the client (like a web browser) with the right information. It formats data into a usable form (like JSON), handles errors, and ensures the client gets what it needs to display or use.
API ( Application Programming Interface)
An API, or Application Programming Interface, is a set of rules and protocols that allows different software applications to communicate with each other. It works like a middleware.
Some Important Features of an API:
Endpoints: APIs define specific endpoints (URLs) that represent different functionalities or resources.
Methods: APIs specify the methods or actions that can be performed on each endpoint.
Common methods include:
GET: Retrieves data from a server.
POST: Sends data to a server to create or update a resource.
PUT Updates an existing resource on a server.
DELETE: Deletes a resource from a server.
PATCH: Partially updates an existing resource on a server.
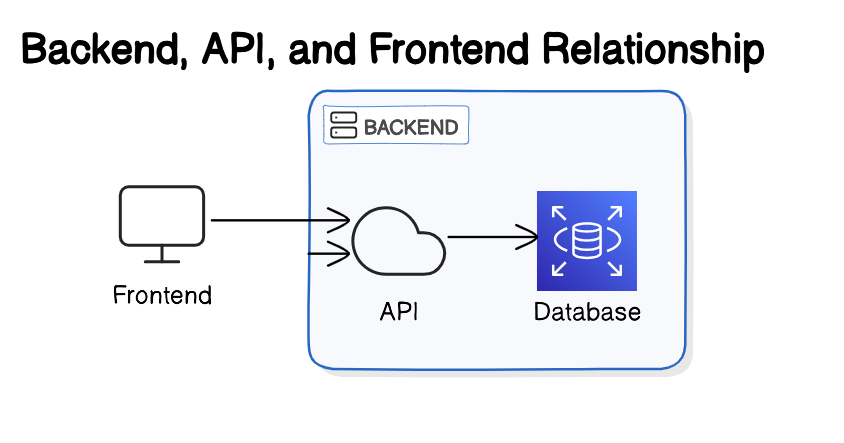
Example to explain the relation between api, frontend and backend :
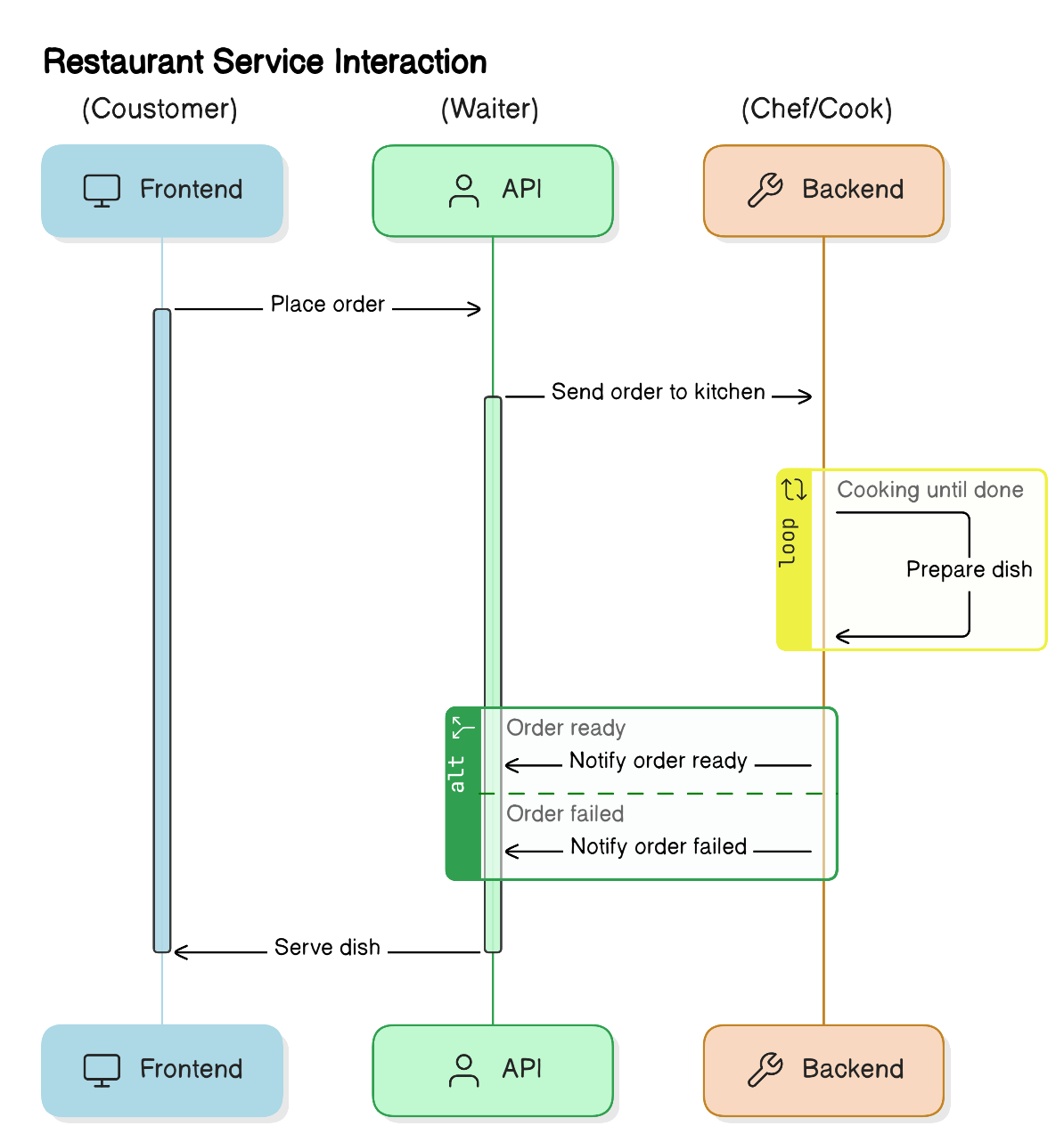
Assume the backend is the Chef in a Hotel Kitchen, the front end is the Hotel Dining Area and the API is the Waiter in the Hotel.
Backend (Chef in a Hotel Kitchen):
The back end of a hotel operates like a kitchen where all the cooking, preparation, and ingredients management happen.
Frontend (Hotel Dining Area): The frontend of the hotel is like the dining area where guests interact directly with the hotel's services.
API (Waiter in the Hotel): The API in the hotel is like the waiter who acts as an intermediary between guests (frontend) and the kitchen (backend). It manages communication and requests to the chef or it takes orders from guests and gives them to the chef in the hotel.
In summary, the frontend is like the dining area where guests choose what they want to eat; it shows the menu and takes orders. The backend is like the kitchen where the chef prepares the meals; it handles all the cooking and preparation. The API is like the waiter who takes the guests' orders to the kitchen and brings the prepared food back to the guests. This shows how the frontend (dining area), backend (kitchen), and API (waiter) work together to serve the guests efficiently.