Four Pillars 0f OOPs
There are Four Pillars in Python
- Inheritance
- Encapsulation
- Abstraction
- Polymorphism
Inheritance
Inheritance means deriving properties of one class into another class.
The class whose properties are being derived is called as Parent Class or Super Class or Base class and class which derives the properties of base class is called as Child Class or Sub Class or Derived Class.
Syntax :
class BaseClass:
.....
.....
class DerivedClass(BaseClass):
.....
.....
Types of Inheritance :
There are four types of inheritance in Python Programming:
- Single inheritance
- Multiple inheritances
- Multilevel inheritance
- Hierarchical inheritance
1. Single inheritance :
Single inheritance means, when a derived class derives one base class.
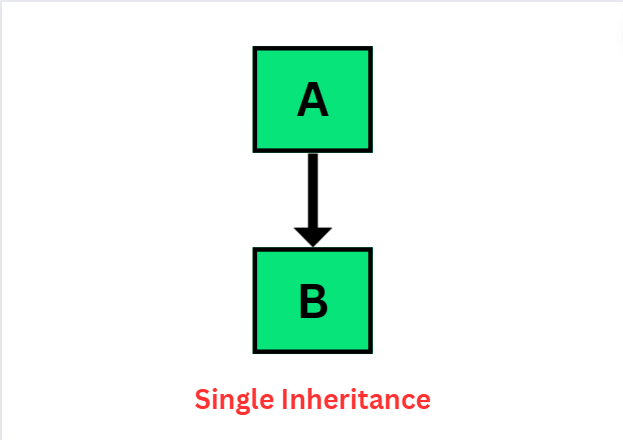
Example :
class A:
def showA(self):
print("I am ShowA")
class B(A):
def showB(self):
print("I am ShowB")
objB = B()
objB.showA()
objB.showB()
Output :
I am ShowA
I am ShowB
Example Exaplanation :
In the above example, we are creating the A class in that class to create the showA() function with the pass self parameter. Similarly, we are creating the B class in that class to create the showB() function here class B inherit class A.
So, we create only a B object that is objB and call both functions from one object objB.
2. Multilevel inheritance :
Multilevel Inheritance means when a derived class become base class of another class.
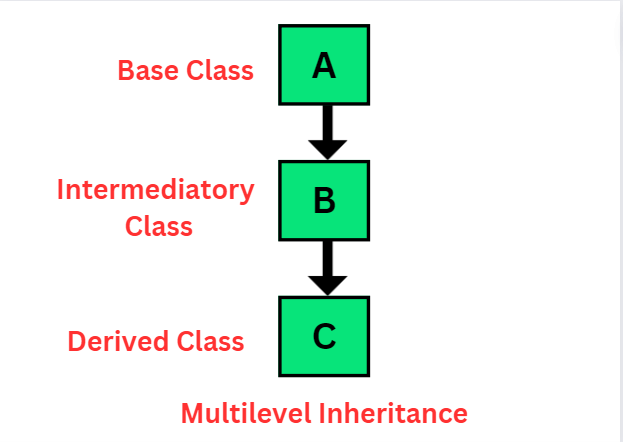
Example :
class A:
def showA(self):
print("This is show A")
class B(A):
def showB(self):
print("This is show B")
class C(B):
def showC(self):
print("This is show C")
objC = C()
objC.showA()
objC.showB()
objC.showC()
Output :
This is show A
This is show B
This is show C
Example Exaplanation :
In the above example, we are creating the A class in that class to create the showA() function with the pass self parameter. Similarly, for class B & class C we are creating the B & C class in that class to create the showB() & showC function here class B inherit class A and class C inherit class B respectively.
So, we create only a C object that is objC and call all the functions from one object objC.
3. Multiple inheritance :
When a class can be derived from more than one base class this type of inheritance is called multiple inheritance.
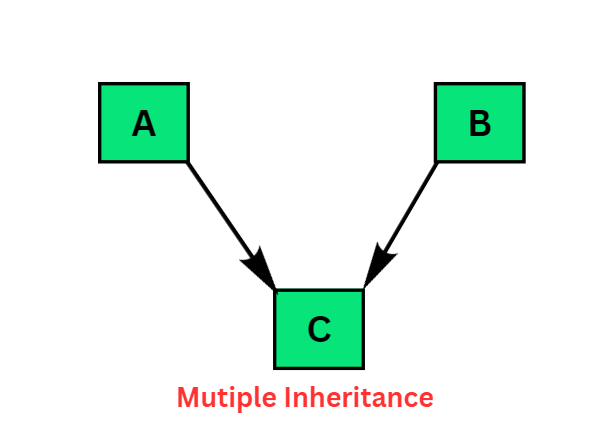
Example :
class Mother:
def showMotherName(self):
print("Mother Name is ABC")
class Father:
def showFatherName(self):
print("Father Name is PQR")
class child(Mother,Father):
def showChildName(self):
print("I am Child")
obj = child()
obj.showMotherName()
obj.showFatherName()
obj.showChildName()
Output :
Mother Name is ABC
Father Name is PQR
I am Child
Example Exaplanation :
In the above example, we are creating the Mother class in that class to create the showMotherName() function with the pass self parameter. Similarly, for class Father & class Child we are creating the Father & Child classes in that class to create the showFatherName() & showChildName() functions here class Child inherit both the classes that is class Mother and class Father respectively.
So, we create only a Child object that is obj and call all the functions from one object obj.
4. Hierarchical inheritance :
When more than one derived classes are created from a single base this type of inheritance is called hierarchical inheritance.
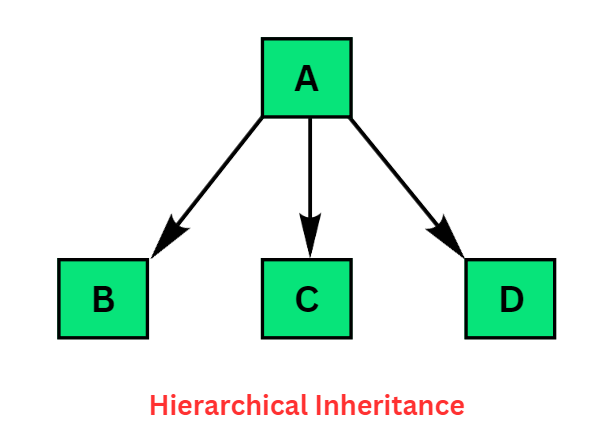
Example :
class parent:
def showParent(self):
print("Mother Name : ABC")
print("Father Name : PQR")
class A(parent):
def showName(self):
print("A")
class B(parent):
def showName(self):
print("B")
class C(parent):
def showName(self):
print("C")
objA = A()
objA.showName()
objA.showParent()
objB = B()
objB.showName()
objB.showParent()
objC = C()
objC.showName()
objC.showParent()
Output :
A
Mother Name : ABC
Father Name : PQR
B
Mother Name : ABC
Father Name : PQR
C
Mother Name : ABC
Father Name : PQR
Example Exaplanation :
In the above example, we are creating the Parent class in that class to create the showParent() function with the pass self parameter. Similarly, for class A, class B & class C we are creating the A, B & C classes in that classes to create the showName() functions here class A, class B and class C inherit class Parent respectively.
So, we create the object for class A that is objA, for class B that is objB & for class C that is objC. And most important we are calling the class Parent function in them.
Encapsulation
Encapsulation is one of the fundamental principles of object-oriented programming (OOP) and is commonly used in Python. It is used to binding similar data and its functionality.
Example :
class helper:
def cal_si(self, p ,r, t):
si = (p*r*t)/100
print(si)
def cal_area(self,l,b):
area = l * b
print(area)
class bank:
def loan(self):
print("Loan")
obj1 = bank()
obj1.loan()
obj2 = helper()
obj2.cal_si(5000,3,2)
obj2.cal_area(10,20)
Output :
Loan
300.0
200
Example Exaplanation :
In the above example, we create class helper in that class create one function cal_si() this function carries default parameter self & p, r &t also pass then print si.
we create a second function cal_area() this function also carries the self default parameter as well as l & b and then print area.
we are creating class bank in this class create function loan with self parameter & print "Loan".
create the object for class bank that is obj & calling the loan function. again create the object for class helper that is obj2 & calling the cal_si() function with parameter p, r & t values, calling cal_area() function with parameter l & b values.
Abstraction
Show the necessary things and hiding unnecessary information from the user.
Example :
class student :
studentName = ''
def getStudent(self):
self.studentName = input("Enter Name :")
def showStudent(self):
print("Student Name :", self.studentName)
obj = student()
obj.getStudent()
obj.showStudent()
Output :
Enter Name :pinki
Student Name : pinki
Example Exaplanation :
In the above example, we create one class student in that class and create the variable studentName. here two function getStudent() & showStudent(). In the getStudent() function we access the variable studentName with the self parameter & In the showStudent() function we print them.
create the object for the student class that is obj and call both the functions that are getStudent() & showStudent().
Polymorphism
Polymorphism in python defines methods in the child class that have the same name as the methods in the parent class.
Example :
class Cat :
def speak(self):
print("Meowwwww^$%^$^$^%")
class Dog :
def speak(self):
print("BHoooooo!")
obj1 = Cat()
obj1.speak()
obj2 = Dog()
obj2.speak()
Output :
Meowwwww^$%^$^$^%
BHoooooo!
Example Exaplanation :
In the above example, we create classes cat and dog in both classes we pass the same function that is speak() with the self parameter, and create the object for both classes obj1 & obj2 respectively.