Creating Student Server
Creating a Basic Express Server in Node.js
In this section, we'll create a basic Express server in Node.js. This server sets up a foundation for a RESTful API to manage student data.
import express from 'express';
const app = express()
app.use(express.json())
const PORT = 5000;
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server is running on port ${PORT}.`)
})
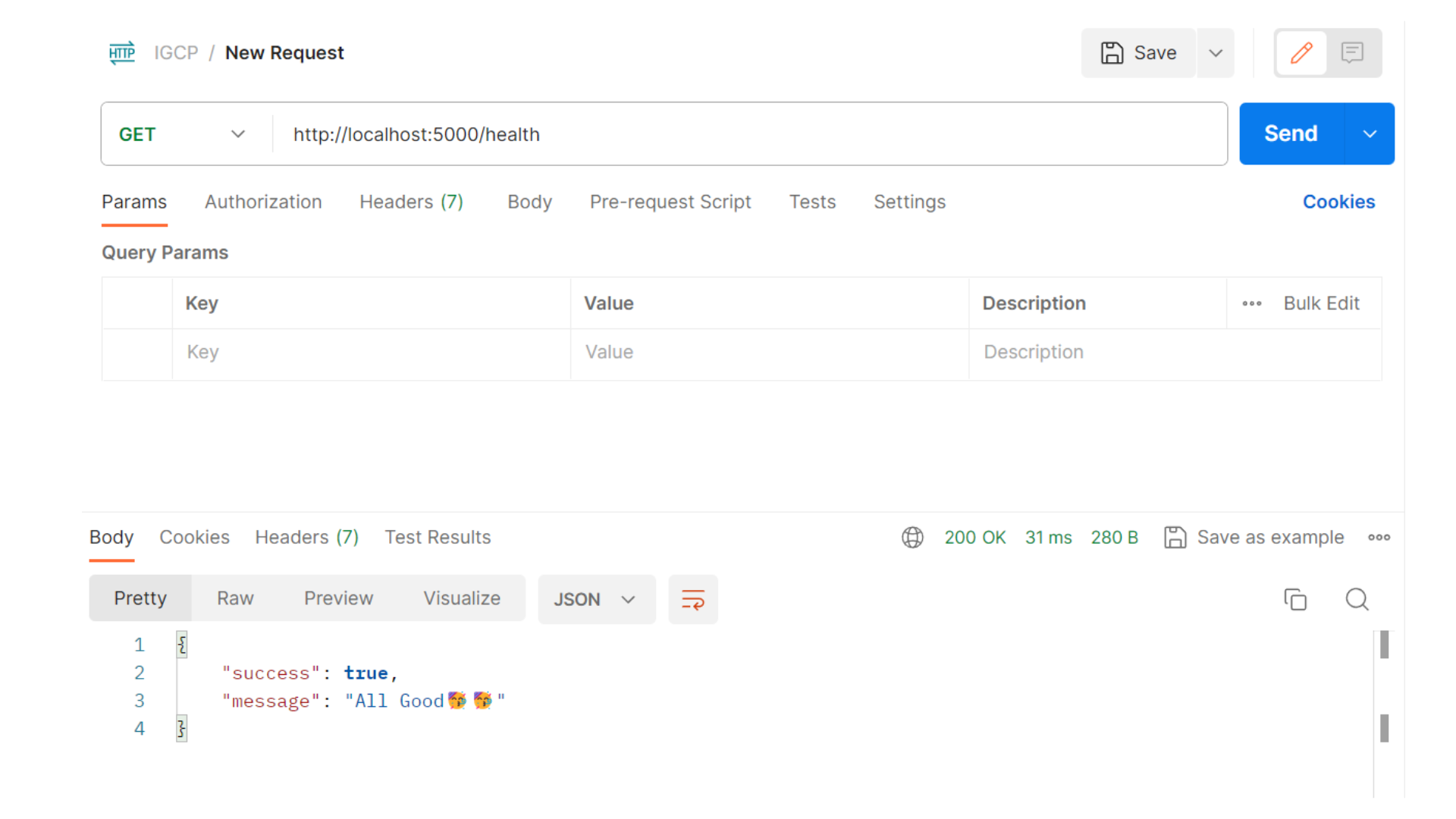
Health Check API
Let's start by implementing a simple health check API endpoint that confirms the server is running smoothly.
import express from 'express';
const app = express()
app.use(express.json())
const PORT = 5000;
app.get('/health', (req, res) => {
res.json({status: 'All Good!'})
})
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server is running on port ${PORT}.`)
})
Output:
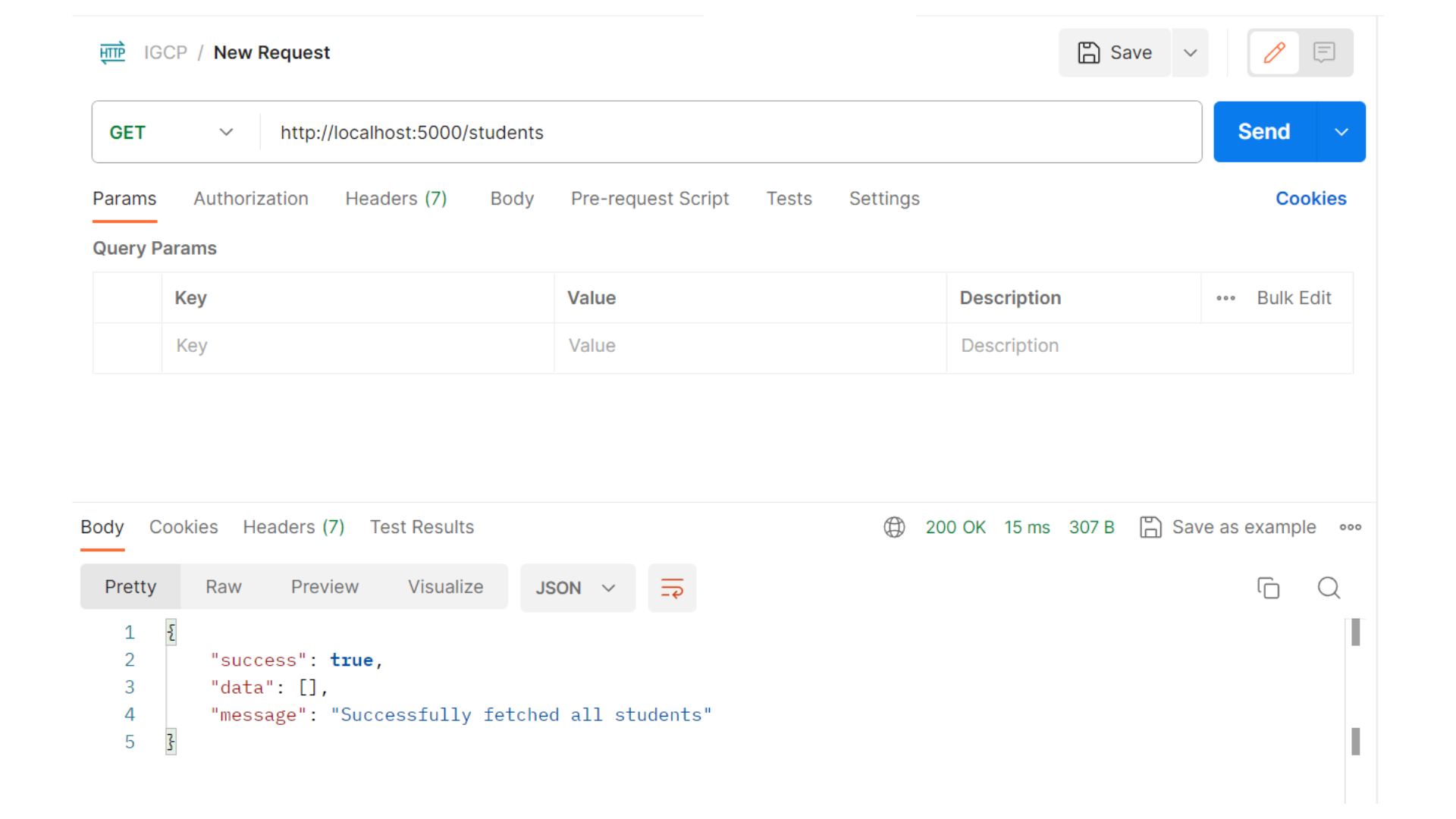
Fetching Student Data
Now, we'll add an API endpoint to fetch student data. This endpoint will return a list of students.
import express from 'express';
const app = express()
app.use(express.json())
const PORT = 5000;
const students = [];
app.get('/students', (req, res) => {
res.json({
success: true,
data: students,
message: "Successfully fetched all students",
})
})
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server is running on port ${PORT}.`)
})
Output:
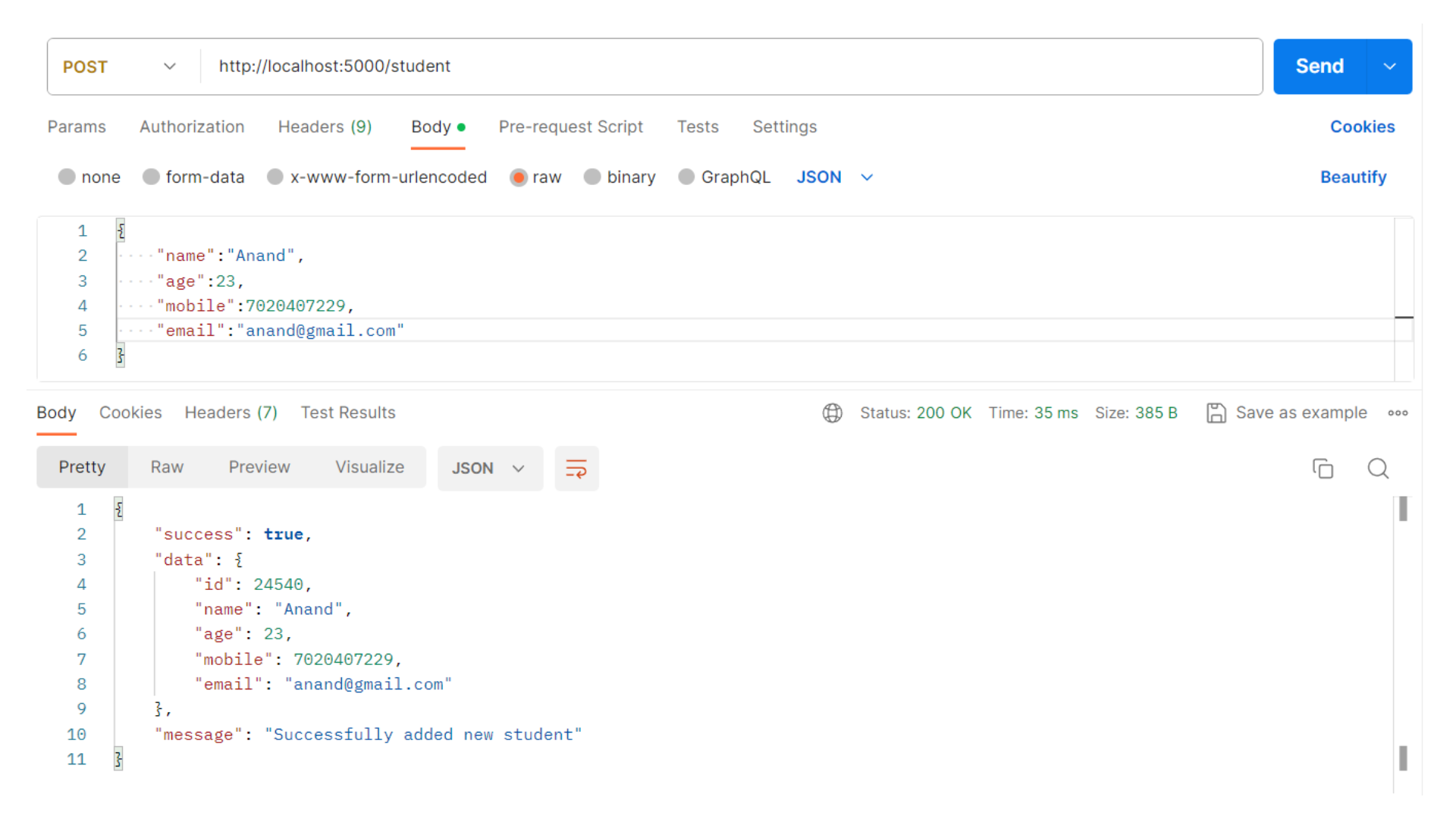
Adding a New Student
We'll now extend our API to allow the addition of new student records. This involves handling POST requests and validating the data.
const students = [];
app.post('/student', (req, res) => {
const {name, age, mobile, email} = req.body;
if (!name) {
return res.json({
success: false,
message: "name is required",
});
}
if (!age) {
return res.json({
success: false,
message: "age is required",
});
}
if (!mobile) {
return res.json({
success: false,
message: "mobile is required",
});
}
if (!email) {
return res.json({
success: false,
message: "email is required",
});
}
const id = Math.floor(Math.random() * 100000) + 1;
const newStudent = {
id,
name,
age,
mobile,
email,
}
students.push(newStudent);
res.json({
success: true,
data: newStudent,
message: "Successfully added a new student"
});
})
Output:
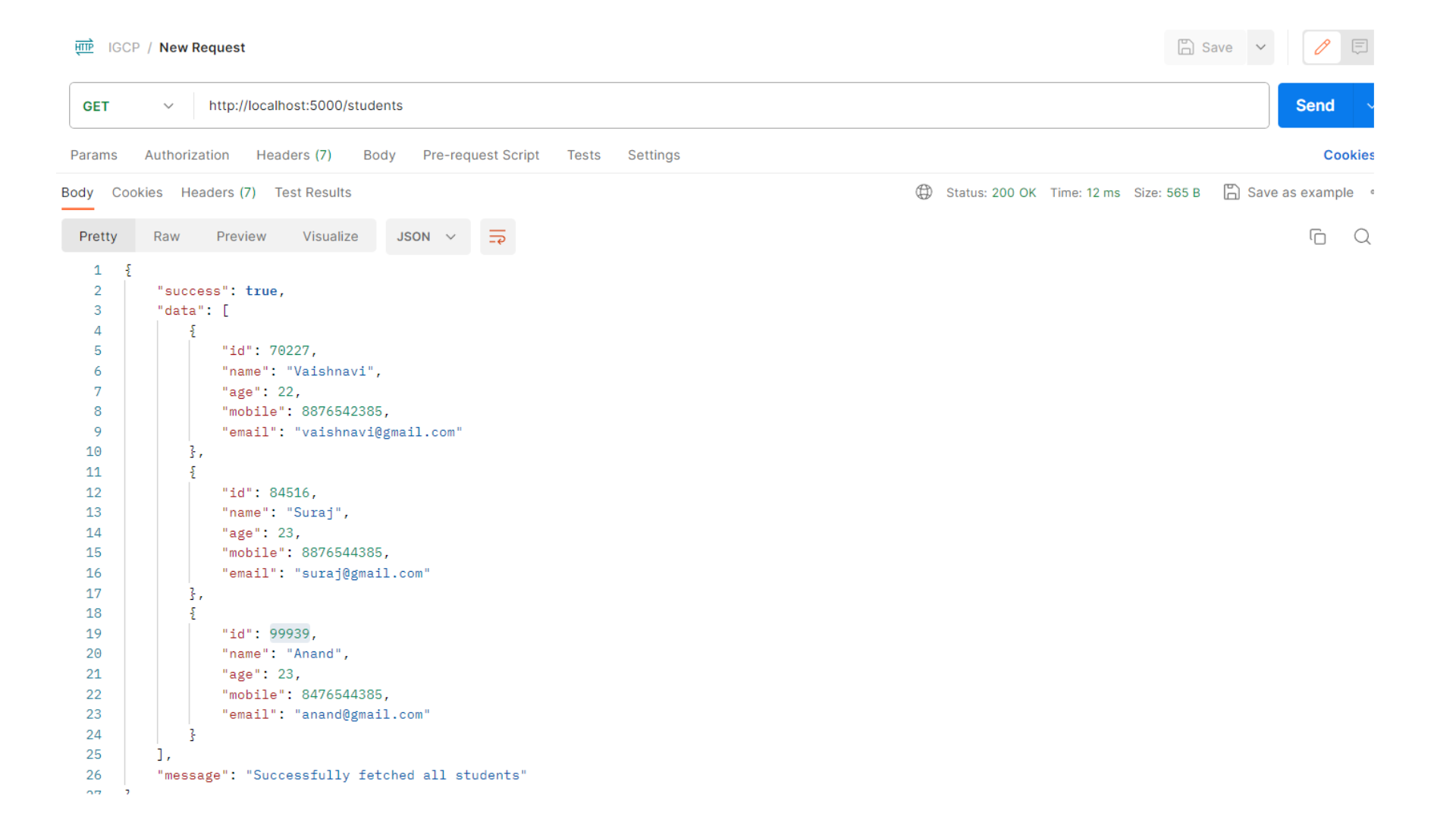
Fetching Student Data
implemented a route to fetch student data through a GET request
const students = [];
app.get('/students', (req, res) => {
res.json({
success: true,
data: students,
message: "Successfully fetched all students",
})
})
Output:
school API now allows the addition of new student records using a POST request and provides a way to retrieve all student data using a GET request.
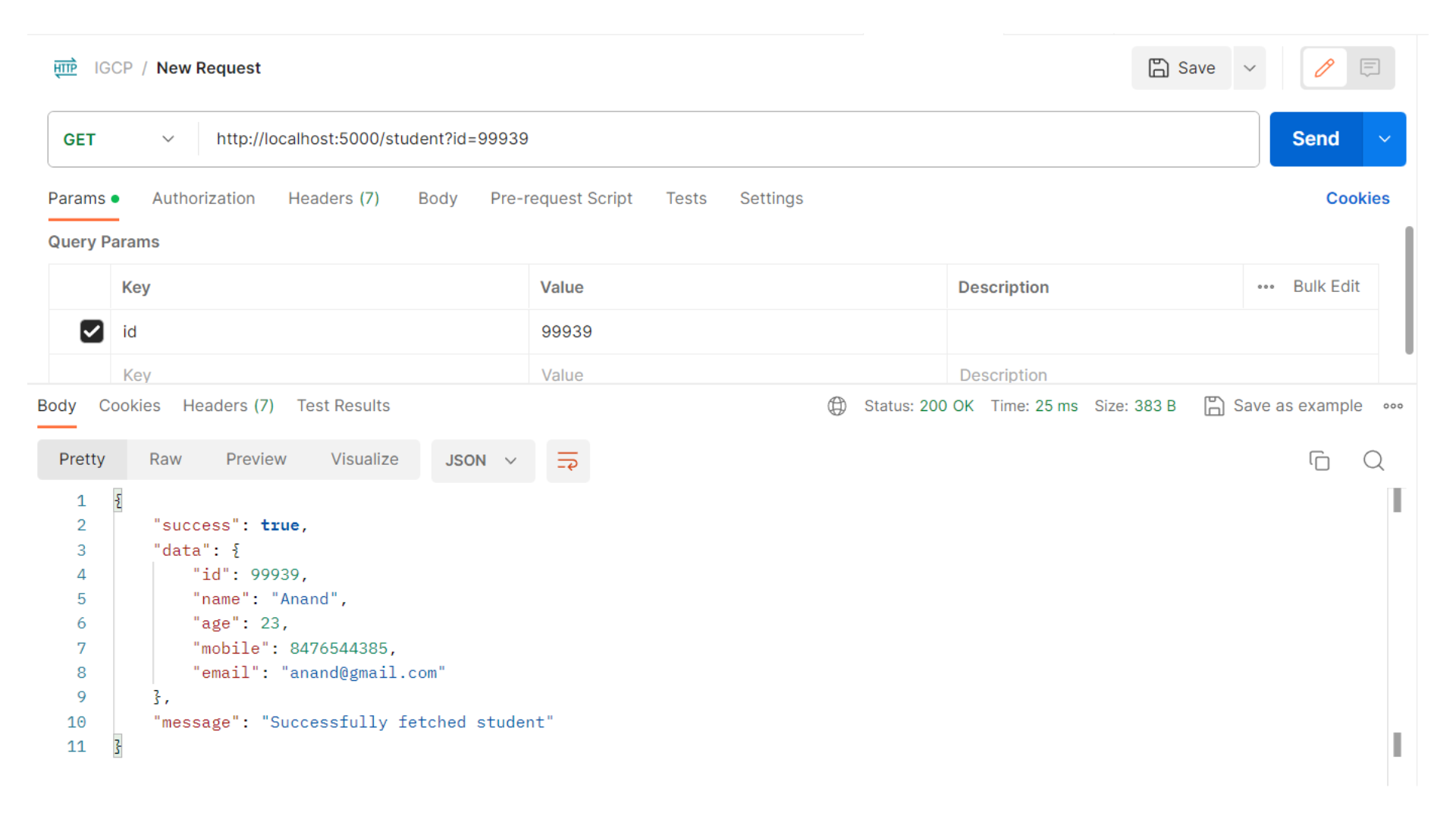
Fetch student using query parameter
Lastly, we'll implement an API endpoint to retrieve a specific student based on their ID.
const students = [];
app.get("/student", (req, res) => {
const { id } = req.query;
let student = null;
students.forEach((stud) => {
if (stud.id == id) {
student = stud;
}
});
if (student == null) {
return res.json({
success: false,
message: "Student not found",
});
}
res.json({
success: true,
data: student,
message: "Successfully fetched student",
});
})
Output:
Creating a Node.js server using Express to manage student data, including endpoints for health checks, fetching all students, adding a new student, and retrieving a single student.