Introduction to javascript
🤔What is JavaScript ?
JavaScript is a dynamic programming language, a scripting language used to develop web applications, games, and more. It allows us to implement dynamic features on web pages that cannot do with just HTML and CSS. Javascript are supported by all browsers.
Brendan Eich invented JavaScript in 1995.
Where does JavaScript runs ?
JavaScript mainly runs in web browsers that have built-in engines to interpret and execute JavaScript code. JavaScript isn't just for web browsers, it also runs in node js, It provides a runtime environment that allows JavaScript to run.
JavaScrip Engines with different browsers
1.Chrome uses V8 JavaScript engine and it is known for the speed and efficiency
2.Safari: Safari utilizes the JavaScriptCore engine, developed by Apple.
3.Mozilla Firefox: Firefox employs the SpiderMonkey JavaScript engine, developed by the Mozilla Foundation.
4.Microsoft Edge: Edge used the Chakra JavaScript engine, but with its transition to the Chromium-based engine, it now also relies on the V8 engine
What is Console ?
Console is global object which has different method log, warn, error
these methods commonly used for logging information, debugging, and outputting messages to the console.
console.log, console.warn, console.error.
1. console.log()
console.log() is a built-in JavaScript function used to display messages, variables, or other information in the browser's console. It's commonly used for debugging and providing insights into the behavior of JavaScript code.
Code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Javascript</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
console.log('Normal message');
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output
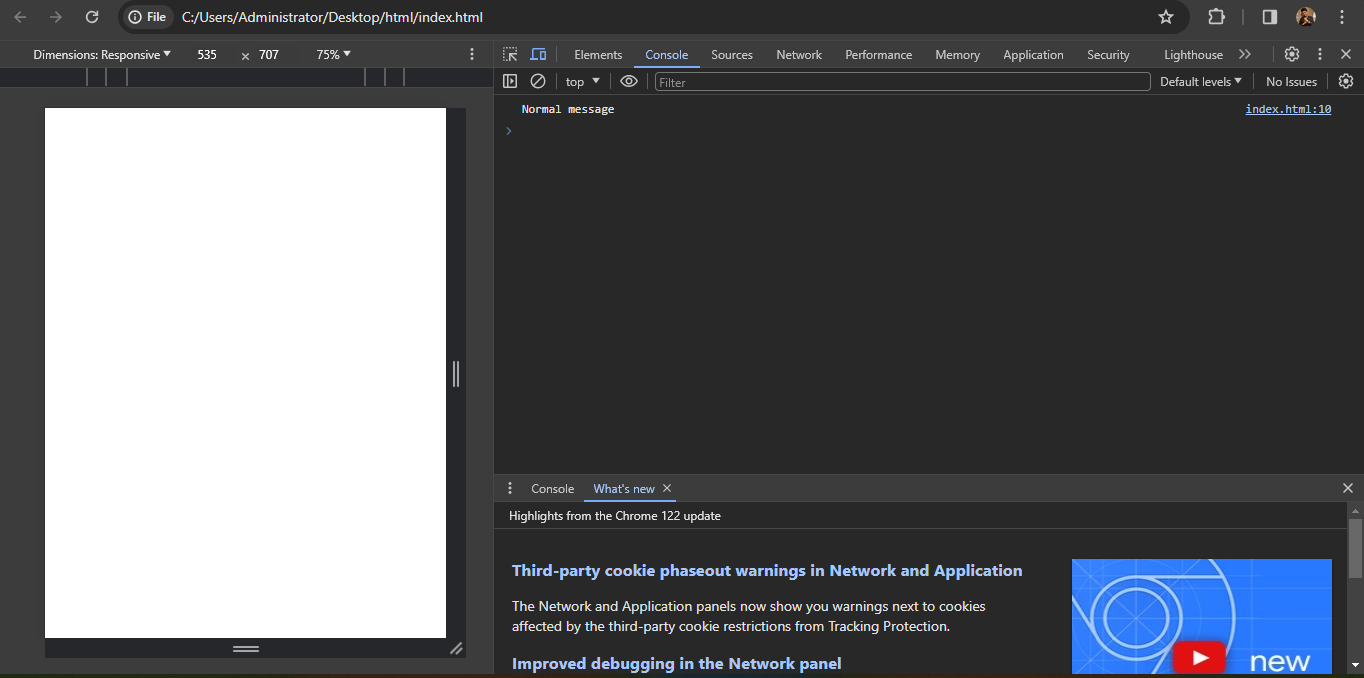
In the given code, <script> tag is used to embed JavaScript code within an HTML document. Inside the <script> tag, the JavaScript code console.log('Hey there!'); is present.
console.log(): This built-in JavaScript function outputs a message or variable to the browser's console for debugging and informational purposes.
The message 'Hey there!' is passed as an argument to the console.log() function. When this code is executed, it will log the message 'Hey there!' to the browser's console, without displaying any dialog boxes to the user.
You can execute JavaScript code directly within your web browser's developer console. The console serves as a powerful tool for interacting with web pages, facilitating tasks such as code testing, manipulation, and debugging. Specifically, console.log() allows you to output messages, variables, or any JavaScript data directly to the console, enabling you to monitor the behavior of your code and debug any issues efficiently.
2. console.warn()
console.warn() is a built-in JavaScript function similar to console.log() but it's specifically designed to display warning messages in the browser's console. While console.log() is used for general logging purposes, console.warn() is useful when you want to highlight potential issues or noteworthy events in your code.
Code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Javascript</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
console.warn('Warning: This is a warning message!');
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output
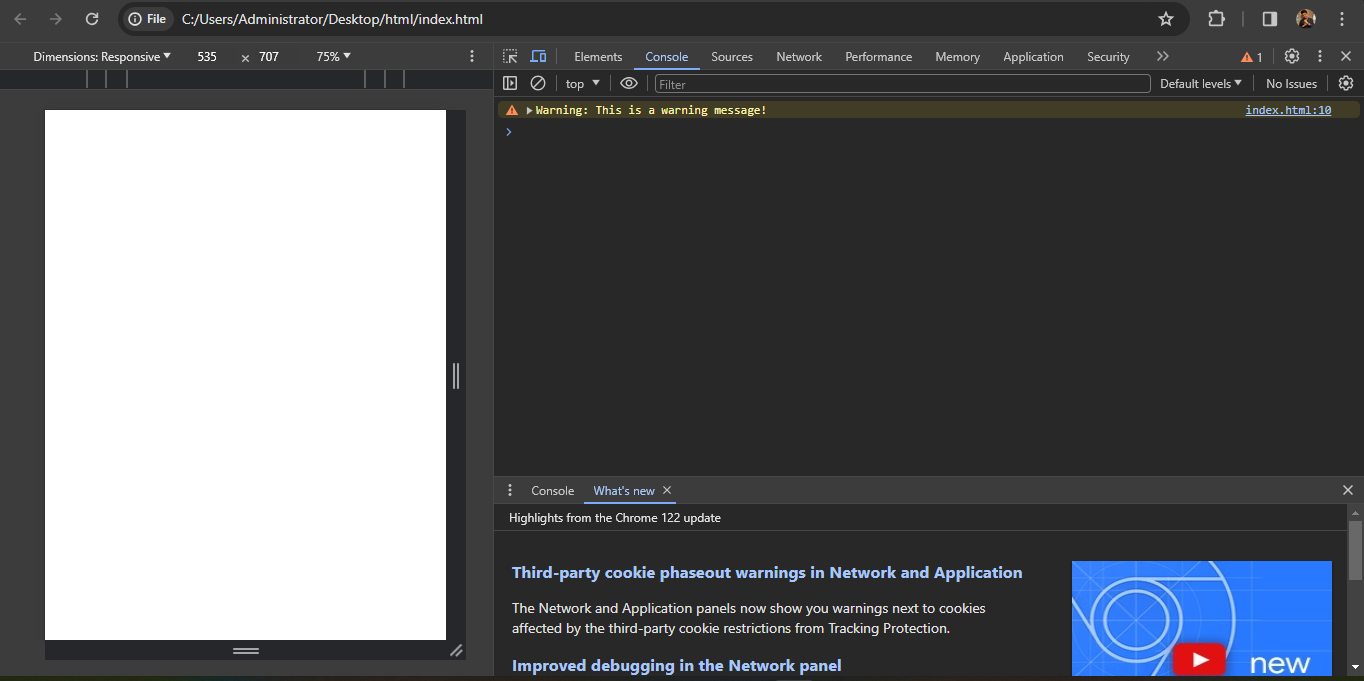
In the given code, the <script> tag is used to embed JavaScript code within an HTML document. Inside the <script> tag, the JavaScript code console.warn('Warning: This is a warning message!'); is present.
console.warn(): This built-in JavaScript function outputs a warning message to the browser's console, signaling potential issues or noteworthy events in the code.
The warning message 'Warning: This is a warning message!' is passed as an argument to the console.warn() function. When this code is executed, it will log the warning message to the browser's console, typically displaying it with a distinctive visual style to draw attention to it.
You can execute JavaScript code directly within your web browser's developer console. The console serves as a powerful tool for interacting with web pages, facilitating tasks such as code testing, manipulation, and debugging. Specifically, console.warn() allows you to highlight potential issues or noteworthy events in your code, making it easier to identify and address them during development..
3. console.error()
console.error() is a built-in JavaScript function similar to console.log(), but it serves the specific purpose of displaying error messages in the browser's console. While console.log() is employed for general logging tasks, console.error() is particularly valuable when you need to signify critical issues or unexpected occurrences in your codebase.
Code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Javascript</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
console.error('Error: This is an error message!');
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output
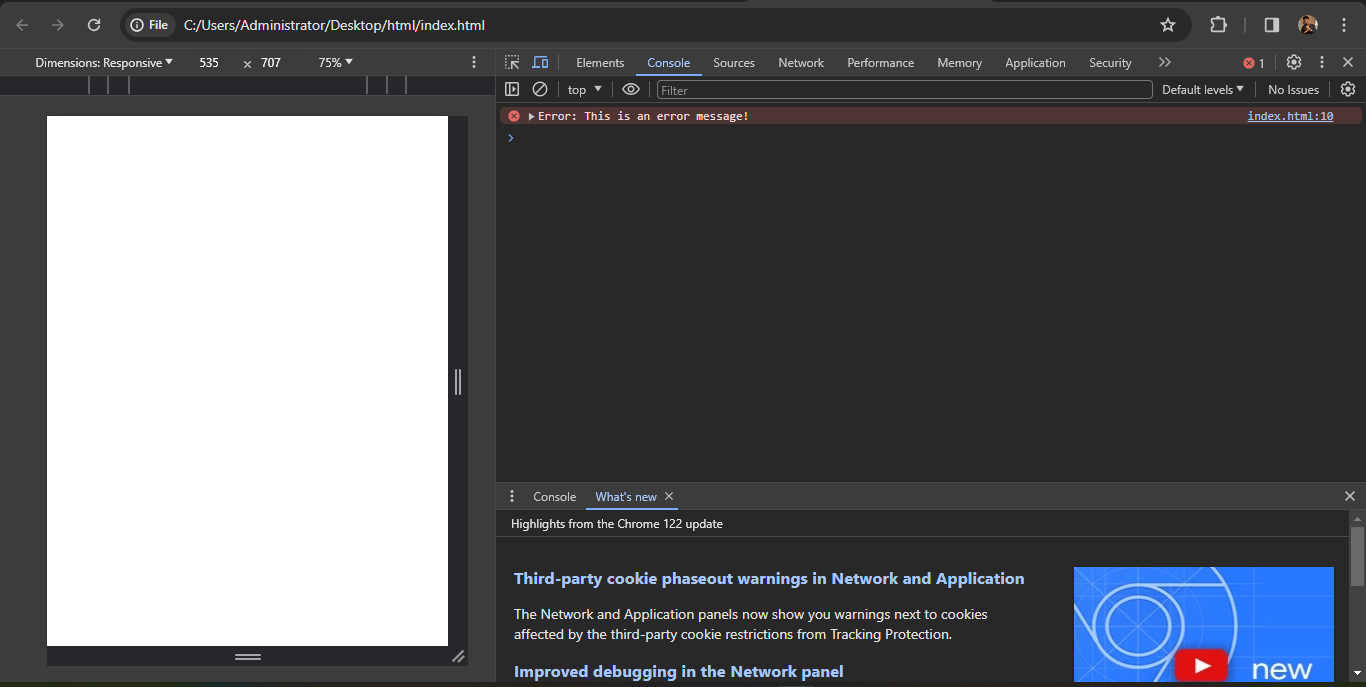
In the given code, the <script> tag is used to embed JavaScript code within an HTML document. Inside the <script> tag, the JavaScript code console.error('Error: This is an error message!'); is present.
console.error(): This built-in JavaScript function outputs an error message to the browser's console, indicating critical issues or unexpected behavior in the code.
The error message 'Error: This is an error message!' is passed as an argument to the console.error() function. When this code is executed, it will log the error message to the browser's console, typically displaying it with a distinctive visual style to draw attention to it.
You can execute JavaScript code directly within your web browser's developer console. The console serves as a powerful tool for interacting with web pages, facilitating tasks such as code testing, manipulation, and debugging. Specifically, console.error() allows you to indicate critical issues or unexpected behavior in your code, making it easier to identify and address them during development..
What is document ?
document (DOM) is a global object that represents the HTML document loaded in the browser.
The document object provides a way to interact with and manipulate the content and structure of the web page. It has bunch of method write, etc
The document.write() method is a way to write text or HTML directly into the HTML document. It can be used to insert content into the document at the time it is being loaded.
Linking JavaScript with HTML
1. Internal
You can add JavaScript before the closing of the body tag in HTML elements, then use this script tag. 👇
Code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>JavaScript is ❤️</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
document.write("Hello World");
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output
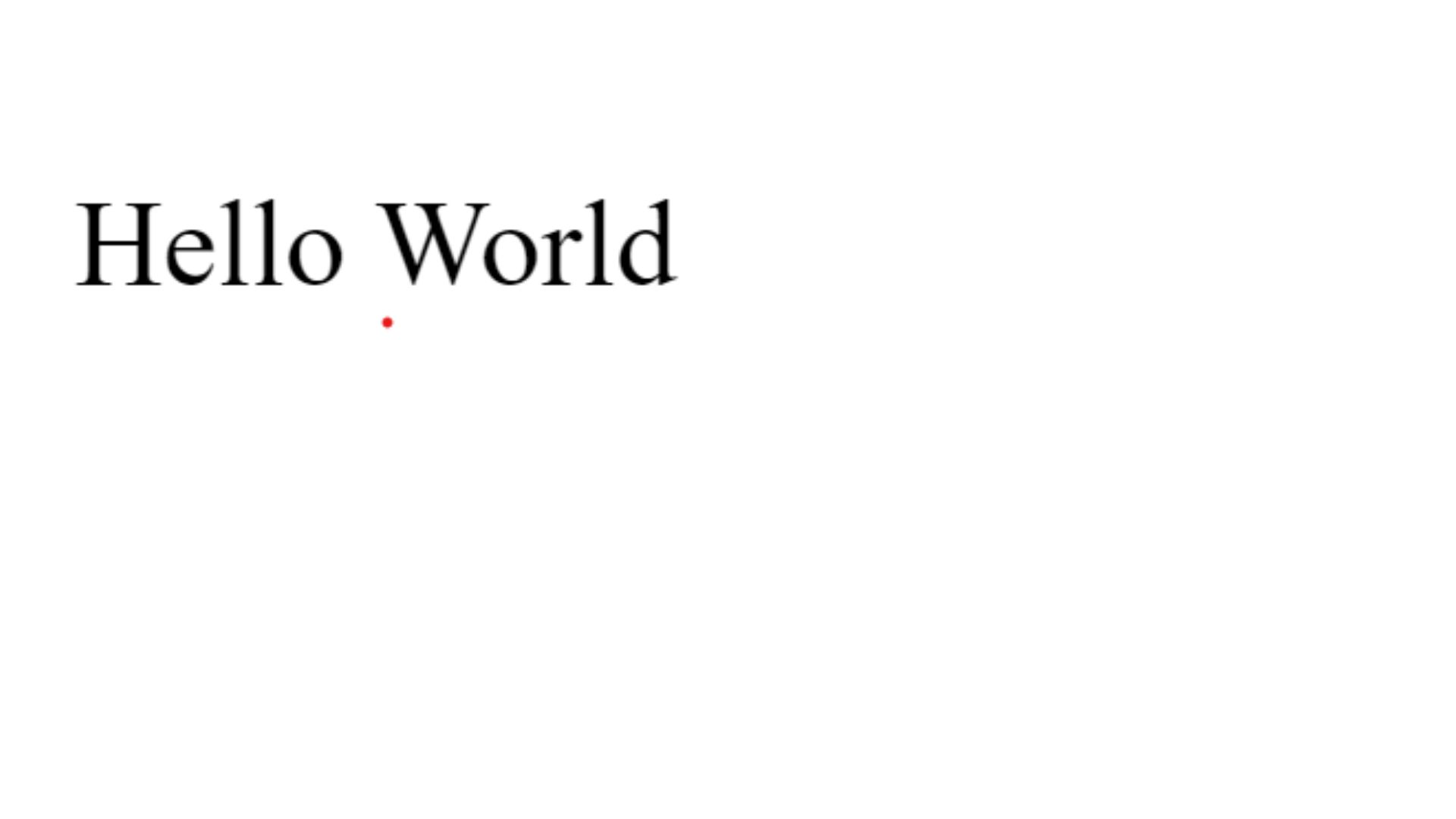
In the above example <script> tag is used to embed JavaScript code within an HTML document.
Inside the <script> tag, you have the above JavaScript code document.write("Hello World");. Here's what this code does:
document: This is a built-in object in JavaScript that represents the web page/document.write(): This is a method of the document object. It allows you to write content directly to the HTML document.
2. External javascript
HTML file
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>JavaScript is ❤️</title>
</head>
<body>
<script src="scrip.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
javascript file
While linking the JS file with HTML, always use the .js extension. This tells the browser to get and run the JavaScript code from a file called script.js
document.write("Hello World");
Output
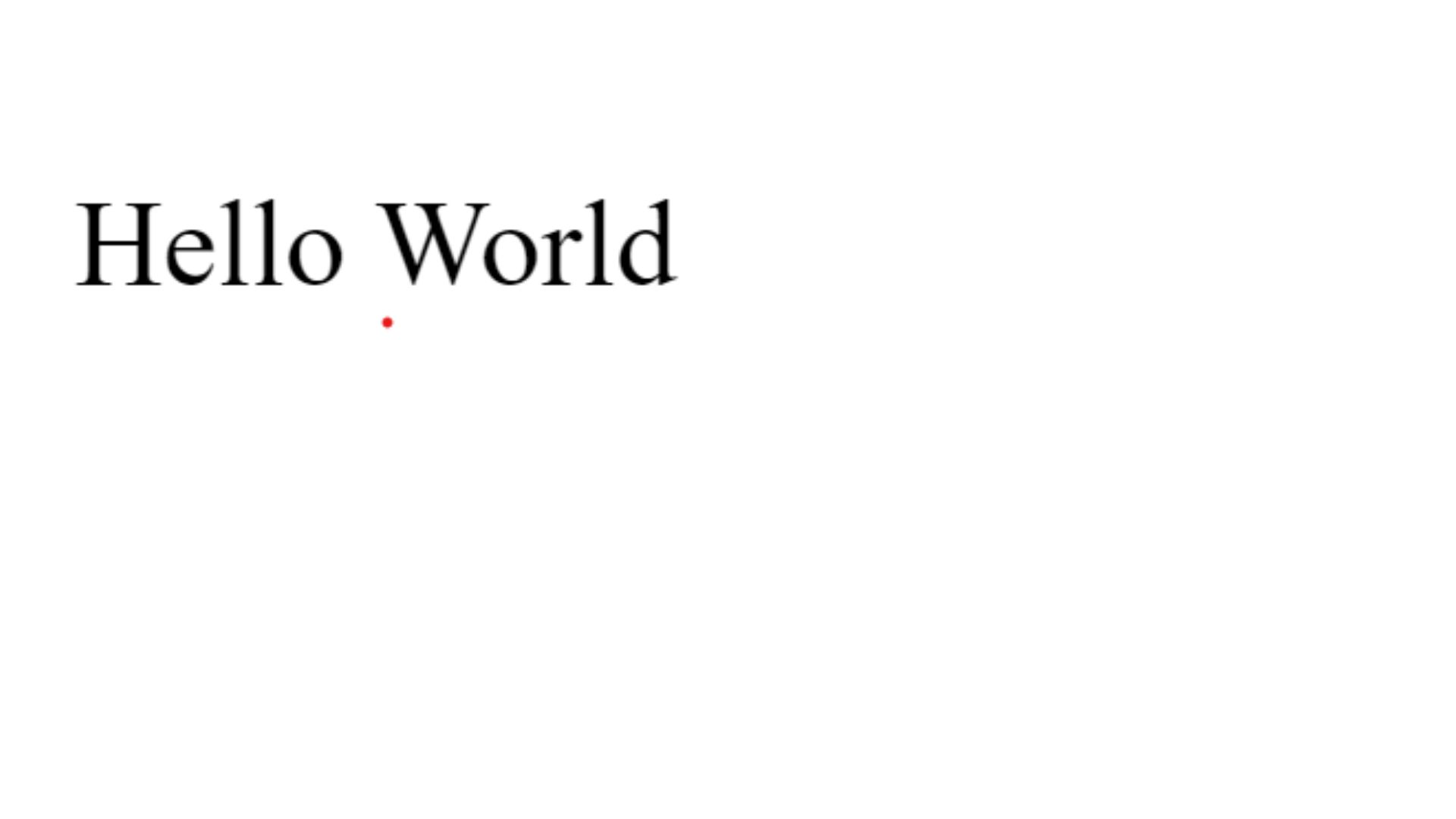
In JavaScript, you can use both single quotes (') and double quotes (") to define strings. Both serve the same purpose of representing textual data. The choice between single and double quotes often comes down to personal preference and specific use cases.
Example 1:
document.write("I'm Suraj");
In this example, the string contains a single quote (') within it. To avoid confusion with the string delimiter, which is also a single quote, you've used double quotes (") to define the entire string. This way, JavaScript knows that the string starts with the first double quote and ends with the closing double quote, allowing the single quote within the string to be treated as part of the text.
Example 2:
document.write('He said, "How Are You?"');
Here, the string contains double quotes (") within it. To handle this scenario, you've used single quotes (') to define the string. By doing so, the JavaScript interpreter understands that the string begins with the first single quote and ends with the closing single quote, allowing the double quotes within the string to be interpreted as part of the text.
In summary:
- If your string contains single quotes, you can define the string using double quotes.
- If your string contains double quotes, you can define the string using single quotes.
What is Window ?
window object represents the global context in which the JavaScript code runs within a web browser. It provides a variety of properties and methods for interacting with the browser window and the web page.
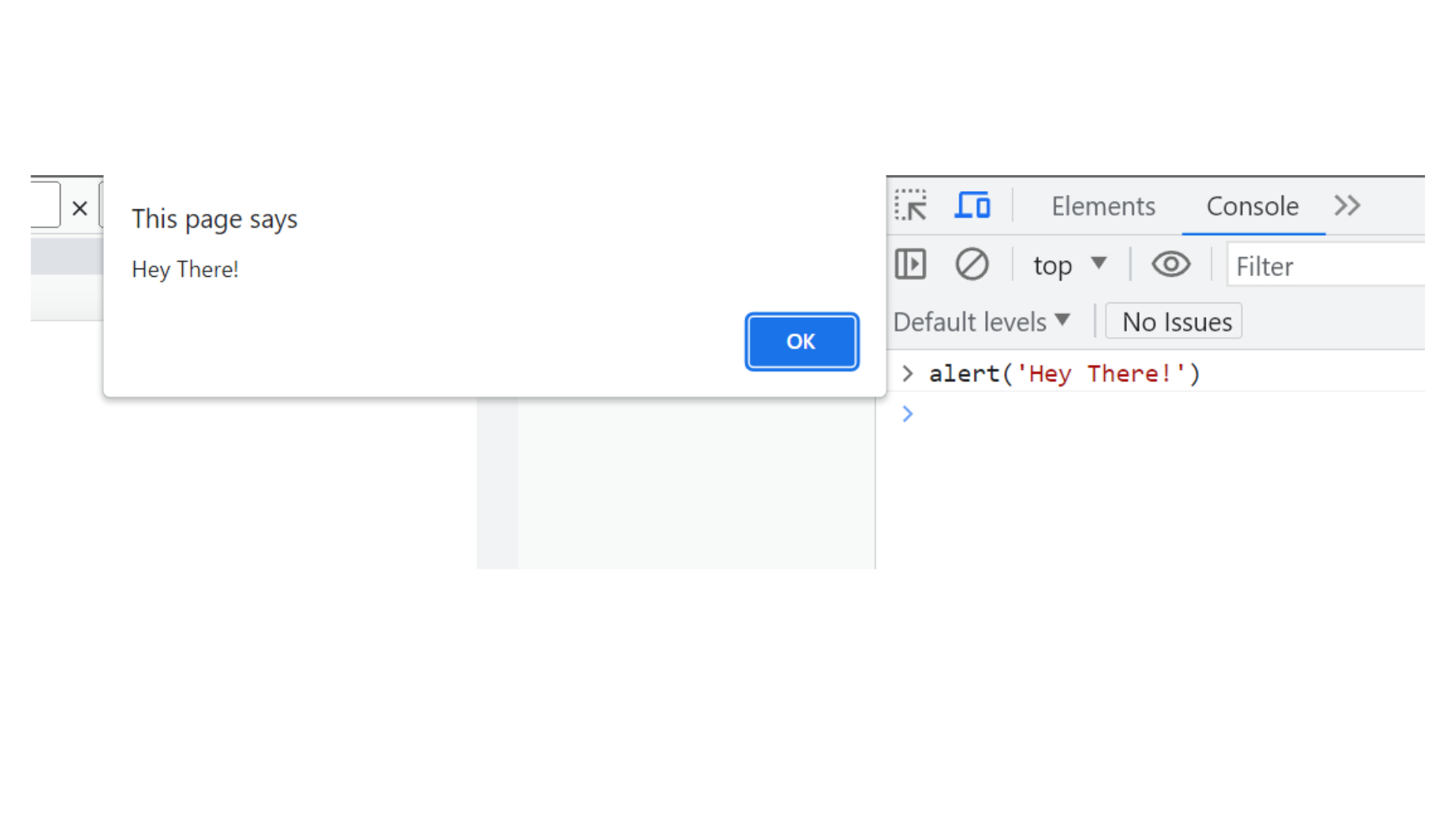
alert()
The alert() function is a built-in JavaScript function that displays a simple dialog box or popup in the user's web browser with a specified message. This message is often used to convey important information, warnings, or prompts to the user. The user needs to acknowledge the alert by clicking the `OK`` button before they can continue interacting with the web page.
Code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Javascript</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
alert('Hey there!')
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output
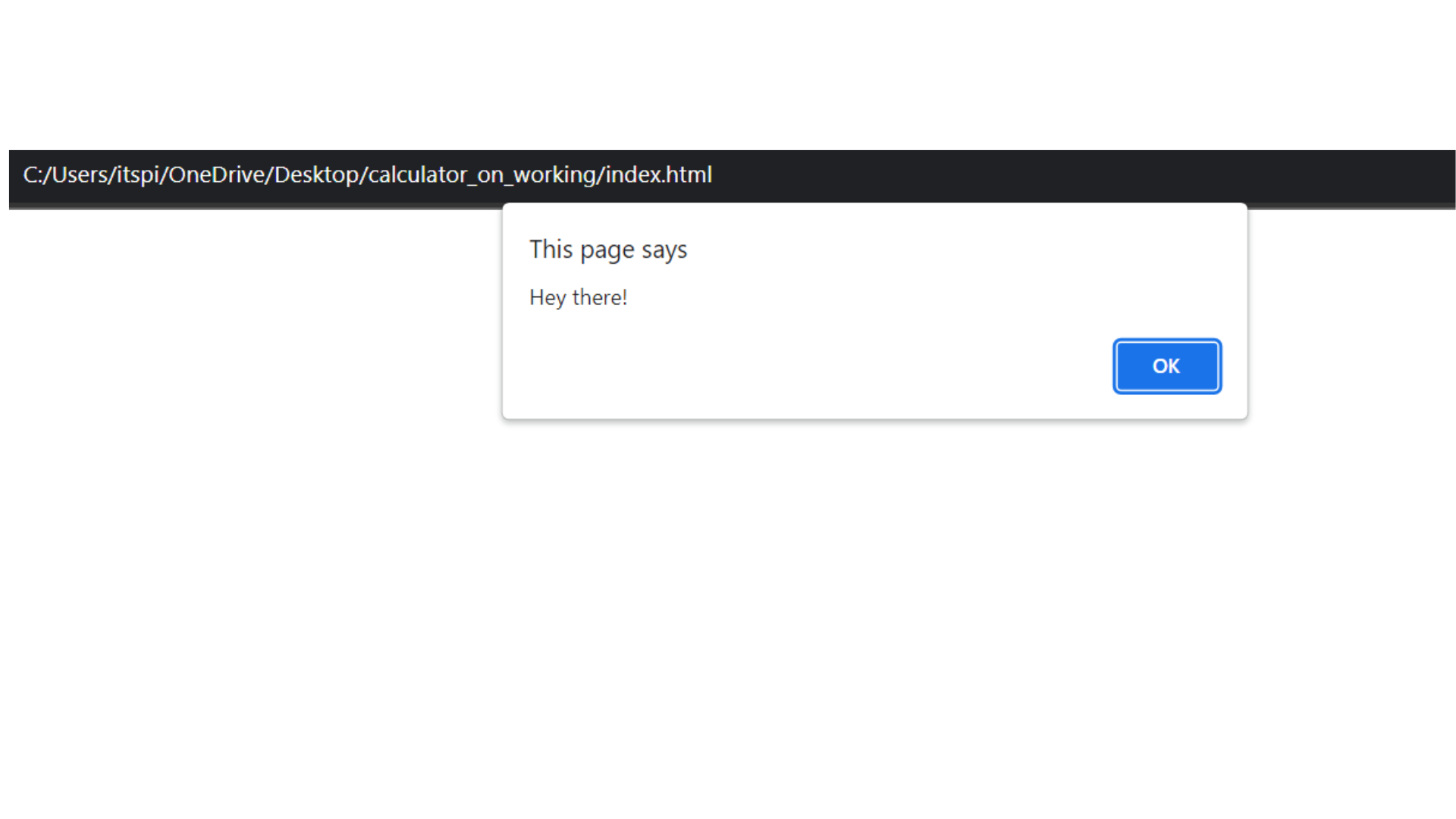
In the above Code, <script> tag is used to embed JavaScript code within an HTML document. Inside the <script> tag, you have the above JavaScript code alert('Hey there!'); Here's what this code does:
alert(): This is the built-in JavaScript function that triggers a dialog box (alert) with the specified message.
The message Hey there is provided as an argument to the alert() function. When this code is executed, it will display a dialog box with the message `Hey there!`` in the user's web browser.
You can run JavaScript code directly in your web browser's developer console. The developer console is a tool that allows you to interact with and manipulate web pages, test code snippets, and debug your JavaScript code. It provides an environment where you can execute JavaScript commands and see their results immediately.
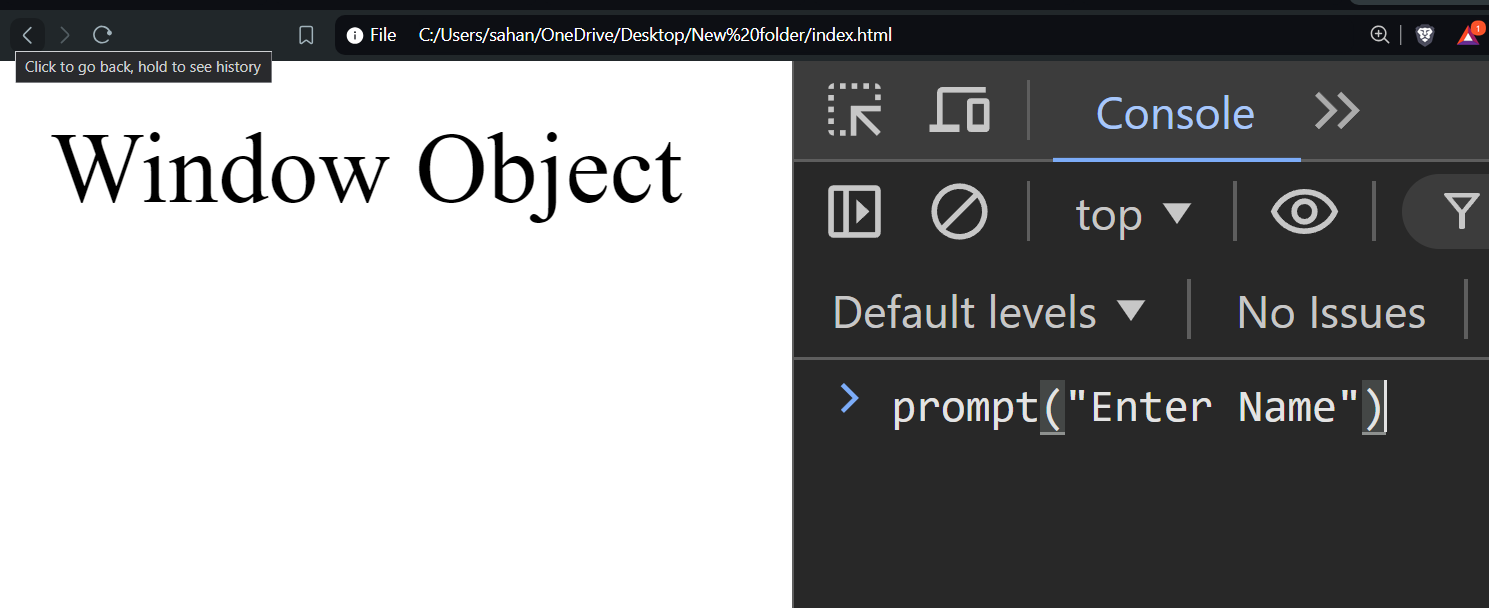
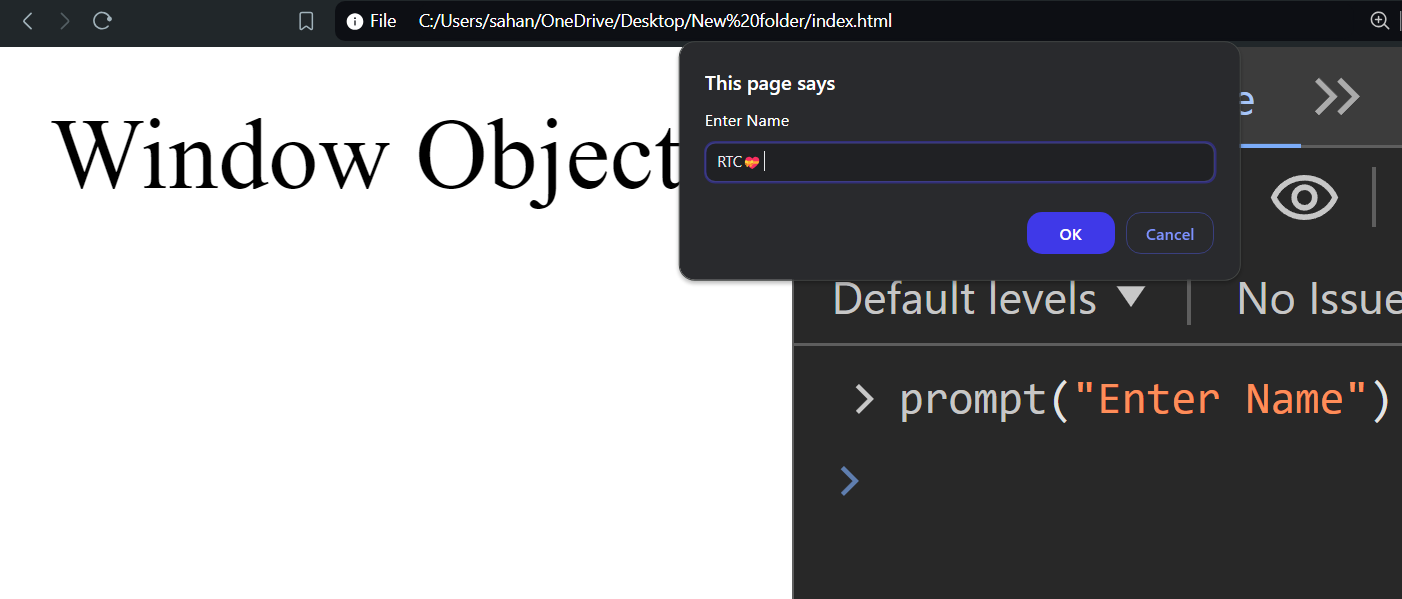
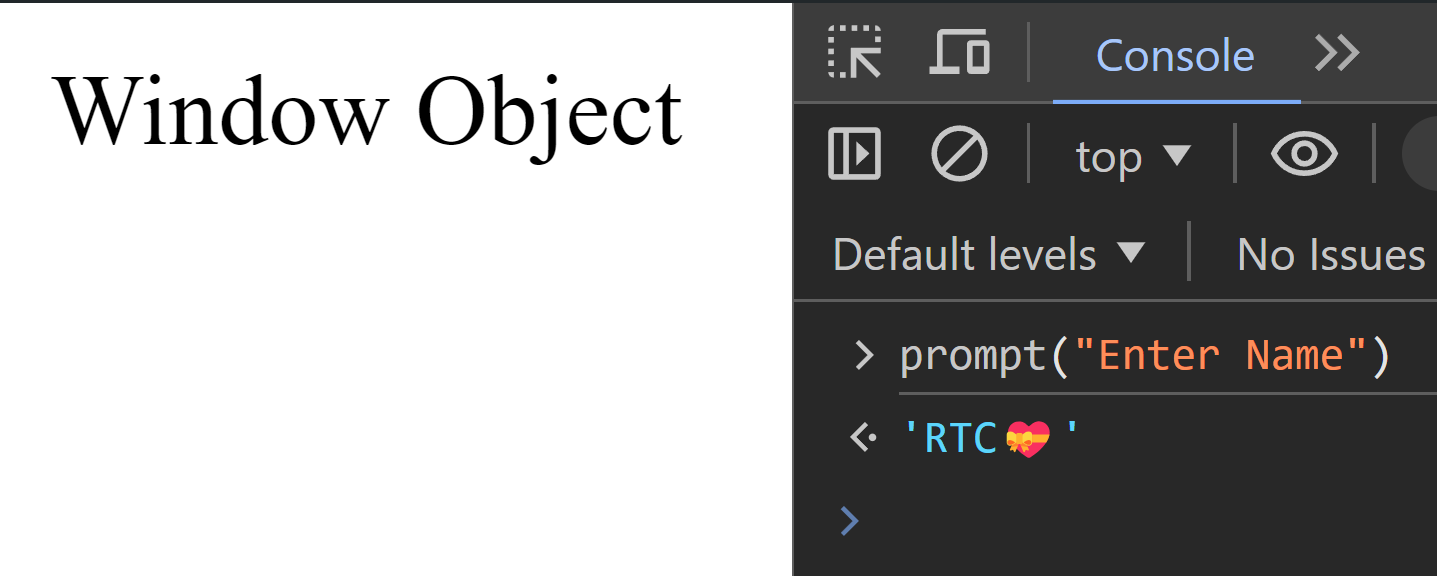
prompt()
prompt() method displays a dialog box that prompts the user for input. It includes a text field where the user can enter a response.
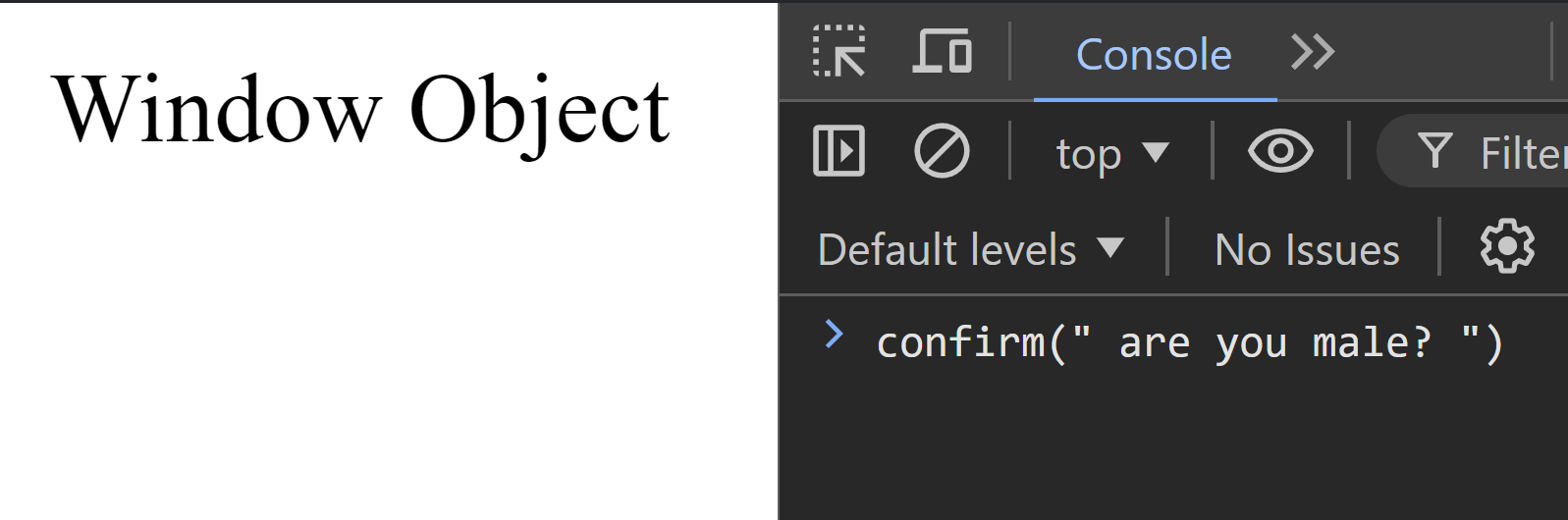
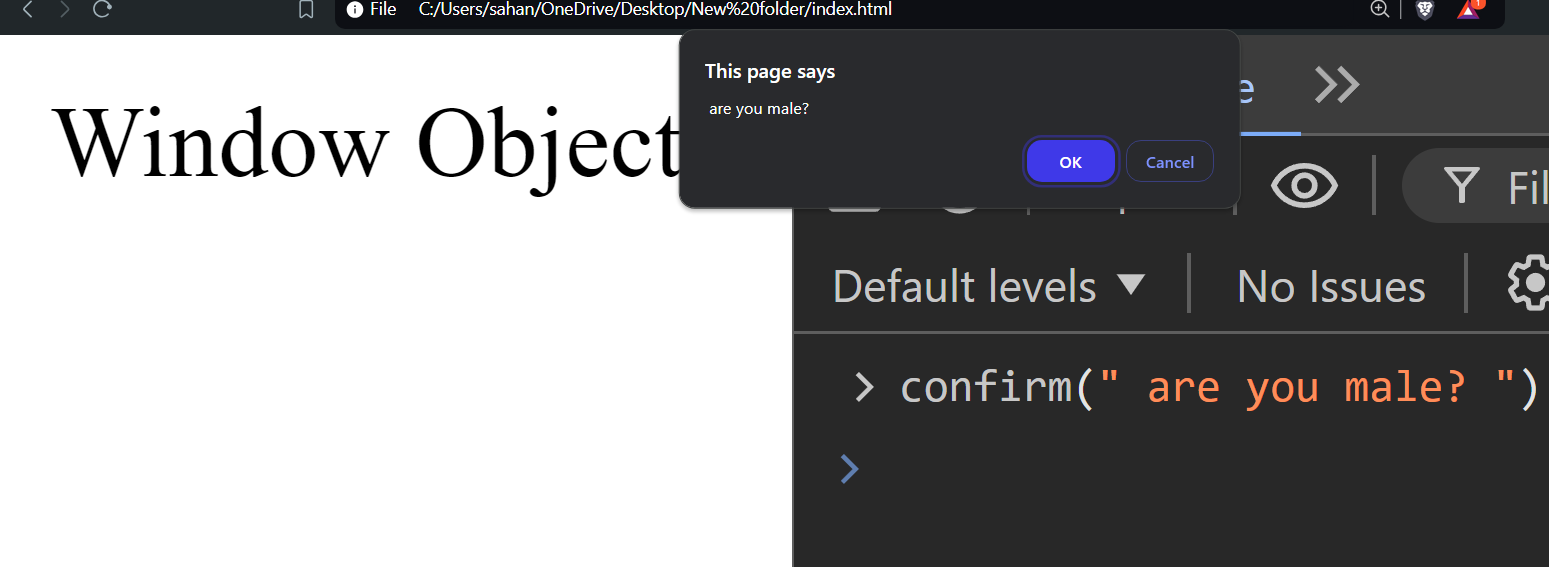
confirm()
confirm() method displays a dialog box with a specified message and OK/Cancel buttons. It is used to ask the user to confirm or reject an action.