DOM Manipulation
DOM stands for Document Object Model. It is structured representation of webpage in the form of tree like structure.
Document : Document of webpage it contains tree structure of tags present in the web page.
Object - Each tag can be considered as a node or object in the document.
Model - Model is a structure representation current document in the form of tree like structure.
Element Selectors
Element selector are methods that allow you to access HTML elements from the DOM (Document Object Model).
There are different element selectors in Javascript.
- getElementById()
- getElementsByClassName()
- getElementByTagName()
Let's Learn Selectors one by one...
- getElementById() : The
getElementById()method is commonly used in HTML DOM read or edit an HTML element. It returns an element with a specific value and null if the element does not exist.
Example :
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>DOM</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<h1 id="heading">DOM Manipulation</h1>
[]
</div>
</body>
</html>
Output :
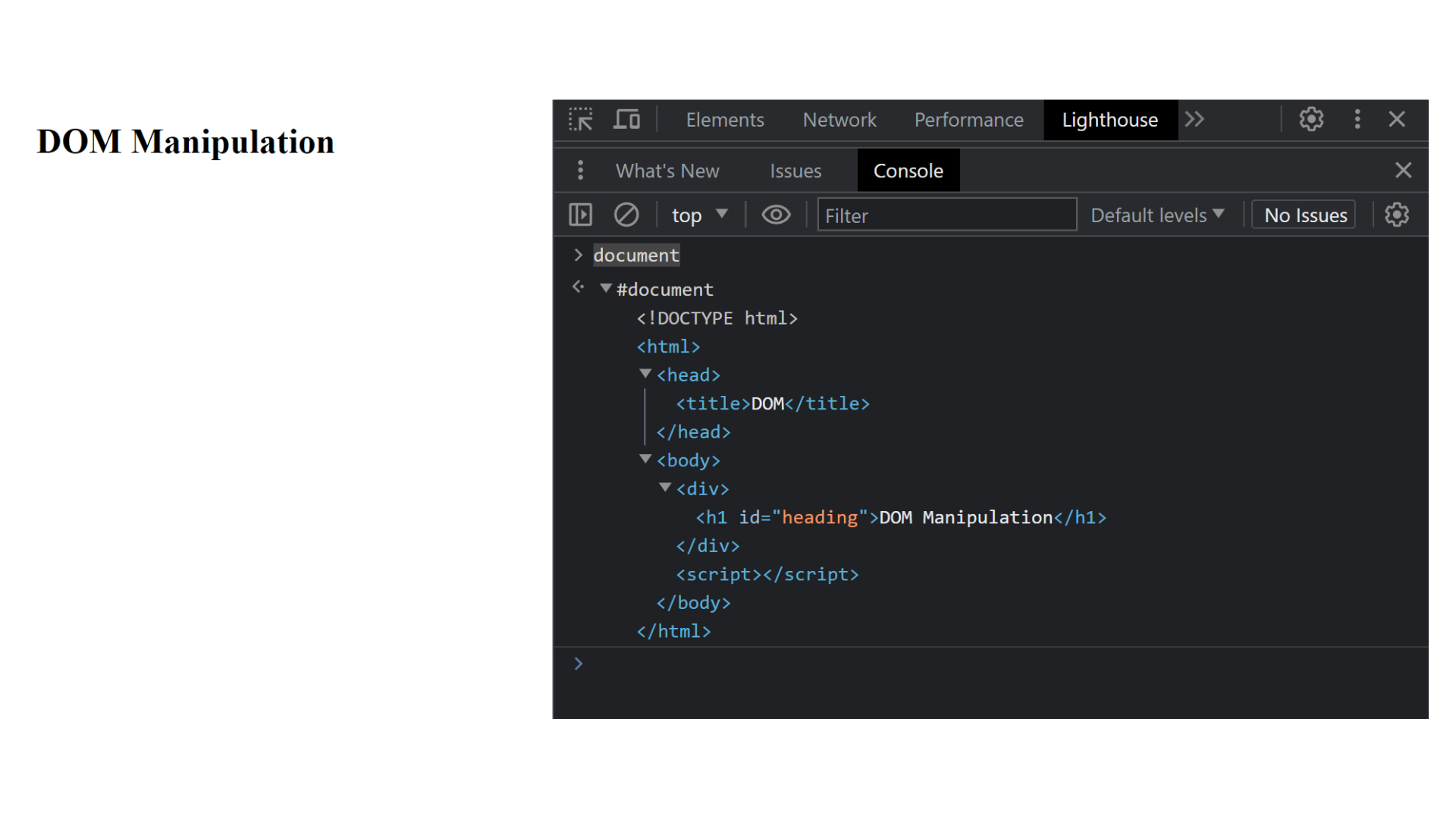
Explanation :
In the above example, open the console and print the document then you see document tree like #document. In this document you see document tree which is show in output. document is a global object. In this code html is a parent element and head, body both are siblings elements.
Global objects are objects that can be accessed from anywhere in your code.
Example :
document.write('Hii);
Output :
Hii
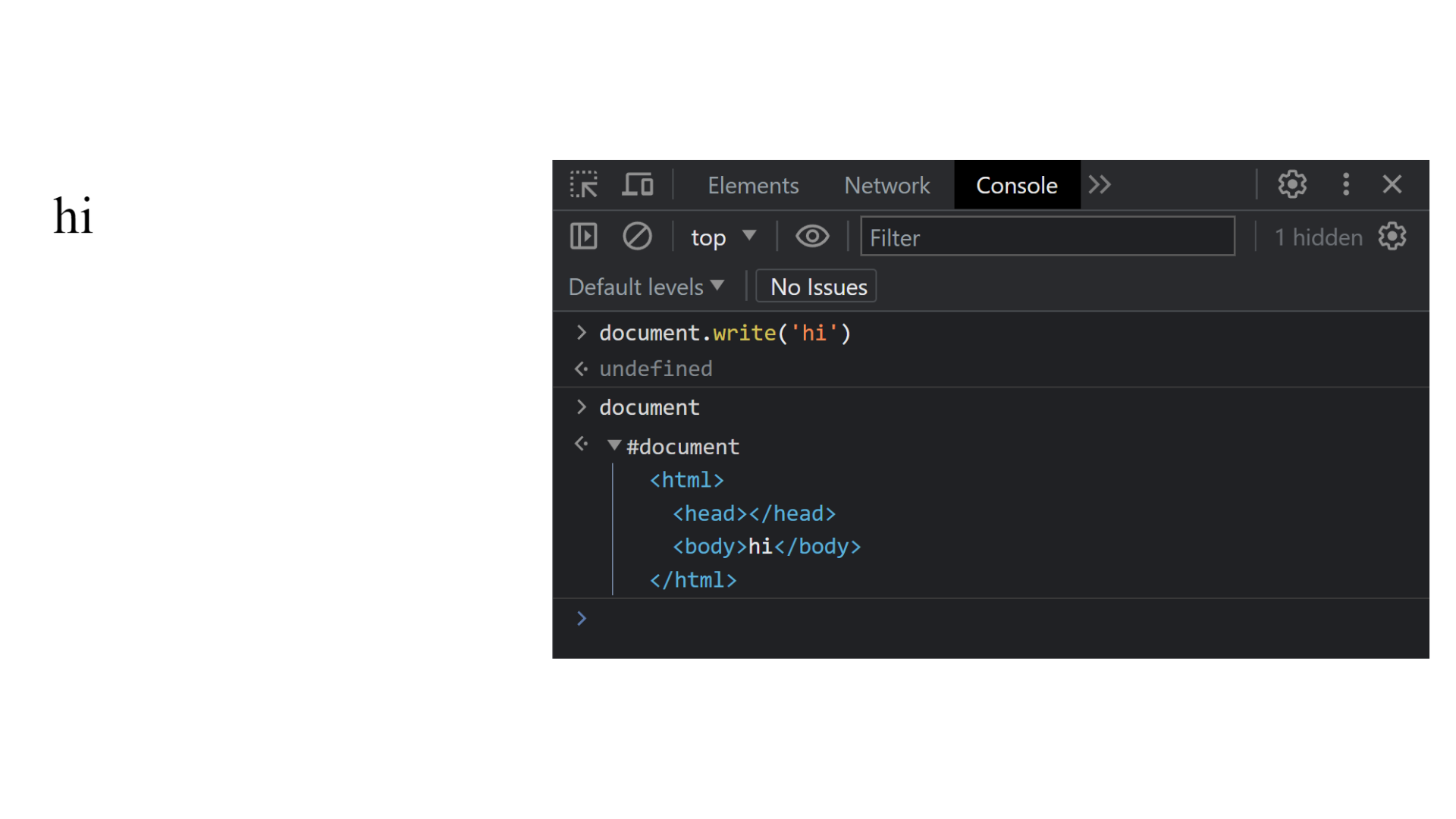
Explanation :
In the above example, we use the document it is a global object and the write() function to print the string Hii which display in LHS.
How to find out element using getElementById()?
Example :
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>DOM</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p>
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Sint beatae,
corporis officiis odit soluta harum facilis aspernatur ipsum, fugit
quisquam quas aperiam nobis eius. Fugit voluptatibus ea nemo tempora
maxime?
</p>
<h1 id="heading">DOM Manipulation</h1>
<p id="text">This is Paragraph.</p>
</div>
<script></script>
</body>
</html>
Output :
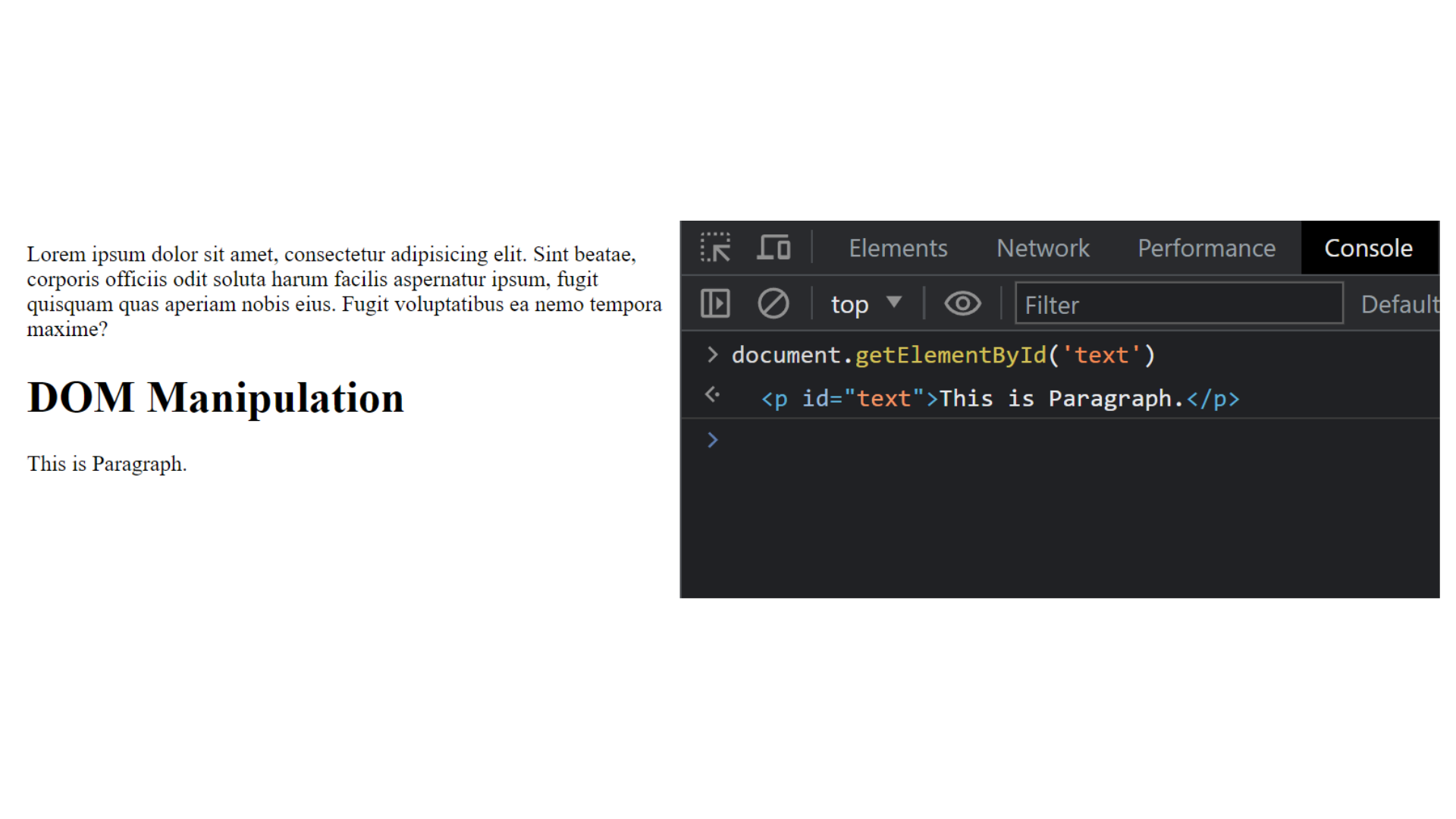
Explanation :
In the above example, we open the console and use the command document.getElementById('text') to locate the text ID in the HTML code. This will then print the paragraph <p id="text">This is a Paragraph.</p>.
Example :
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>DOM</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div id="container">
<h1 id="heading">DOM Manipulation</h1>
<p id="text">This is Paragraph.</p>
</div>
</div>
<script></script>
</body>
</html>
Output :
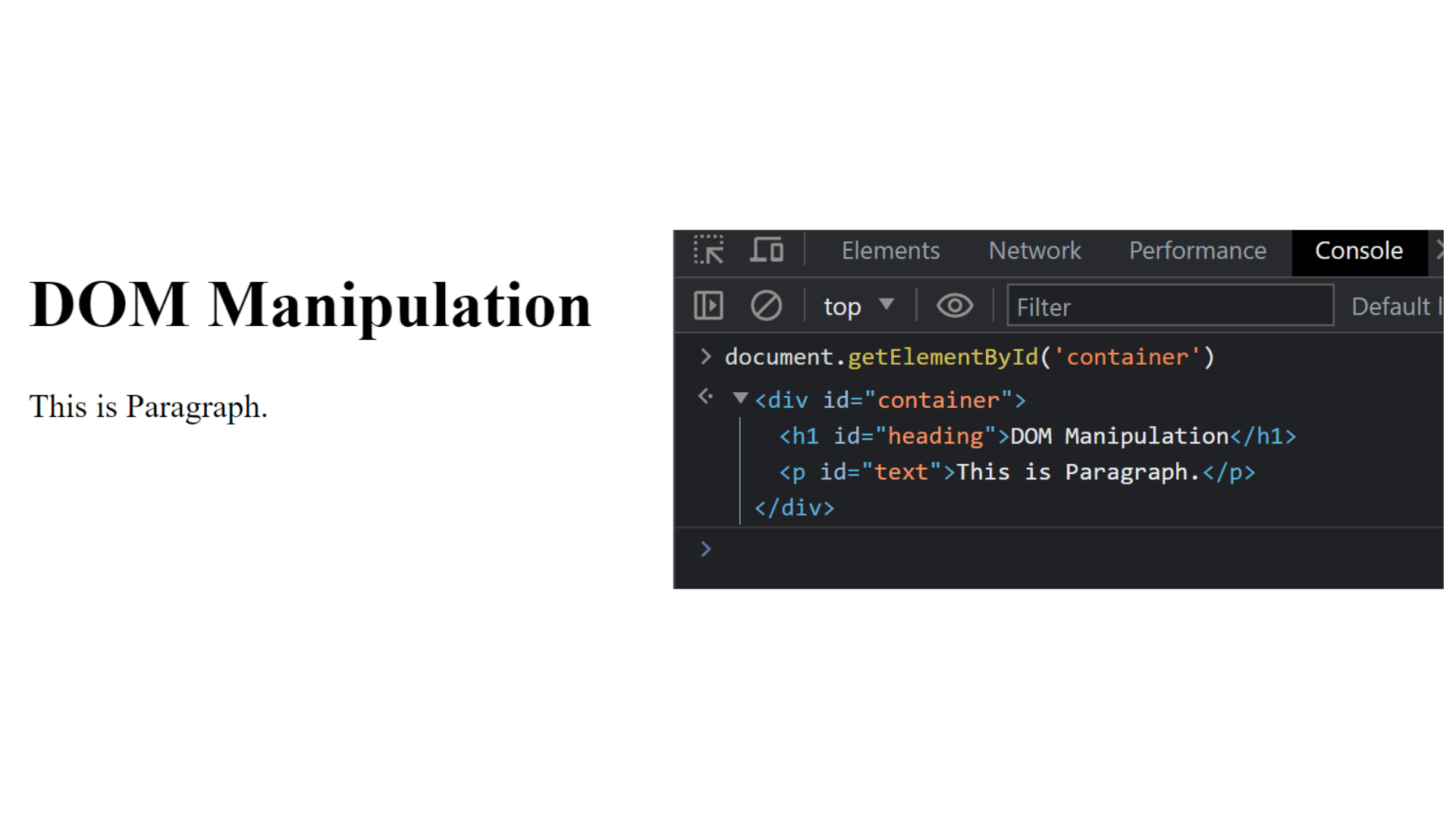
Explanation :
In the above example, we open the console and pass input document.getElementById('container') it find container id and this is returns the entire parent tag with the ID of container.
How to use innerText and innerHTML?
innerText and innerHTML are always apply on elements.
innerText - It ignores the tags and only returns the textual content (text).
innerHTML - It returns tags with textual content.
Example :
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>DOM</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div id="container">
<h1 id="heading">DOM Manipulation</h1>
<p id="text">This is Paragraph.</p>
</div>
</div>
<script>
const element = document.getElementById("container");
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output :
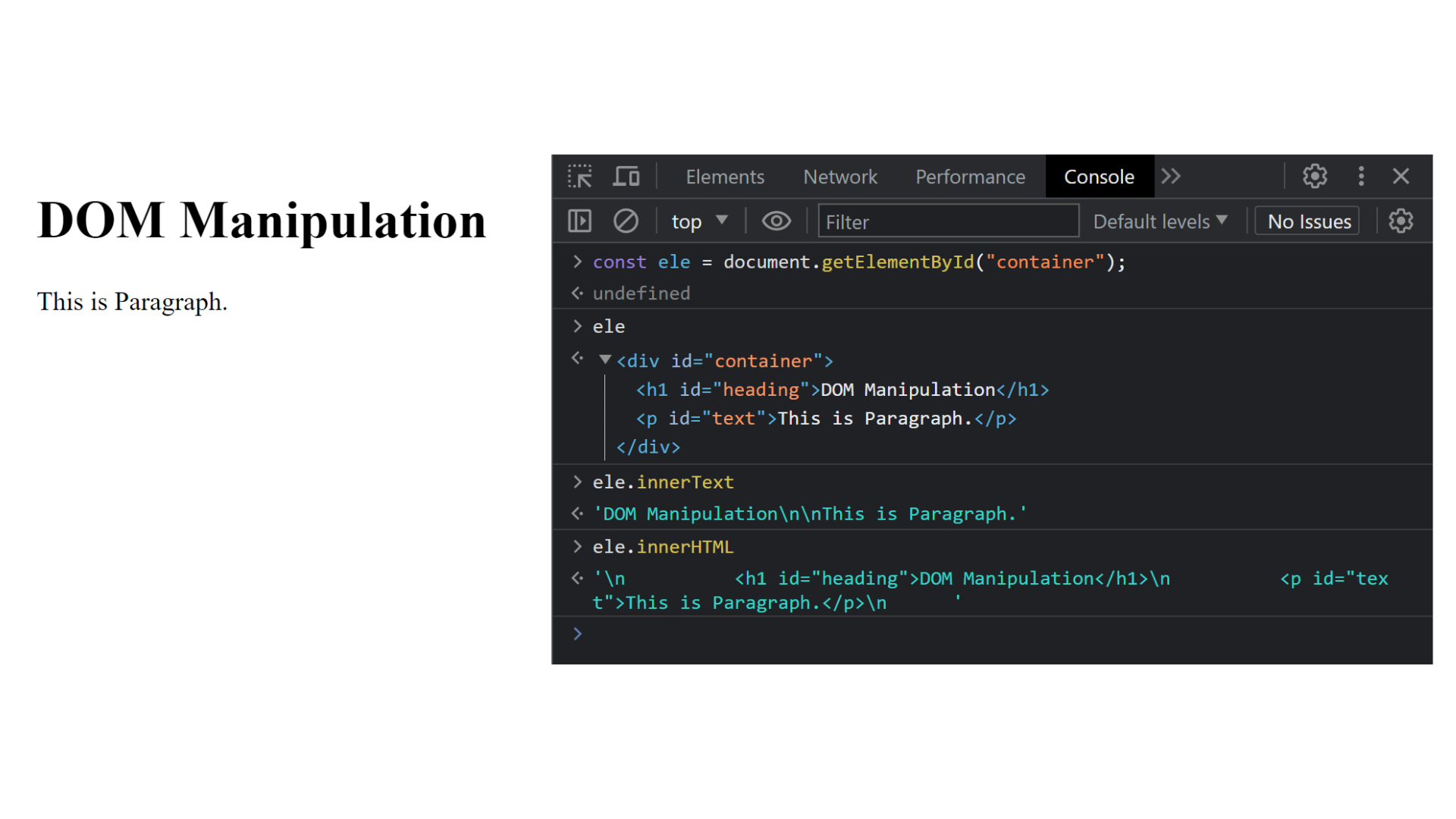
Explanation :
In the above example, we create a variable named ele in the console. We then find the ID container, store the parent tag of ID in ele variable, and write ele.innerText in the console to find textual content. It returns output like this, 'DOM Manipulation\n\nThis is Paragraph.'. \n indicates that the blank spaces.
Then, we write ele.innerHTML in the console to find tags with textual content. It returns output like this '\n <h1 id="heading">DOM Manipulation</h1>\n <p id="text">This is Paragraph.</p>\n '.
Example :
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>DOM</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div class="container">
<h1 id="heading">DOM Manipulation</h1>
<p id="text">This is Paragraph.</p>
</div>
</div>
<script>
const element = document.getElementById("heading");
element.innerText = "This is Structural Paragraph.";
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output :

Explantion :
<div class="container"> : This is another <div> tag with a class attribute set to container. It's used to group elements together and apply styling.
<h1 id="heading"> : DOM Manipulation </h1>: This line contains an <h1> (header) tag with an id attribute set to heading. It displays the text DOM Manipulation as a main heading.
<p id="text">This is Paragraph.</p> : This line contains a <p> tag with an id set to text. It displays the text This is Paragraph. as a paragraph of content.