Datatypes and Variables
Primitive Data types
- String
- Number {int , float}
- Boolean
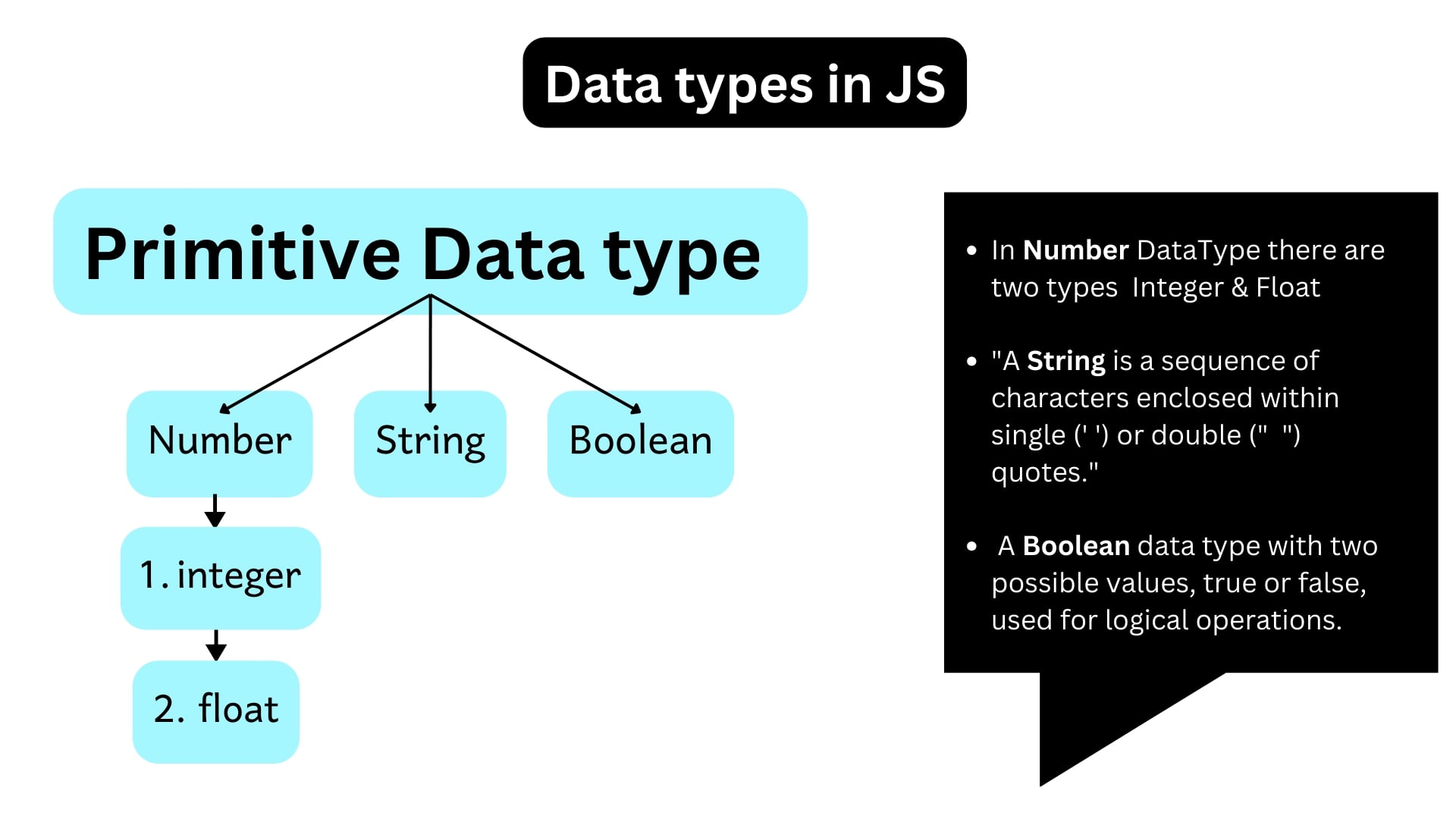
CHECK BELOW TO KNOW ALL THE DATA TYPES 👇
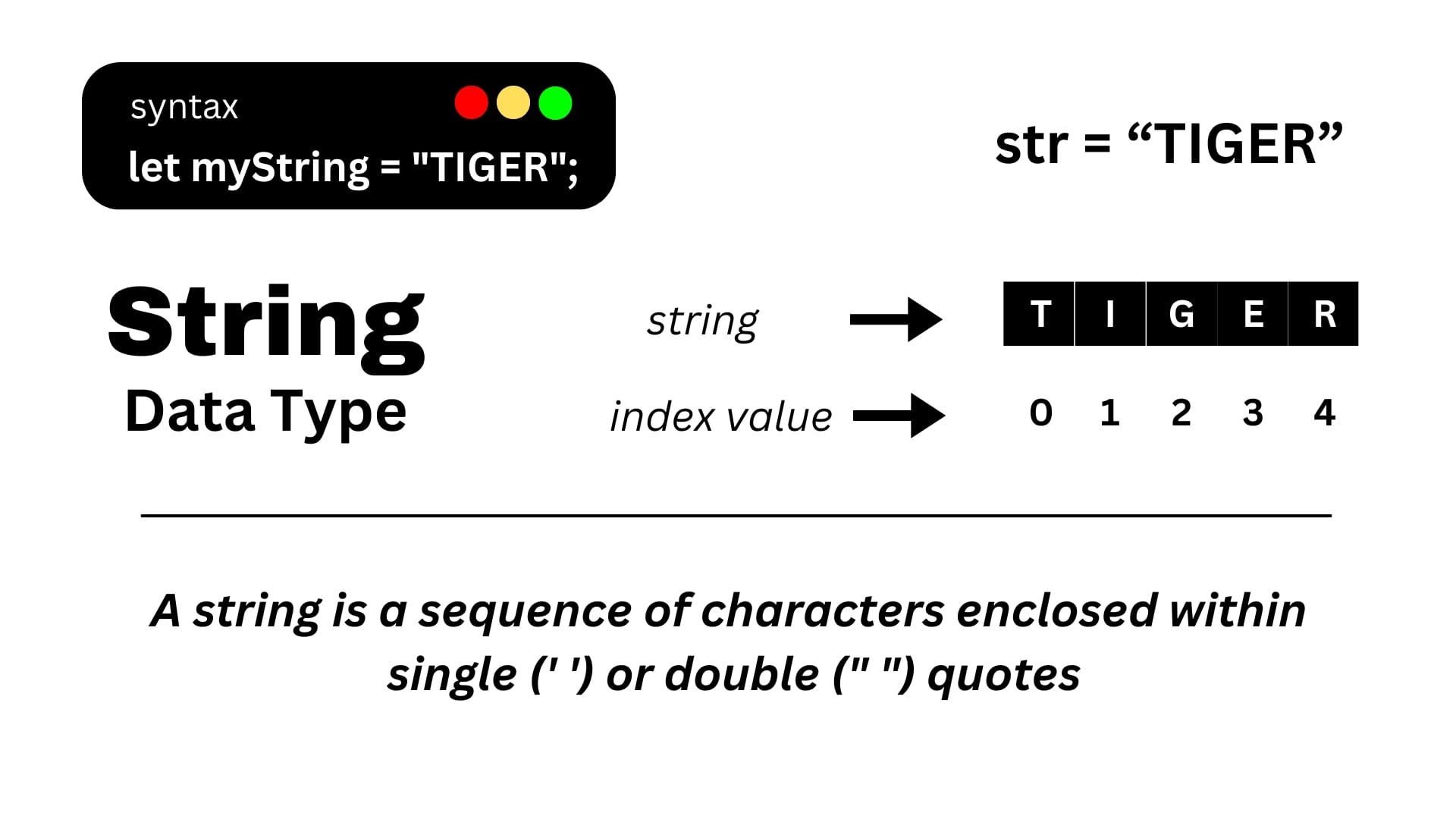
- String
A string is a data type used to represent textual data. It consists of a sequence of characters enclosed within single ('') or double ("") quotation marks.
Example :
"Hello, I'm a string"
'Hello, How are you...'
- Number
It Represents numeric values, both integer and floating-point numbers.
int float
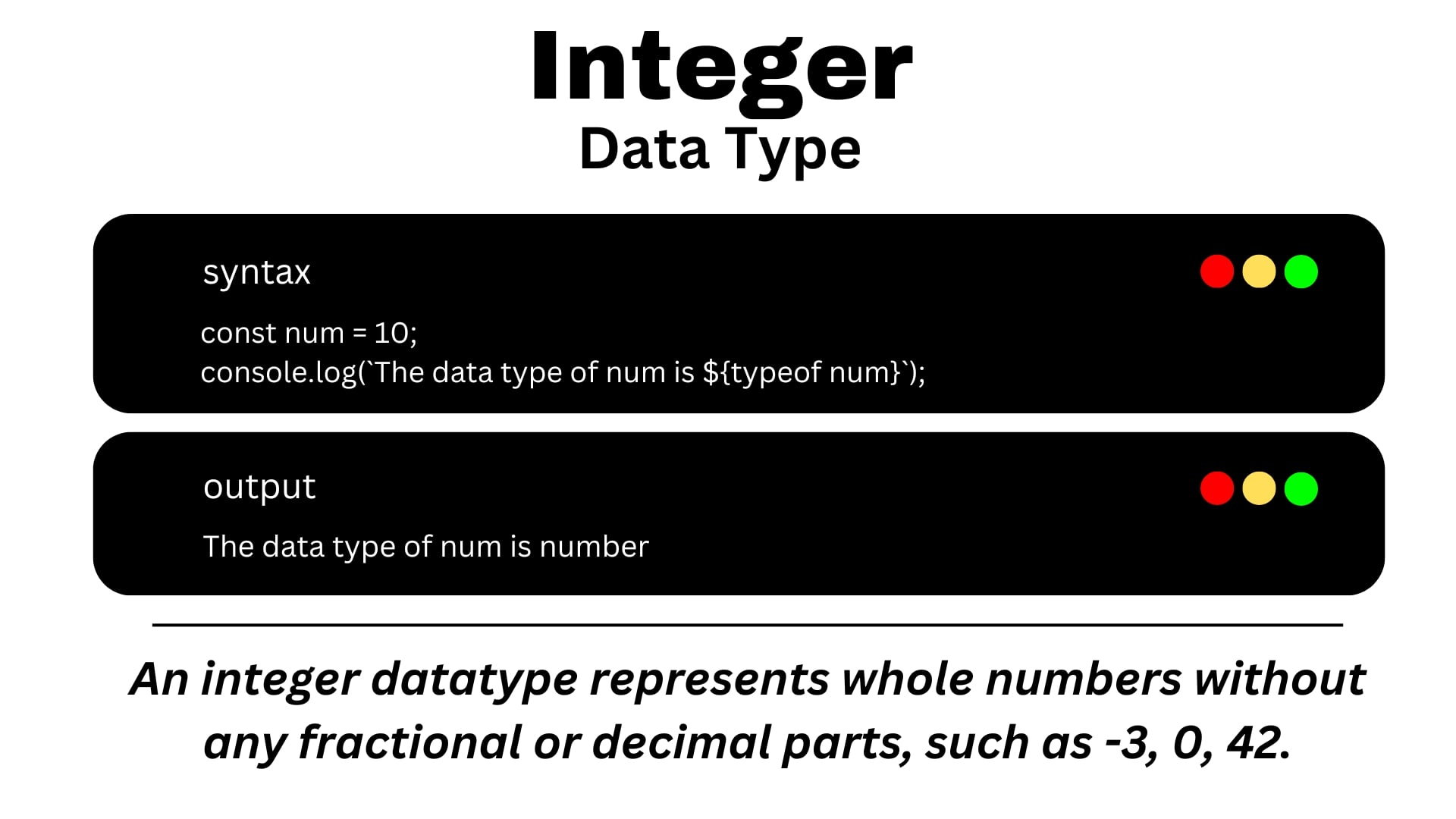
a. Int
Integer numbers are whole numbers without decimal points.
Example :
123456
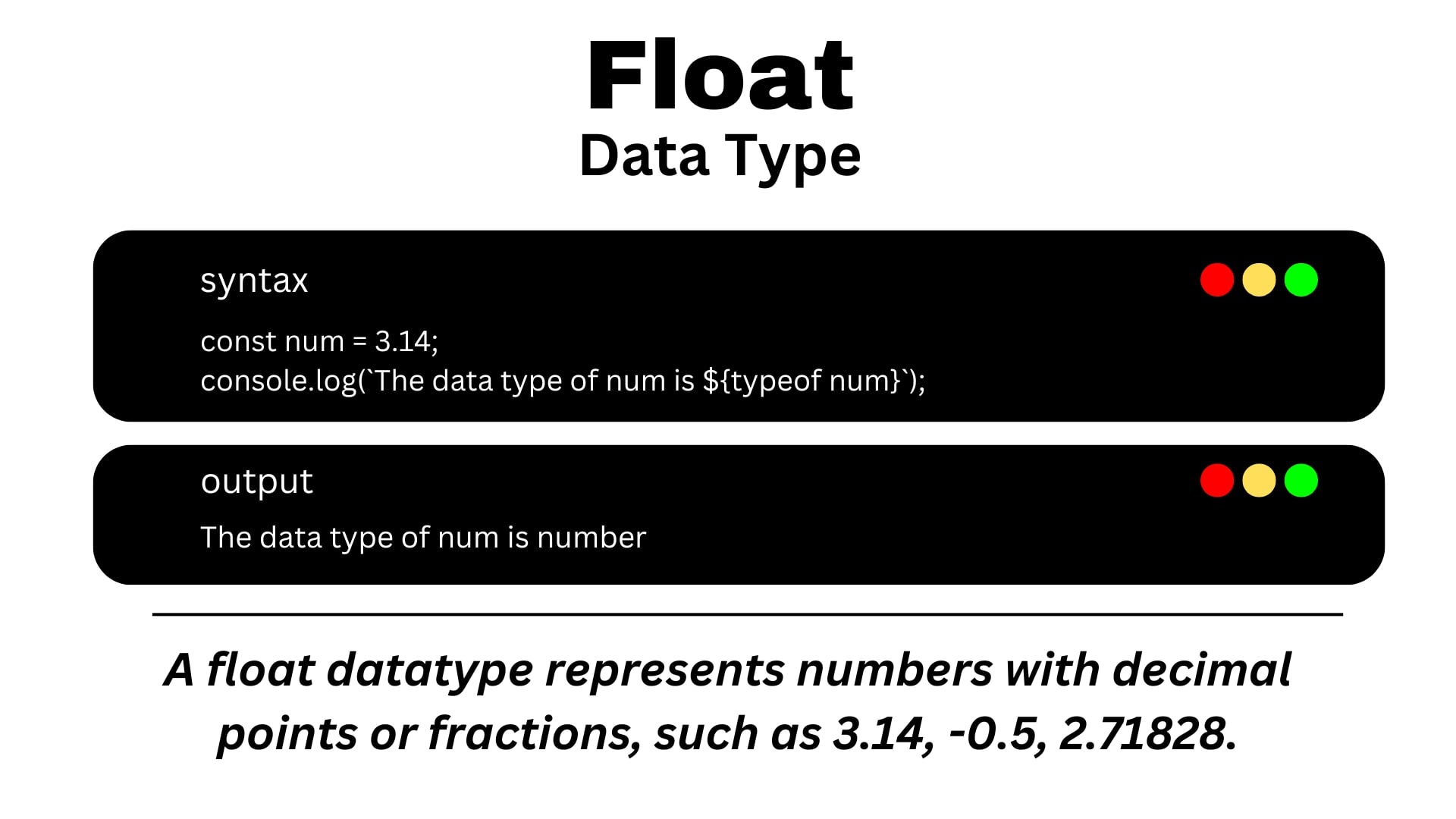
b. Float
Floats are numbers with decimal points.
8793.90
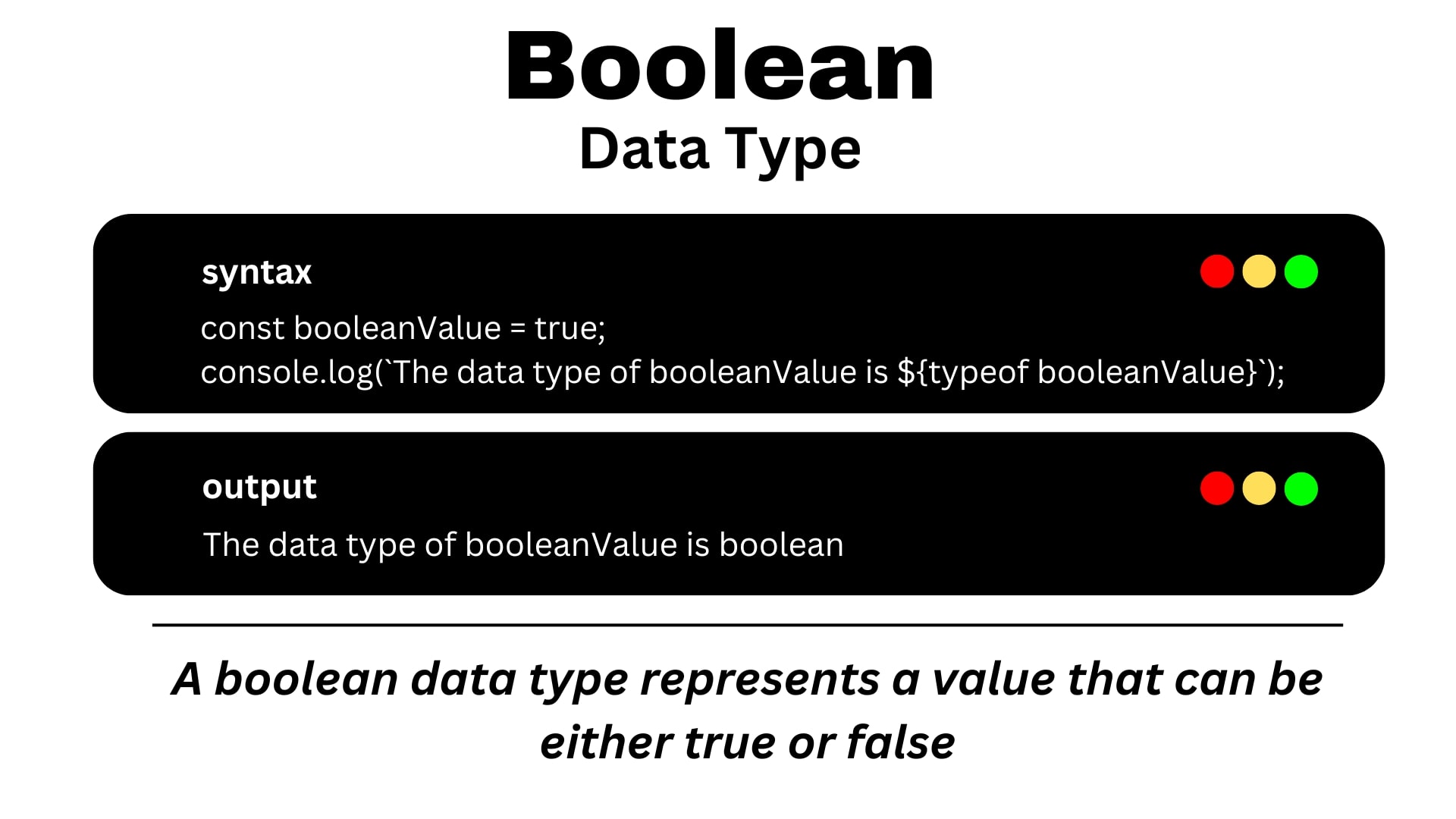
- Boolean
A boolean represents Logical values Like : true or false( one of two possible values).
true or false
What is Javascript Engine?
A JavaScript engine is responsible for executing JavaScript code in a web browser. Browsers utilize engines like V8 (used in Chromium-based browsers), which compiles JavaScript code and produces the desired output.
Variables In Javascript
A variable is used to store data. There are three keywords to declare variables:
let, const, var
Syntax :
keyword variableName;
Example
let age;
In The above example we can use let keyword and declare one variable name of that variable is age. This is declaration part of in the variable.
age = 20;
In The above example we assign 20 value for age variable. This 20 value is stored in age variable. This is assignment part of in the variable.
Example
let age = 20;
In the above example we create declaration and assignment part at same time.
let
Let keyword used to declare variables in JavaScript. Variables defined using let Cannot be re-declared within the same scope.
Code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head> </head>
<body>
<script>
let age = 20;
console.log(age);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output
20
In the above example we can create one variable using let keyword name of that variable age. we store 20 value in age variable. In next line we print value of console.log(age);age variable.
Code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head> </head>
<body>
<script>
let age = 20;
console.log(age);
age = 50;
console.log(age);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output
20
50
In the above example we can create one variable using let keyword name of that variable age. we store 20 value in age variable. In next line we store 50 value in same variable. In next line we print value of console.log(age); age variable. But the output of above eaxmple is 50 because one variable store only one value at a time.
Code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head> </head>
<body>
<script>
let age = 20;
let name = "Suraj";
console.log("Name:", name);
console.log("Age:", age);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output
Name: Suraj
Age: 20
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head> </head>
<body>
<script>
let age;
console.log(age);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output
undefined
const
const declares a constant variable that cannot be reassigned.
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head> </head>
<body>
<script>
const age = 20;
console.log(age);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output
20
var
var is an older way to declare variables with functional scope.
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head> </head>
<body>
<script>
var age = 20;
var age = 30;
console.log(age);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output
30
Difference between var, let and const
| var | let | const | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | The scope of the var variable is the functional scope. | Let allow us to declare a variable that is limited to the scope of a block. | The scope of the const variable is block scope. |
| Updates | It can be updated and re-declared in scope. | It Can be updated, but not re-declared within its scope. | Cannot be updated or re-declared after being defined. |
| Initialization | Can be declared without being assigned a value. | Can be declared without being assigned a value. | Must be assigned a value when declared. |
| Access | It can be accessed without initialization because its default value is undefined. | It cannot accessed without initialization, or a "reference error" will be raised. | It cannot be accessed without initialization because it cannot be declared without initialization. |
Rules to declare variables:
- Use letters
a-z,A-Z, digits0-9, and underscore_. - Variables cannot start with numbers.
- Variable names cannot be reserved keywords.
- Variable names are case-sensitive, which means
nameandNameare considered different variables.