Introduction To CSS
CSS
CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets. It is used to design webpages and control the visual appearance of HTML elements. CSS describes how HTML elements should be displayed on different devices, such as desktops, laptops, tablets, or other media.
Implementing CSS:
CSS can be implemented by three ways:
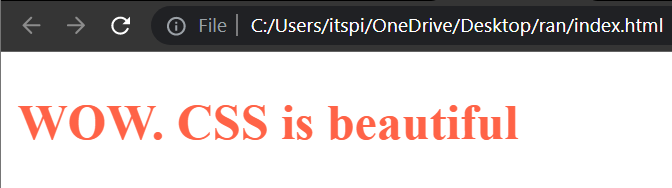
- Inline CSS : Inline CSS is applied directly to HTML elements using the style attribute. It allows you to apply CSS styles to individual HTML tags.
Code :
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2 style="color:tomato; font-size:20px;">Wow. CSS is beautiful</h2>
</body>
</html>
Output :
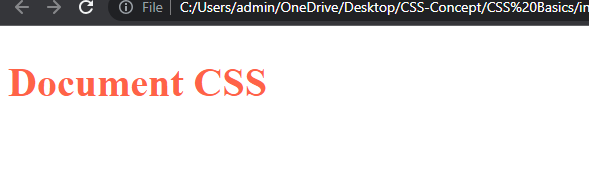
- Document CSS : Document CSS is embedded within the HTML document using the
<style>tag. It is placed in the<head>section of the HTML document.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS</title>
<style>
h2 {
color: tomato;
background-color: grey;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>document CSS</h2>
</body>
</html>
Output :
- External CSS : External CSS is stored in a separate CSS file and linked to the HTML document using the
<link>element. The CSS file is saved with a .css extension
Code :
File Name : index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
</head>
<body>
<h2>WOW. CSS is beautiful</h2>
</body>
</html>
File Name : style.css
h2 {
color: tomato;
background-color: "aqumarine";
}
Output :
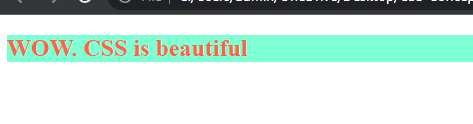
In the above example, the CSS styles are defined in the style.css file and linked to the HTML document using the <link> element.
CSS Selectors :
CSS selectors are used to select HTML elements that you want to style. There are different types of CSS selectors:
There are three types of selectors:
- Tagname Selector: Tagname selector selects HTML elements based on their tag names. For example, h1, h2, p, etc.
<h1>Hii</h1>
CSS of h1 tag 👉
<style>
h1 {
color: red;
}
</style>
- Class Selector : The class selector selects elements based on their class attribute. It is denoted by a dot (.) followed by the class name.
Selectors in CSS
1. Tagname
Tagname selector select attribute by tag for example h1,h2,p...
<h1>Hii</h1>
CSS of h1 tag 👉
<style>
h1 {
color: red;
}
</style>
2. Classname
The .class selector selects elements with a specific class attribute.
<p class="highlight"> Hii </p>
<h1 class="highlight"> Hii </p>
CSS of class 👉
<style>
.highlight{
background-color : yellow
}
</style>
- ID Selector : The ID selector selects elements based on their ID attribute. It is denoted by a hash (#) followed by the ID name
<h1 id="myheading">Hii</h1>
CSS of myheading id 👉
<style>
#myheading {
color: red;
}
</style>
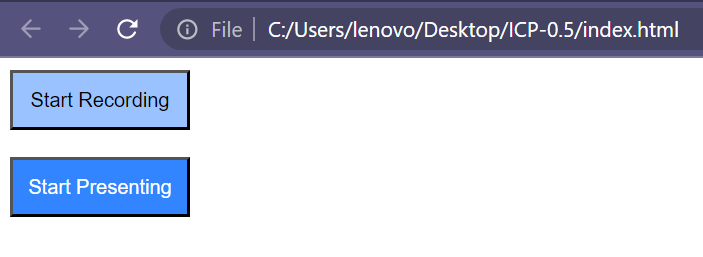
Height, Width For Button
CSS provides various methods to specify the height and width of an image. To set image dimensions using pixel (px) values, you can use CSS, which allows for precise control over the size of the image.
Example :
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Height And Width</title>
<style>
#btn-recording {
background-color: #99c2ff;
}
#btn-presenting {
background-color: #3385ff;
color: white;
}
.google-btn {
height: 40px;
width: 120px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btn-recording" class="google-btn">Start Recording</button>
<br /><br />
<button id="btn-presenting" class="google-btn">Start Presenting</button>
</body>
</html>
Output :