Introduction To API
Introduction To API
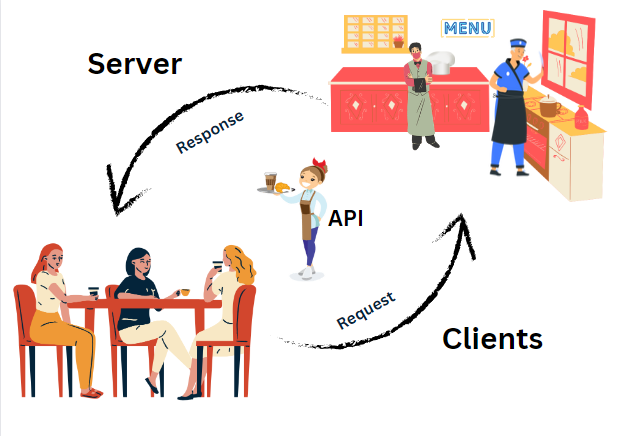
An API Application Programming Interface is a set of rules and protocols that allows different software applications to communicate and interact with each other. In the context of web development, APIs are used to enable communication between the frontend (client-side) and backend (server-side) of a web application.
Frontend : The frontend, also known as the client, refers to the user interface of a web application that users interact with. It is responsible for sending requests to the backend and displaying the data received from the server.
Backend : The backend, also known as the server, handles the processing of requests received from the frontend. It performs various operations such as retrieving data from a database, executing business logic, and generating a response to be sent back to the client.
API : The API acts as an intermediary between the frontend and backend. It defines a set of rules and protocols for how requests and responses should be structured. The API takes the requests from the frontend, processes them, and transforms the data as required. It then sends the transformed data back to the frontend as a response.
Backend Commands:
- npm init -y : This command initializes a new Node.js package in the current directory. The -y flag sets default options for all the prompts, allowing the initialization to proceed without requiring user input.
npm init -y
Create index.js This step involves creating an index.js file. The index.js file typically serves as the entry point of the backend application.
edit package.json : The package.json file contains metadata about the Node.js package and its dependencies. This step likely involves editing the package.json file to include necessary information about the backend application.
Express js:
Express.js is a popular JavaScript framework for building web applications and APIs. It simplifies the process of setting up a server and handling HTTP requests and responses.
Install express :
To install express, you can use the following commands:
npm install express
How to create server :
To create a server using Express, you need to write some code in your index.js file. Here's an
Example :
import express from "express";
const app = express();
app.listen(5000, () => {
console.log("listening on port 5000");
});
In the above code:
- We import the express module and create an instance of the express application.
- The app.listen() method starts the server and makes it listen on port 5000.
- When the server starts listening, the callback function is executed, and it logs a message to the console.
Once the server is running, it can handle incoming HTTP requests from the frontend and send appropriate responses back.
HTTP Methods
GET
The GET method is used to retrieve data from a specified resource on a server. It is a read-only method that does not modify or update any data on the server. In the provided example, an Express server is created using the express package. When a GET request is made to the /students endpoint, the server responds with a JSON array containing student names. The res.json('students') statement sends the response with the string students as the data.
Example:
import express from "express";
const app = express();
app.get("/students", (req, res) => {
res.json("students");
});
app.listen(5000, () => {
console.log("Listening on port 5000...");
});
POST
The POST method is used to send data to the server to create a new resource or perform an action. It submits data in the body of the request to be processed by the server. In the provided example, when a POST request is made to the /student endpoint, the server extracts the name and roll properties from the request body. Then, it sends a response with a JSON object containing a success status and a message indicating the successful creation of a student with the provided information.
Example:
import express from "express";
const app = express();
app.get("/students", (req, res) => {
const students = ["Saurabh", "Yogita", "Bandini", "Harshada", "Darshan"];
res.json(students);
});
app.post("/student", (req, res) => {
const name = req.body.name;
const roll = req.body.roll;
res.json({
status: "success",
message: `Student ${name} created with roll number ${roll}`,
});
});
app.listen(5000, () => {
console.log("Listening on port 5000");
});
Nodemon
Nodemon is a utility that automatically monitors changes in your source code and restarts the server whenever a change is detected. It is commonly used during development to save time and effort in manually restarting the server after each code modification.
To use nodemon, you need to install it globally using npm by running the following command in your terminal:
npm i nodemon
After installing nodemon, you can add it to the scripts section of your package.json file. The provided example adds a script called start to the package.json file. The script executes the command nodemon index.js when you run npm start. This means that nodemon will monitor the index.js file for changes and automatically restart the server whenever a change is detected.
Here's how the scripts section of your package.json file should look like:
"scripts": {
"start": "nodemon index.js"
}
With this setup, you can conveniently start your server using npm start, and nodemon will take care of automatically restarting the server whenever you make changes to the code.
Mongoose
Mongoose is an Object Data Modeling (ODM) library for MongoDB and Node.js. It provides a schema-based solution to model your application data, manage relationships between data, perform validation, and translate between objects in code and their representation in MongoDB.
Why Use Mongoose?
Mongoose offers several advantages for working with MongoDB and Node.js:
Schema Validation: Mongoose allows you to define a schema for your data and perform validation on the incoming data before saving it to the database. This helps maintain data integrity and consistency.
Relationship Management: Mongoose provides features to define and manage relationships between different data models. You can establish references or embed documents within each other.
Type Casting: Mongoose handles type casting of data, allowing you to define the types for fields in your schema. It automatically converts data to the specified types, reducing the need for manual type conversion.
Query Building: Mongoose provides a powerful and intuitive API for building database queries. You can perform CRUD operations, apply filters, sorting, pagination, and more using the query builder methods.
Business Logic Hooks: Mongoose supports pre and post hooks for performing actions before or after specific database operations. This enables you to implement custom business logic and perform additional actions during the data lifecycle.
Middleware Support: Mongoose supports middleware functions that can intercept and modify the behavior of certain operations, such as saving or deleting documents. This allows you to add custom logic and extend Mongoose's functionality.
Installation
To install Mongoose, you can use the npm package manager. Open your terminal and run the following command:
npm install mongoose
This will download and install the Mongoose package into your project.
Importing Mongoose
The method for importing Mongoose depends on the version of Node.js you are using and your project's configuration.
If you are using Node.js with support for ECMAScript modules (ESM), you can import Mongoose using the import statement:
import mangoose from "mangoose";
Make sure your project's package.json file includes "type": "module".
If you are using an older version of Node.js or your project is not configured for ECMAScript modules, you can use the require statement to import Mongoose:
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
Connecting to MongoDB
To connect to MongoDB using Mongoose, you need to provide the connection URL and handle the connection status.
Here's an example of connecting to MongoDB using Mongoose in an Express.js application:
Syntax :
import mongoose from "mongoose";
mongoose.connect("URL", "CALLBACK FUNCTION");
Example :
import express from "express";
import mongoose from "mongoose";
const app = express();
app.use(express.json());
async function connectionMongoDB() {
const conn = await mongoose.connect(
"mongodb+srv://<username>:<password>@mangodb.4kkisqa.mongodb.net/<dbname>"
);
if (conn) {
console.log("Mongo DB connected");
} else {
console.log("Error");
}
connectMongoDB();
}
app.listen(5000, () => {
console.log("Listen on port 5000");
});
In the example above, we import the express and mongoose packages. Then, we define an asynchronous function connectToMongoDB() that connects to the MongoDB server using mongoose.connect(). The connection URL mongodb+srv://<username>:<password>@mangodb.4kkisqa.mongodb.net/<dbname> specifies the username and password the name of the database dbname. Adjust the URL according to your MongoDB server configuration.
If the connection is successful, it logs a success message. If there's an error, it logs the error message.
Designing Schemas
In Mongoose, a schema represents the structure of a document, defining the fields, their types, and additional properties. Schemas provide a way to enforce data consistency and define validation rules.
Here's an example of defining a schema for a Student model:
File: models/Student.js
import { Schema, model } from "mongoose";
const studentSchema = new Schema({
fullname: String,
email: String,
regNo: Number,
});
const Student = model("Student", studentSchema);
export default Student;
In the example above, we import the Schema and model from Mongoose. We define a studentSchema using the Schema constructor, specifying the fields and their types. Each field can have additional properties such as required and unique to enforce constraints.
The model function is then used to create a model named Student based on the studentSchema. This model can be used to perform CRUD operations on the corresponding MongoDB collection.
Using the Schema in an Express.js Application
Now let's integrate the Student model into an Express.js application for creating and fetching students.
File Name : index.js
import express from "express";
import mongoose from "mongoose";
import Student from "./models/Student.js";
import dotnv from "dotenv";
dotnv.config();
const app = express();
app.use(express.json());
async function connectMongoDB() {
const conn = await mongoose.connect(process.env.MONGO_URL);
if (conn) {
console.log("Mongo DB Connected");
} else {
console.log("Error");
}
}
connectMongoDB();
app.post("/student", async (req, res) => {
const fullName = req.body.fullName;
const email = req.body.email;
const regNo = req.body.regNo;
const newStud = new Student({
fullName: fullName,
email: email,
regNo: regNo,
});
const savedStudent = await newStud.save();
res.json({
success: true,
message: "Student Saved Successfully",
data: savedStudent,
});
});
app.get("/students", async (req, res) => {
const students = await Student.find();
res.json({
success: true,
message: "Students fetched Successfully",
data: students,
});
});
app.listen(5000, () => {
console.log("Listen on port 5000");
});
In the example above, we import the necessary packages and models. We configure the Express.js application to parse JSON requests using app.use(express.json()). Then, we define two routes: one for creating a student /student and another for fetching all students /students.
In the /student route, we retrieve the fullName, email, and regNo from the request body. We create a new instance of the Student model and save it to the database using newStudent.save(). The saved student data is returned in the response.
In the /students route, we use Student.find() to retrieve all students from the database. The fetched students are returned in the response.
Make sure to create a .env file in the root directory of your project and add your MongoDB connection URL like this:
- Create a
modelsfolder and then createjsfile take first letter of js file always be capital.
File Name : .env
MONGO_URL = mongodb+srv://<username>:<password>@mangodb.4kkisqa.mongodb.net/<dbname>
Adjust the URL according to your MongoDB server configuration.
Put your username and password in the url for database connection.