API Methods in ExpressJs
REST ( Representational State Transfer ) API standard
Five main methods used in web APIs, which are based on HTTP methods. These methods are often referred to by the acronym CRUD, which stands for Create, Read, Update, and Delete.
1.GET
The GET method in HTTP requests data from a specified resource (such as a web server). It's used to fetch or read information like web pages, images, files, or data stored on a server without altering the resource's state. Body not allowed .
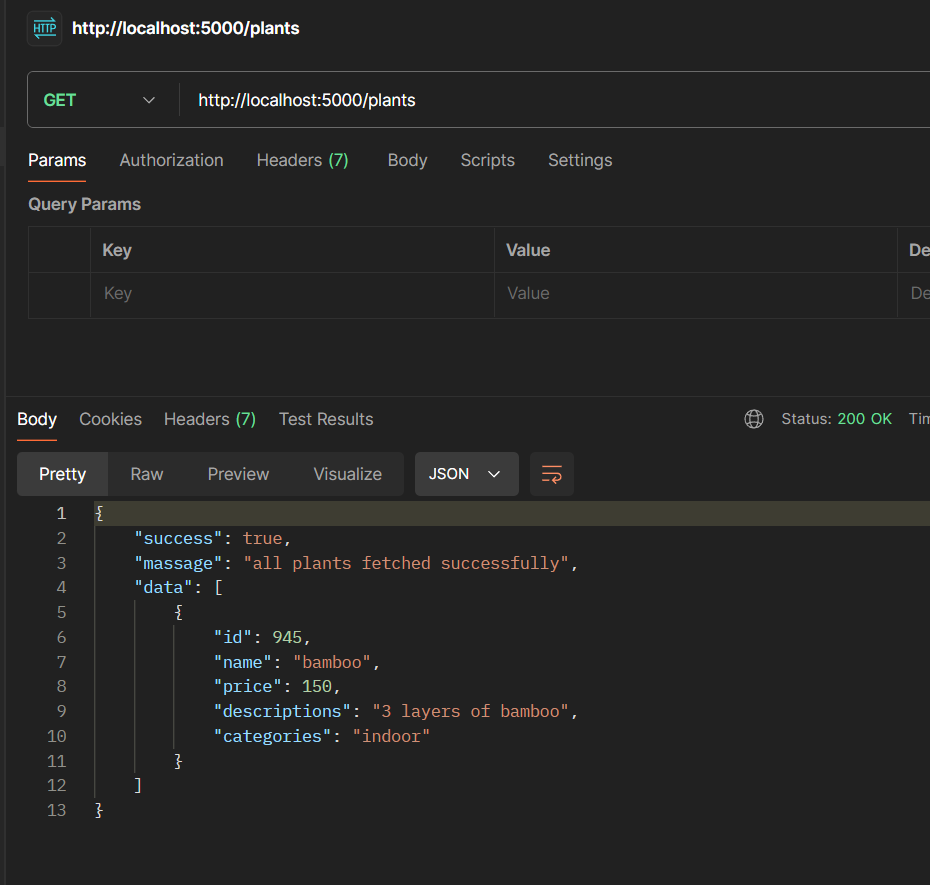
app.get("/plants", (req, res) => {
res.json({
success: true,
massage: "all plants fetched successfully",
data: plants,
});
});
Output
2. POST
The POST method in HTTP sends data to a server to create a resource. It's commonly used to submit form data or upload files, and it can cause changes or side effects on the server's state, such as adding a new user.
app.post("/plant", (req, res) => {
const { name, price, descriptions, categories } = req.body;
if (!name || !price || !descriptions || !categories) {
res.json({
success: false,
massage: `all fields should be filled`,
data: "",
});
}
const randomId = Math.round(Math.random() * 999999);
const newPlant = {
id: randomId,
name: name,
price: price,
descriptions: descriptions,
categories: categories,
};
plants.push(newPlant);
res.json({
success: true,
massage: `New plant added successfully`,
data: plants,
});
});
Output
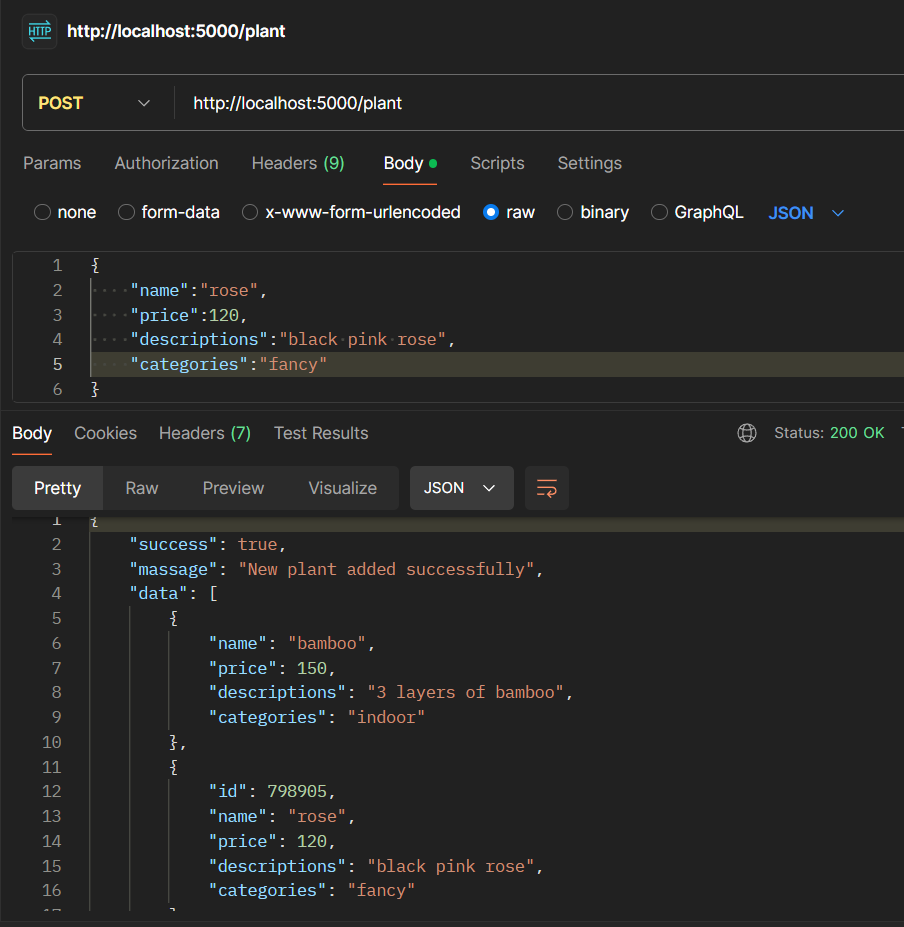
The ("/plant") endpoint. It extracts plant details (name, price, descriptions, categories) from the request body, and if any fields is empty it will through error, generates a unique ID for the new plant, creates a new plant object, and adds it to an array called plants. Finally, it sends a JSON response indicating success, with a message and the updated list of plants.
3. PUT
The PUT method in HTTP is used to send data to a server to update or replace a resource identified by a specific URL. It typically updates the entire resource with the new data provided in the request payload, making it useful for operations that require complete replacement of existing data, such as updating user information or replacing an existing file.
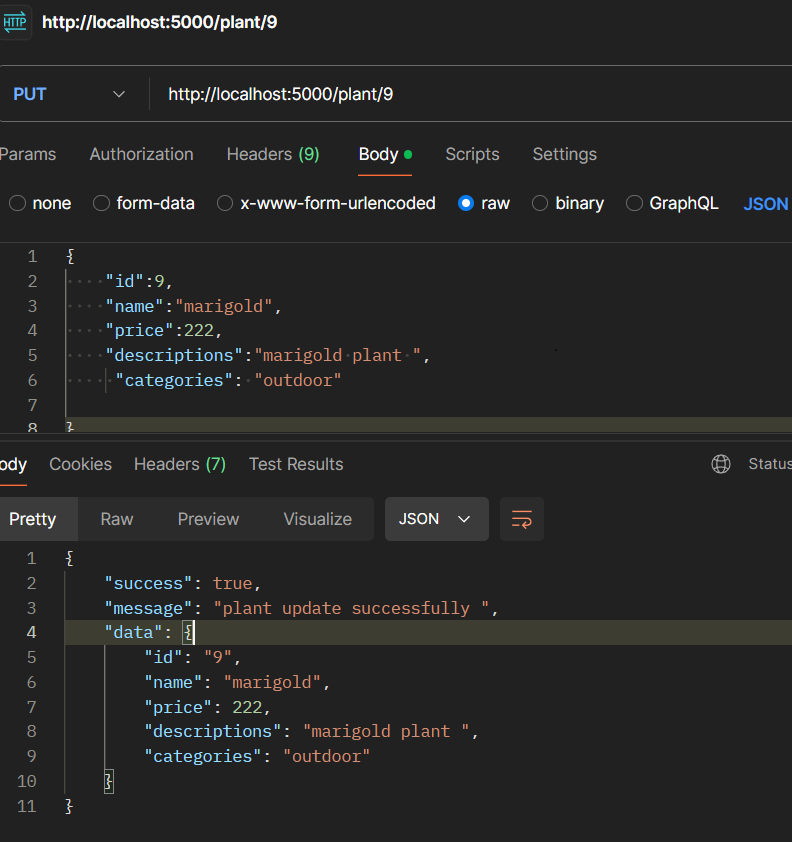
app.put("/plant/:id", (req, res) => {
const { name, price, descriptions, categories } = req.body;
const { id } = req.params;
let index = -1;
plants.forEach((p, i) => {
if (p.id == id) index = i;
});
const newObj = {
id,
name,
price,
descriptions,
categories,
};
if (index == -1) {
return res.json({
success: false,
message: "plant not found",
data: null,
});
} else {
plants[index] = newObj;
return res.json({
success: true,
message: "plant update successfully ",
data: newObj,
});
}
});
Output
4. PATCH
The PATCH method in HTTP is used to send partial data updates to a server, allowing modifications to specific fields of a resource without replacing the entire resource. It's useful for making minor updates or corrections to existing data, such as changing a user's email address or updating specific attributes of a document
app.patch("/plant/:id", (req, res) => {
const { id } = req.params;
const { name, price, descriptions, categories } = req.body;
const plant = plants.find((p) => p.id === parseInt(id));
if (!plant) {
return res.json({
success: false,
message: `Plant with id ${id} not found`,
data: "",
});
}
if (name) plant.name = name;
if (price) plant.price = price;
if (descriptions) plant.descriptions = descriptions;
if (categories) plant.categories = categories;
res.json({
success: true,
message: `Plant with id ${id} updated successfully`,
data: plant,
});
});
5. DELETE
The DELETE method in HTTP requests the removal of a specified resource from the server. It deletes the resource identified by the URL,causing a permanent removal of the resource from the server's state. This method is commonly used to delete records or files, and it does not typically return any response body upon successful deletion.
app.delete("/plant/:id", (req, res) => {
const { id } = req.params;
const plantIndex = plants.findIndex((p) => p.id === parseInt(id));
if (plantIndex === -1) {
return res.json({
success: false,
message: `Plant with id ${id} not found`,
data: "",
});
}
plants.splice(plantIndex, 1);
res.json({
success: true,
message: `Plant with id ${id} deleted successfully`,
data: plants,
});
});
Ways to pass data to APIs
1. query
2. params
3. body
4. headers
query
query parameters are used to send additional data as part of the URL, often for filtering or sorting. They are appended to the URL after a question mark (?) in key-value pairs and can be accessed using req.query.
Example...
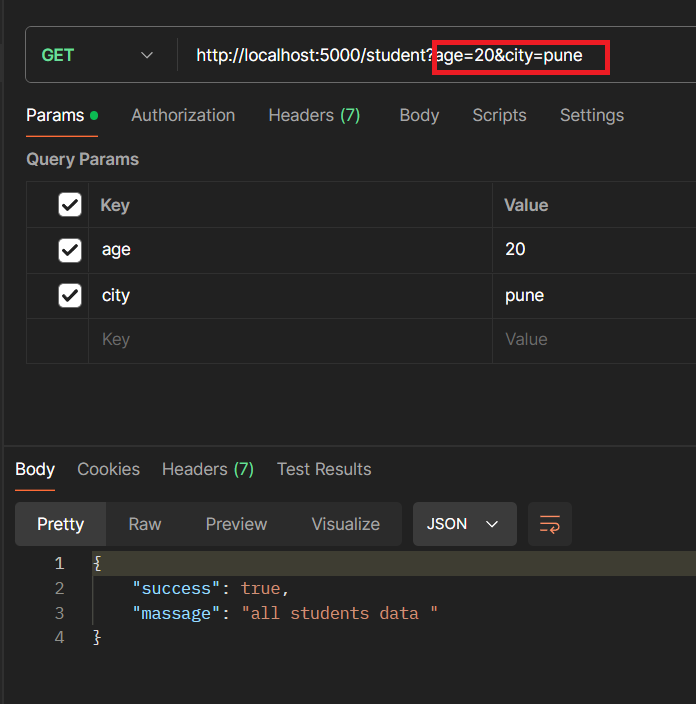
app.get("/student", (req, res) => {
console.log(req.query.age);
console.log(req.query.city);
res.json({ success: true, massage: "all students data " });
});
In above example passing query in key-value pair after the ? mark , we can pass multiple query using & shine .
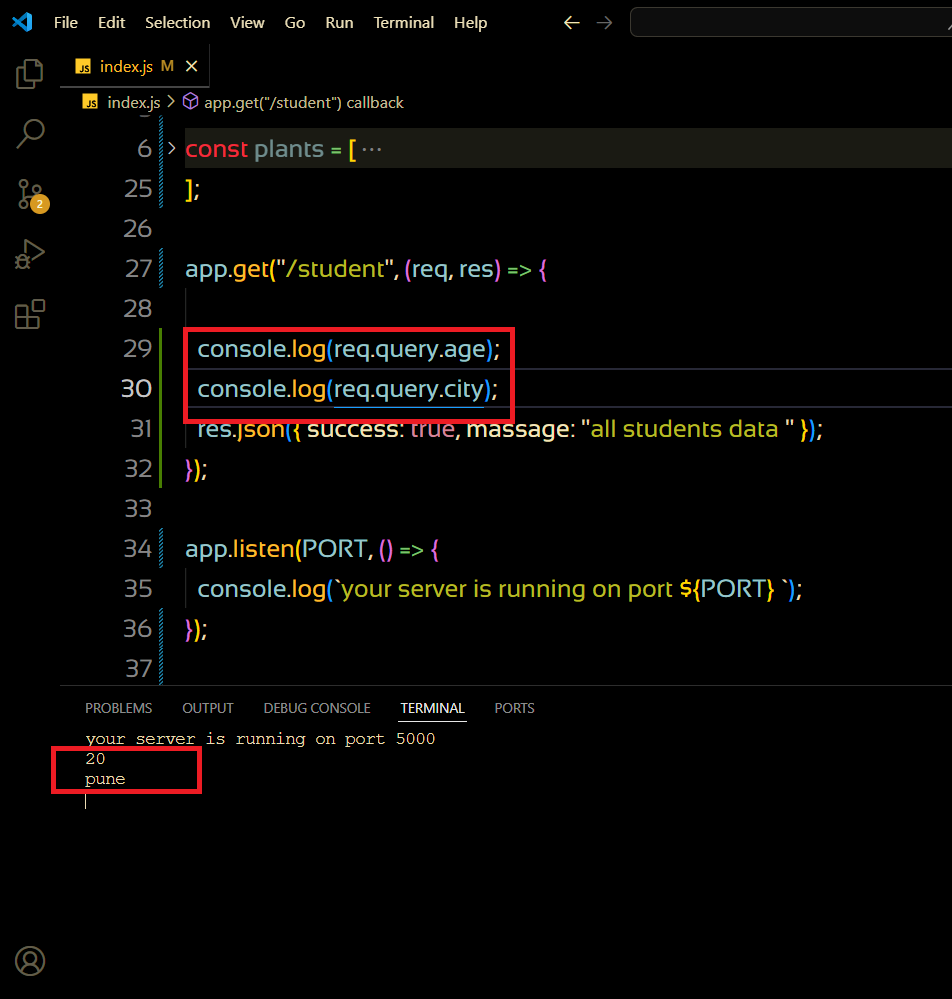
here we can see the result in terminal , and in code req.query.age and req.query.city
params
path parameters (params) are used to capture values from the URL path itself. These parameters are defined in the route and accessed using `req.params.
Example...
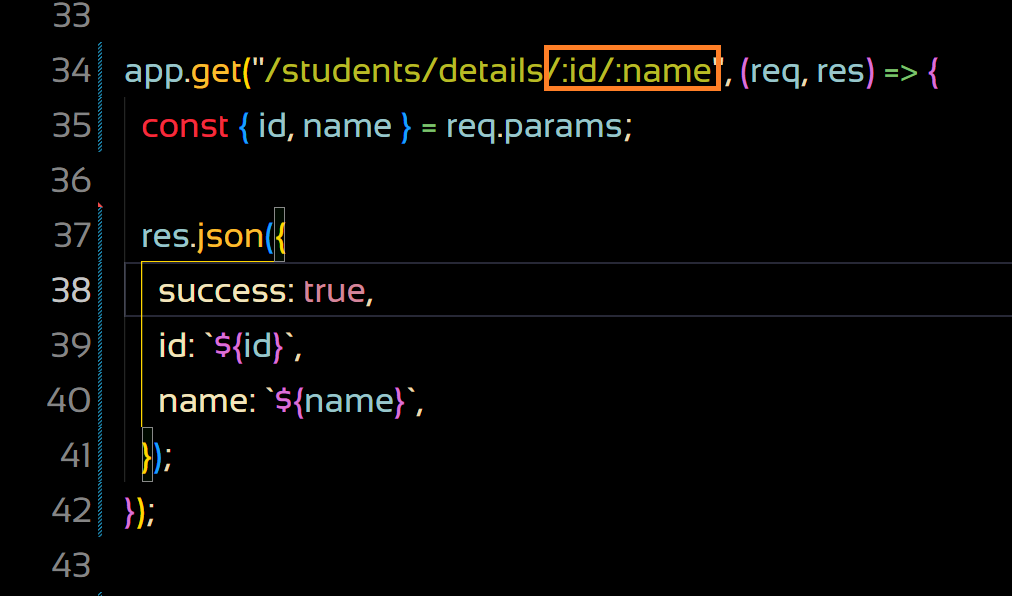
app.get("/students/details/:id/:name", (req, res) => {
const { id, name } = req.params;
res.json({
success: true,
id: `${id}`,
name: `${name}`,
});
});
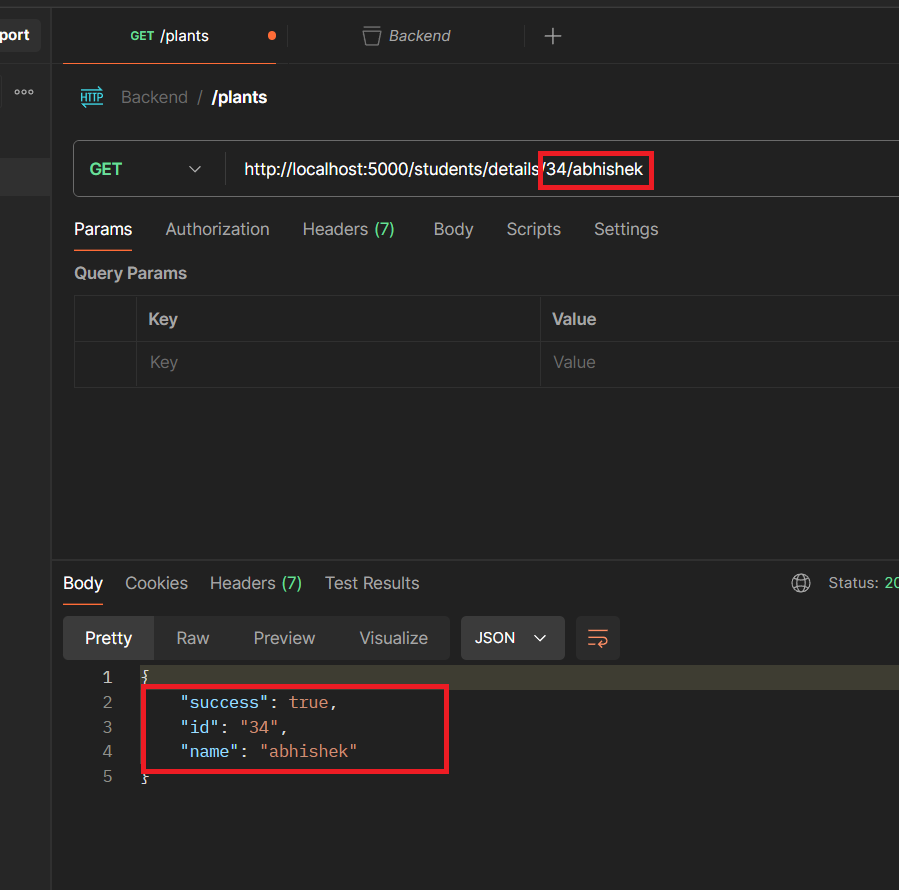
The path parameters id and name are defined in the route (/students/details/:id/:name) .
body
This is commonly used in POST, PUT, and PATCH requests to send data such as form submissions, JSON payloads, or file uploads. In Express.js, the body of a request can be accessed and processed using middleware like express.json()
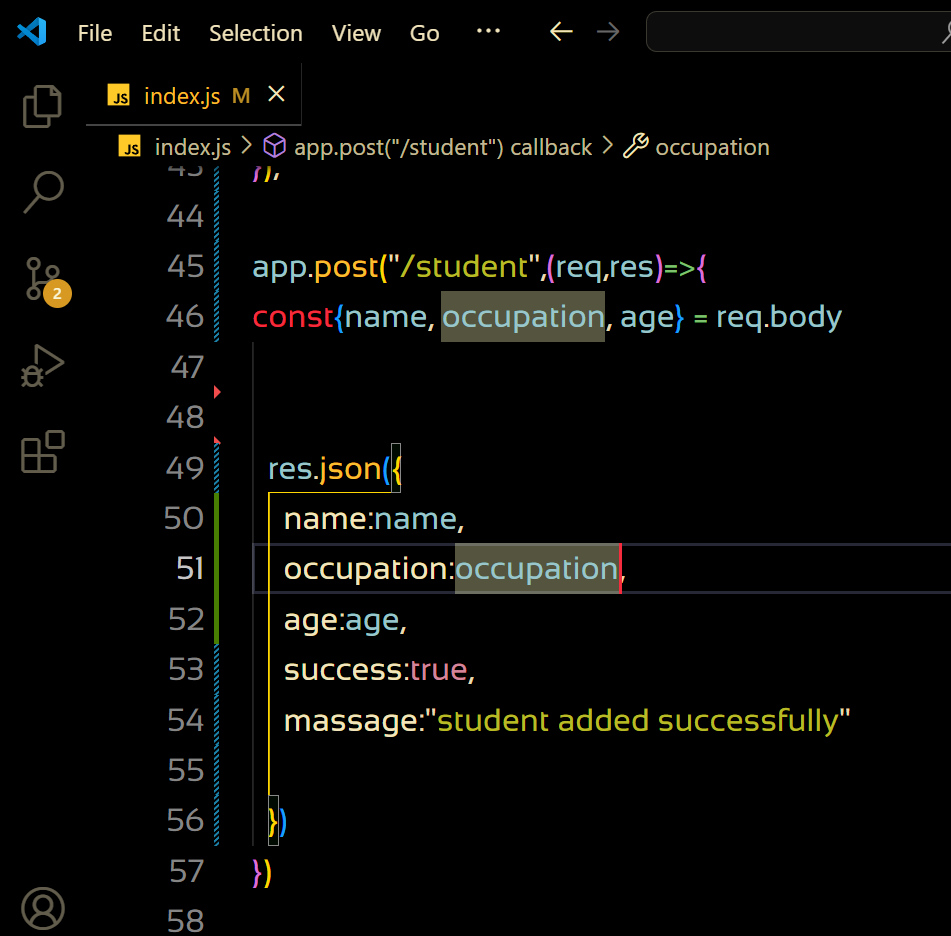
const app = express();
app.post("/student", (req, res) => {
const { name, occupation, age } = req.body;
res.json({
name: name,
occupation: occupation,
age: age,
success: true,
massage: "student added successfully",
});
});
Output
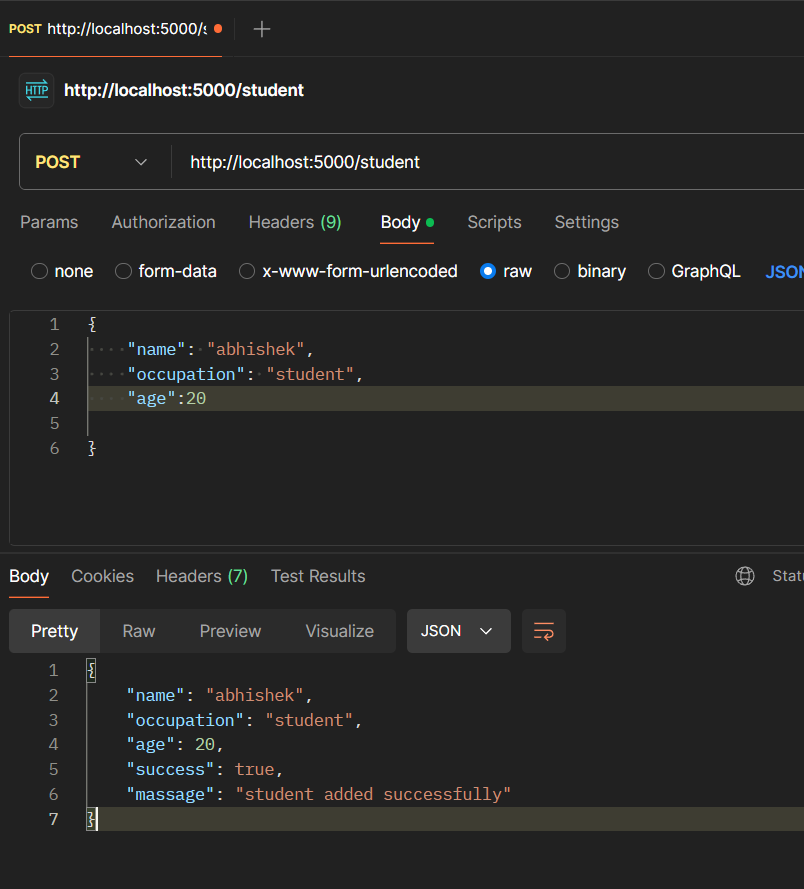
headers
Headers can be used for various purposes, such as specifying content types, handling authentication, and controlling caching.
app.put("/password", (req, res) => {
console.log(req.headers.password);
res.json({
success: true,
massage: "Account created successfully",
});
});
Postman Output
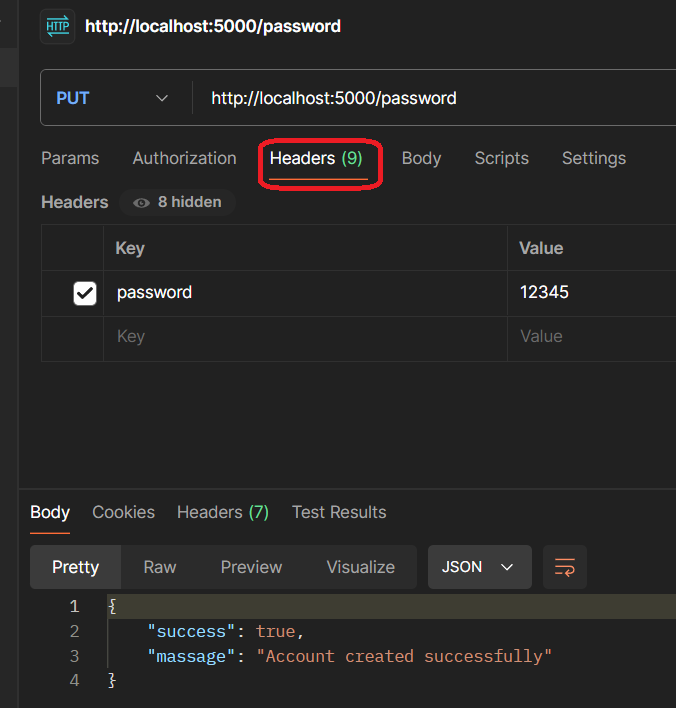
Output