Margin
Margin:
Margin refers to the space around an element, outside of any defined borders. It creates space between elements. The CSS properties used to control margin are similar to padding:
margin-top: Specifies the margin on the top side of the element.margin-right: Specifies the margin on the right side of the element.margin-bottom: Specifies the margin on the bottom side of the element.margin-left: Specifies the margin on the left side of the element.
Here's an example of how margin can be applied to an element:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Margin</title>
<style>
.btn1 {
background-color: red;
color: white;
border: none;
margin-top: 50px;
margin-left: 40px;
margin-right: 30px;
margin-bottom: 100px;
padding: 5px 15px 5px 15px;
}
.box {
background-color: aqua;
border: 2px solid black;
width: 400px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<body>
<div class="box">
<button class="btn1">Button One</button>
</div>
</body>
</body>
</html>
Output
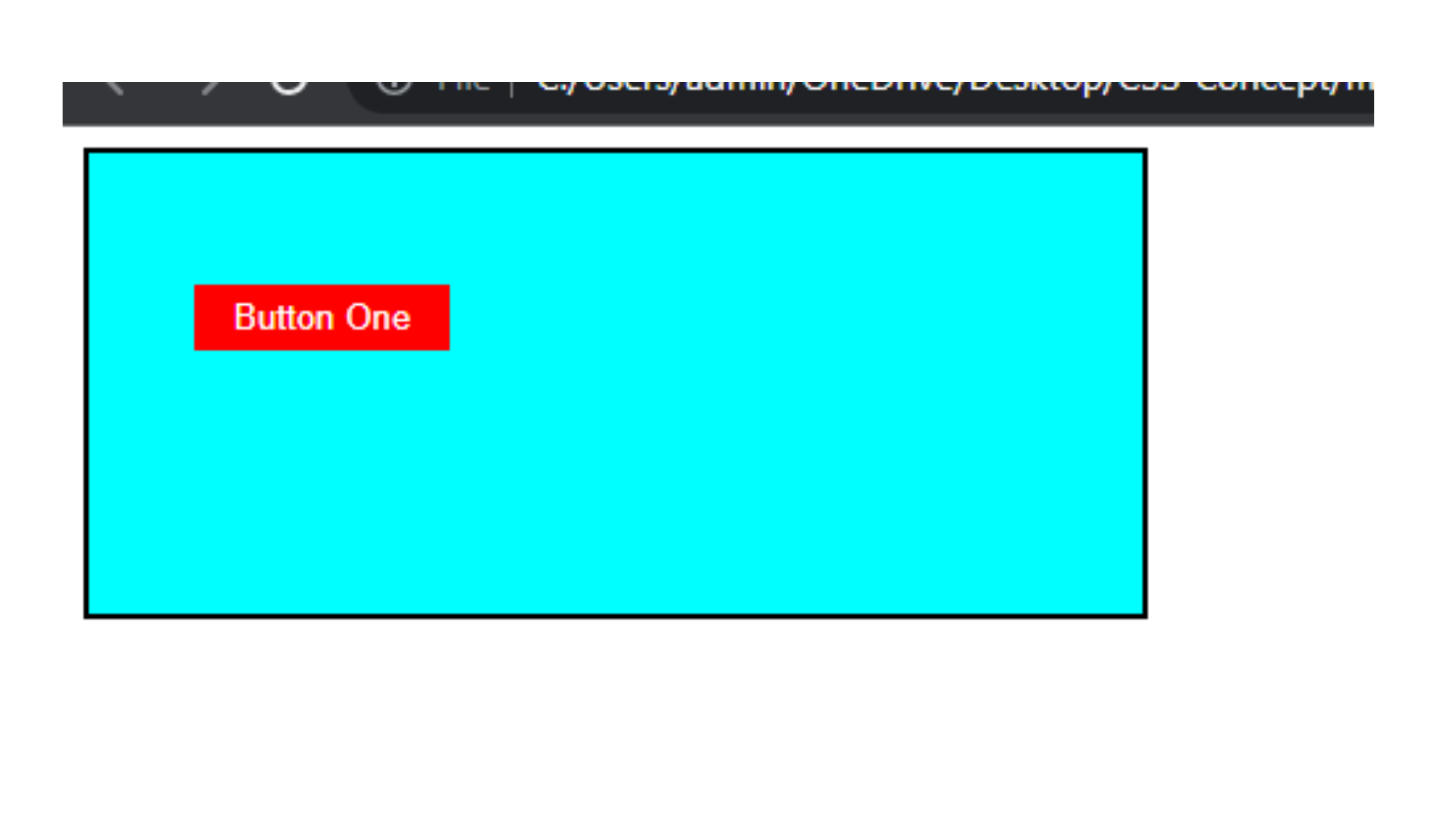
Shorthand Margin
Similar to shorthand padding, you can use the shorthand margin property to define margin for all four sides simultaneously. The values are specified in the same order: top, right, bottom, left.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Margin</title>
<style>
.btn1 {
background-color: pink;
color: white;
border: 2px solid black;
margin: 10px 30px 5 0px 80px;
padding: 5px 15px 5px 15px;
}
.box {
background-color: yellow;
border: 2px solid black;
width: 300px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<body>
<div class="box">
<button class="btn1">Button One</button>
</div>
</body>
</body>
</html>
Output
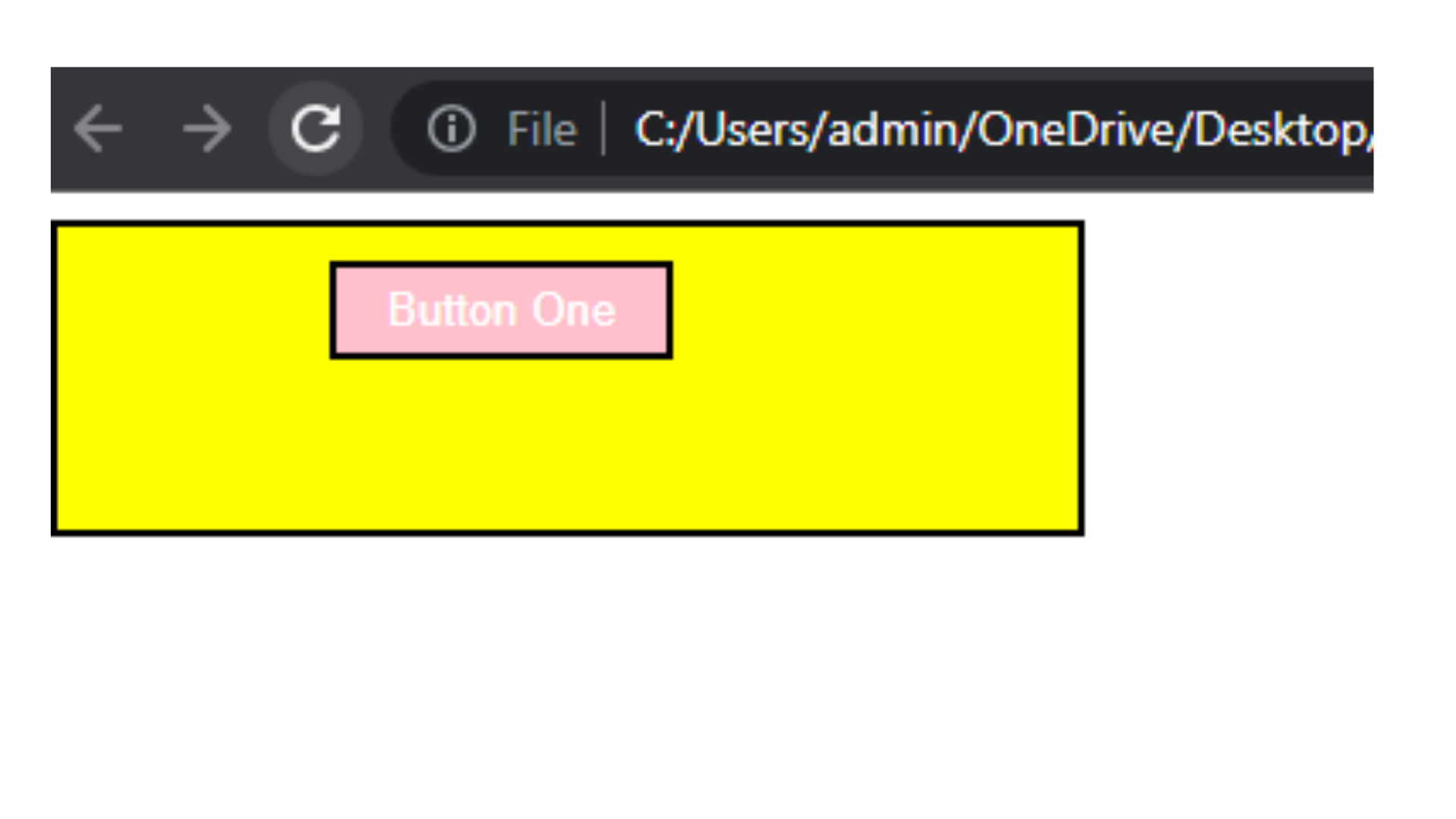
In the example above, the shorthand margin property is used to apply margin to all four sides of the <button> element with the class btn. The values 10px 30px 50px 80px represent the top, right, bottom, and left margins, respectively.