AWS IAM
What is AWS IAM?
- AWS IAM
(Identity and Access Management)helpssecurelymanage access toAWS resources. It allows you to control who can access what by creatingusers,groups, androleswith specificpermissions. This ensures that onlyauthorizedpeople or services canperform actionson your resources.
Step:1. Login to aws
- Open the browser and search https://aws.amazon.com/
- sign in to the console
- Next enter your email.
- Now fill the captcha if you are not able to see the captcha then click on speaker icon and then fill.
- Next enter your password
Step:2. Finally you are on your dashboard
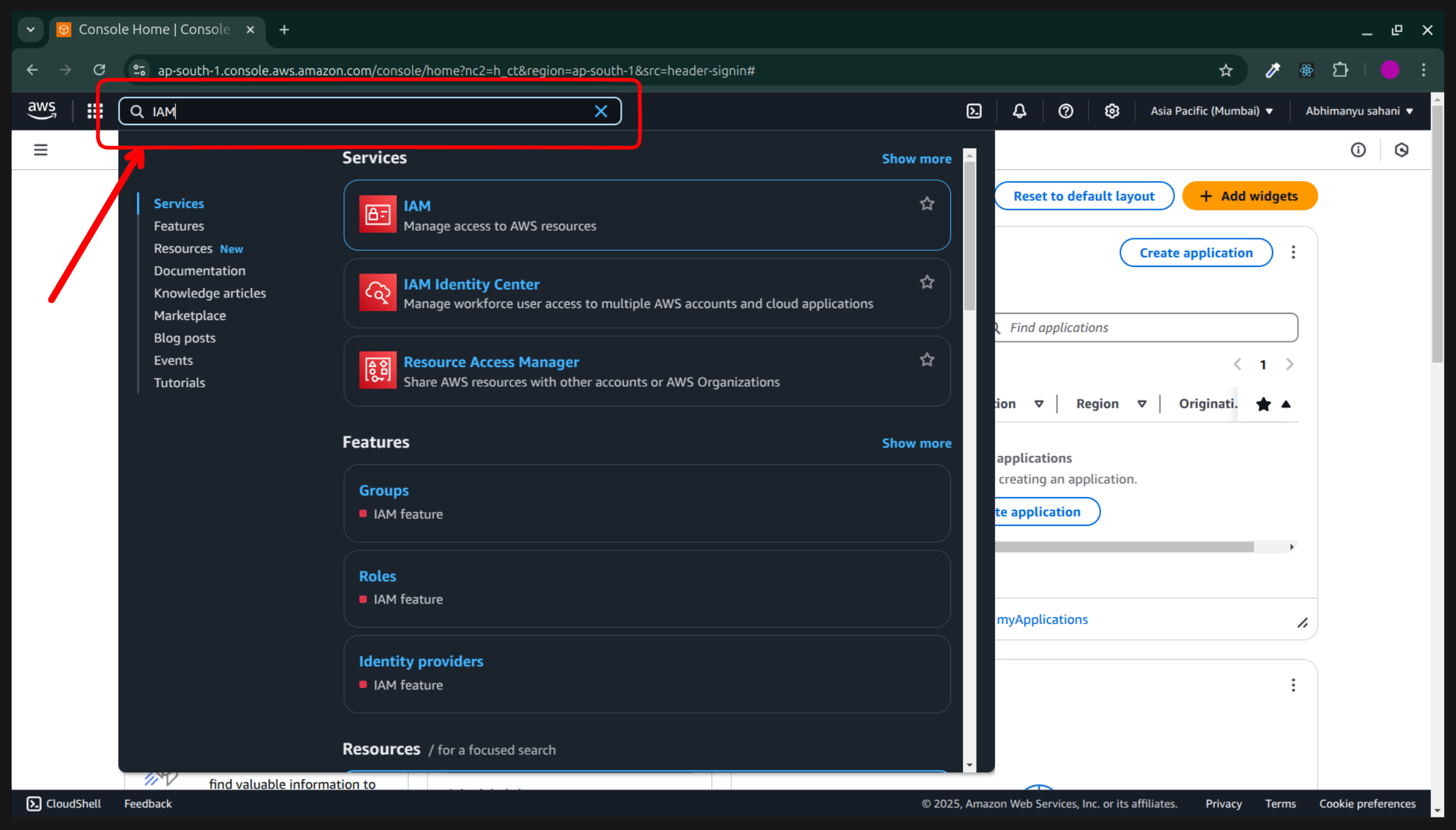
Step:3. Type IAM in the search input box and click on the top result
Step:4. Next you'll be on IAM Dashboard.
Now you see the
Users group,Users,Rolesby default Aws gives 2 roles ,PoliciesandIdentity Provider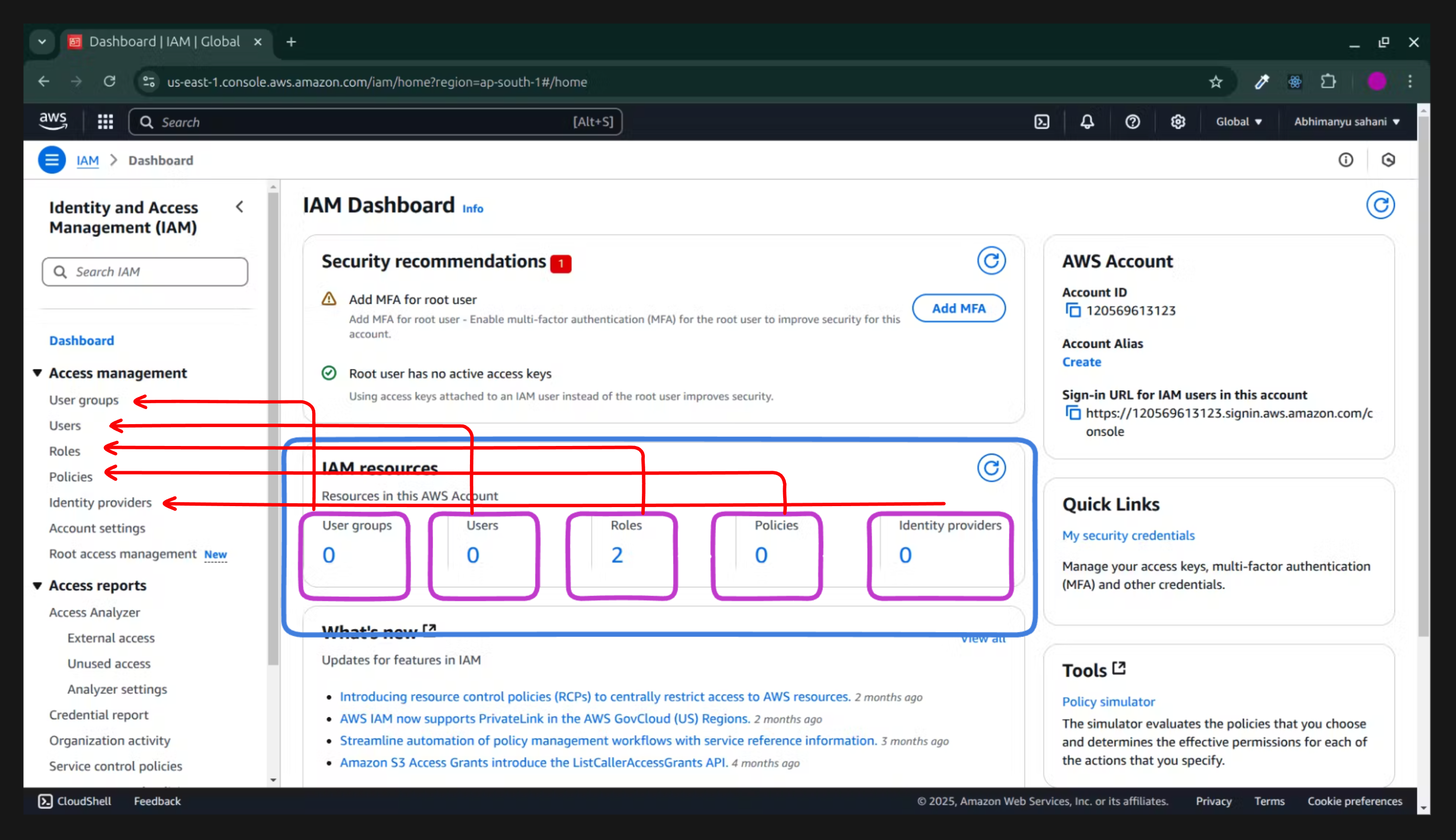
At top you will see
Add MFA(multi-factor authentication )Click on
Add MFA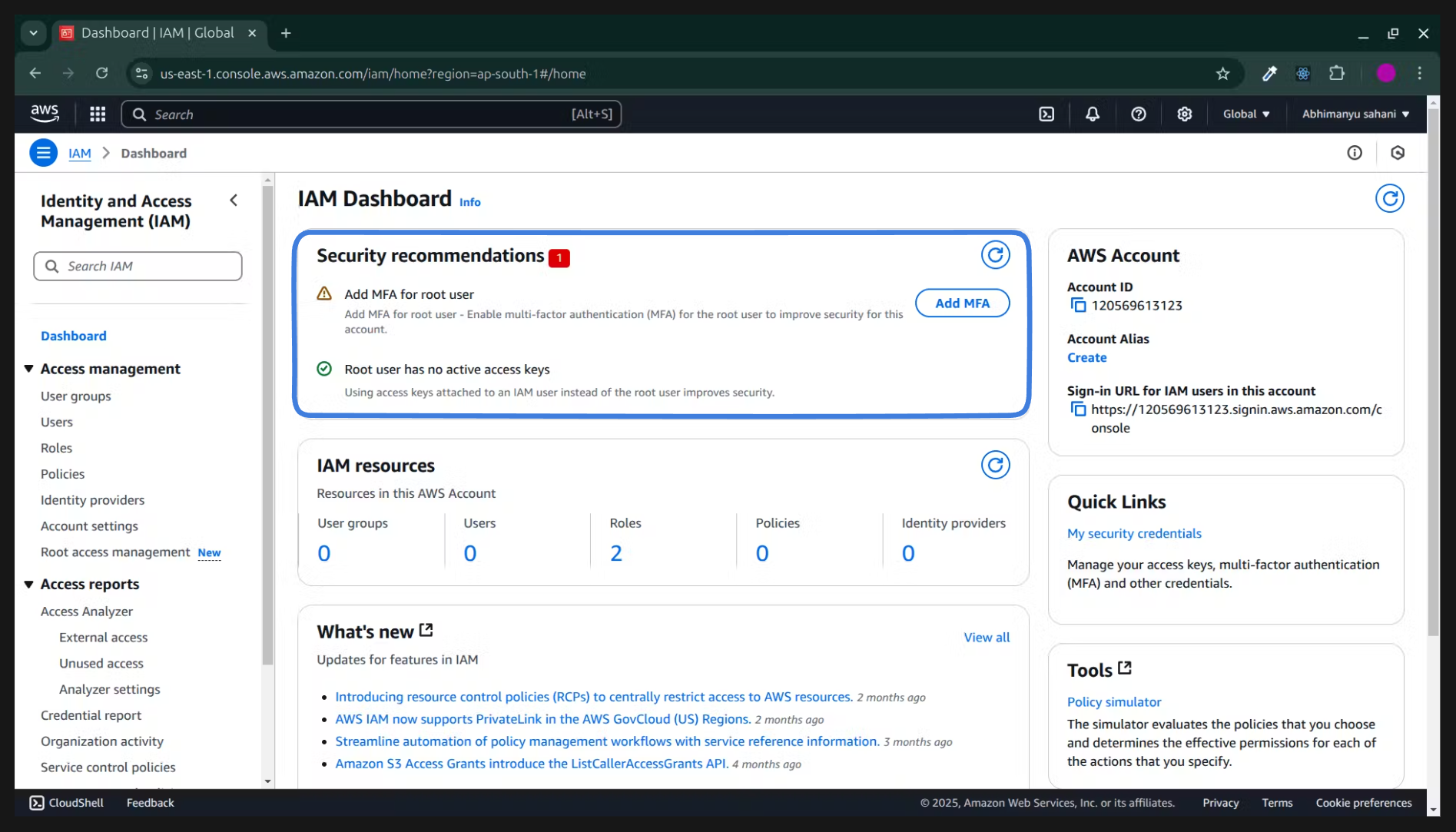
You will be redirected to the
security credentialpage,Enter any name into the
MFA device name, (whenever anyone wil try to login your account these things is going to asked by that user. )Now, next select your
MFA device.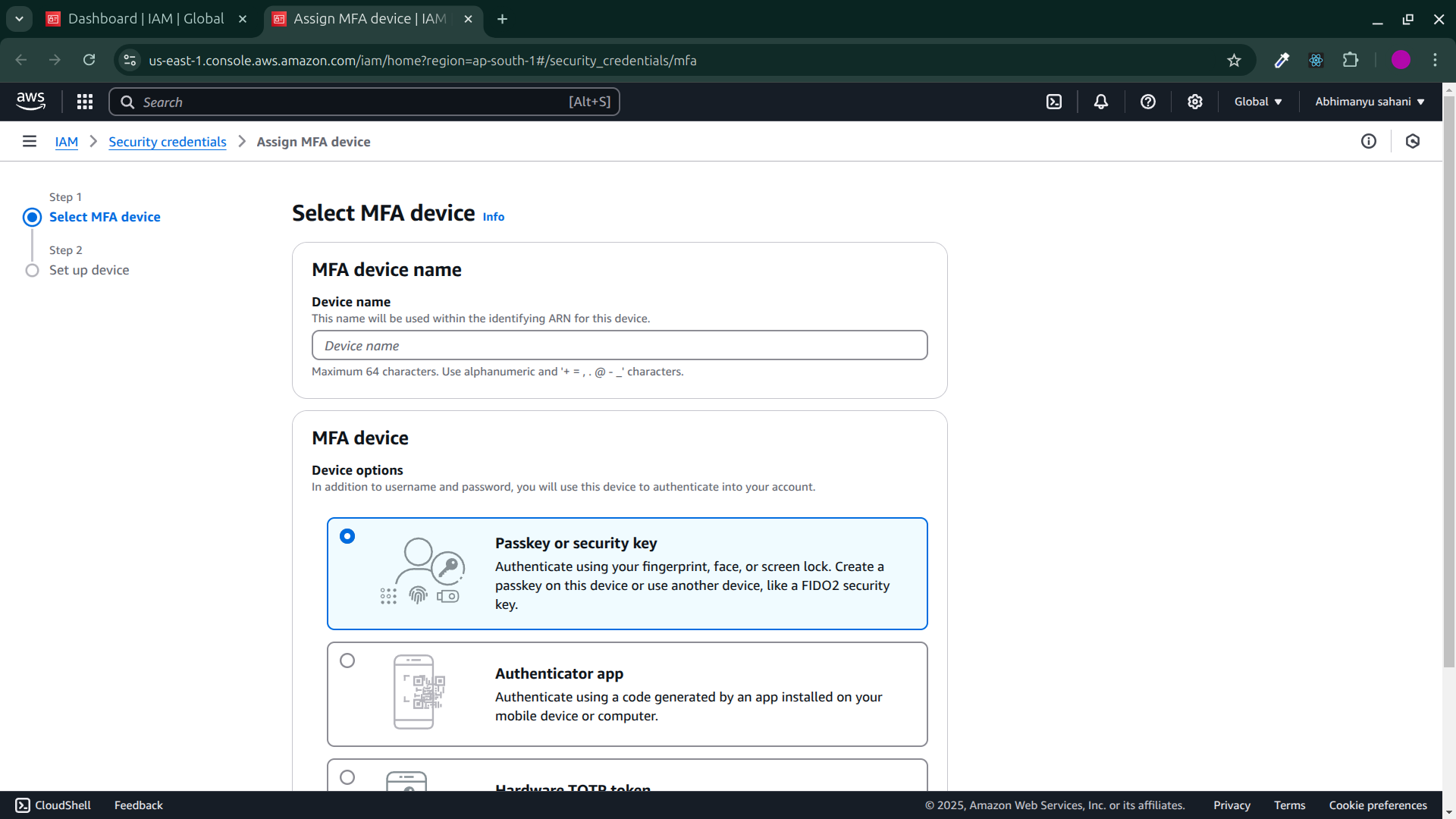
At last click on
next buttonNext you'll see the
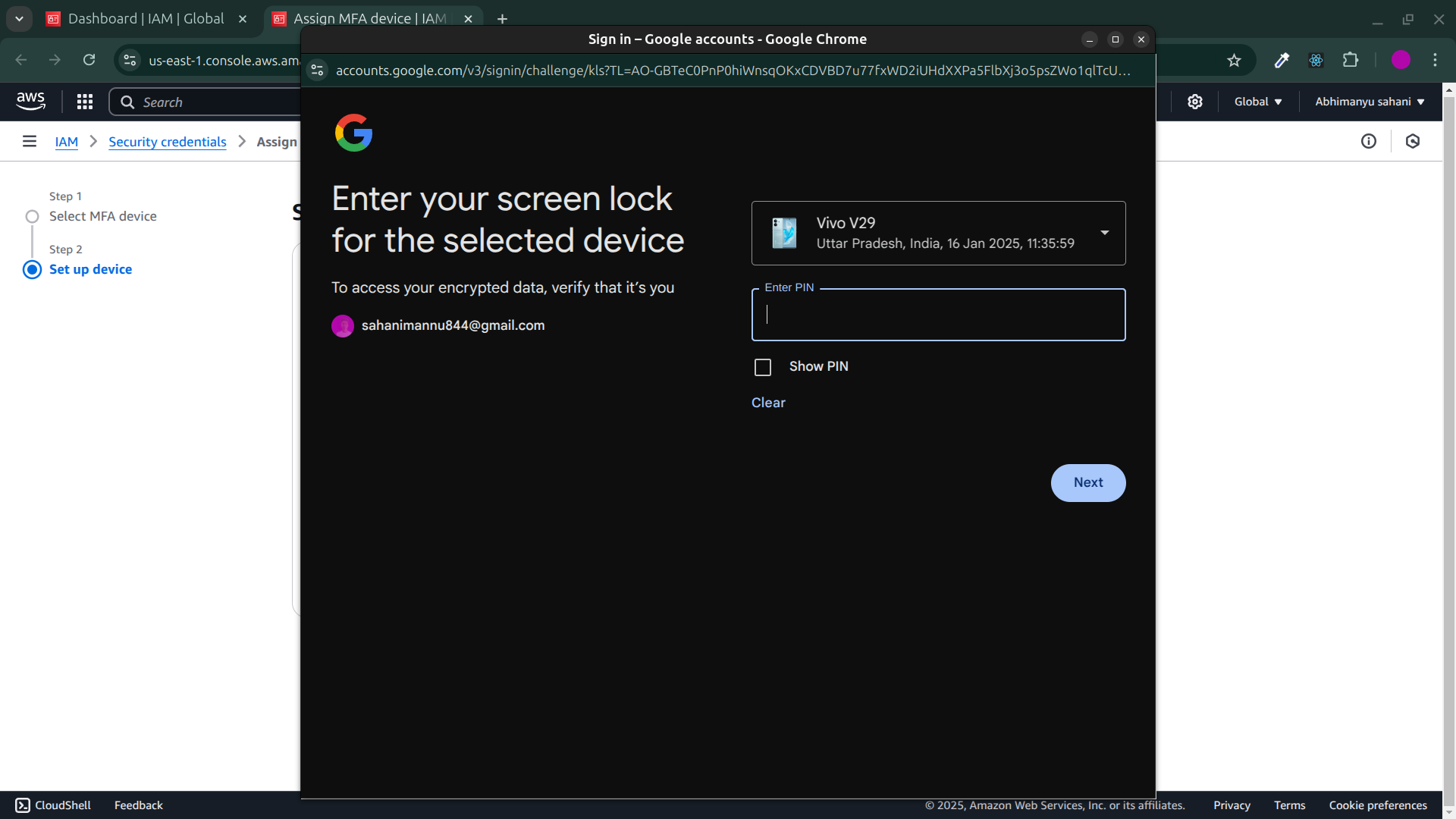
google verification popupEnter the lock-screen password of that devices where that email is logged-in for the confirmation
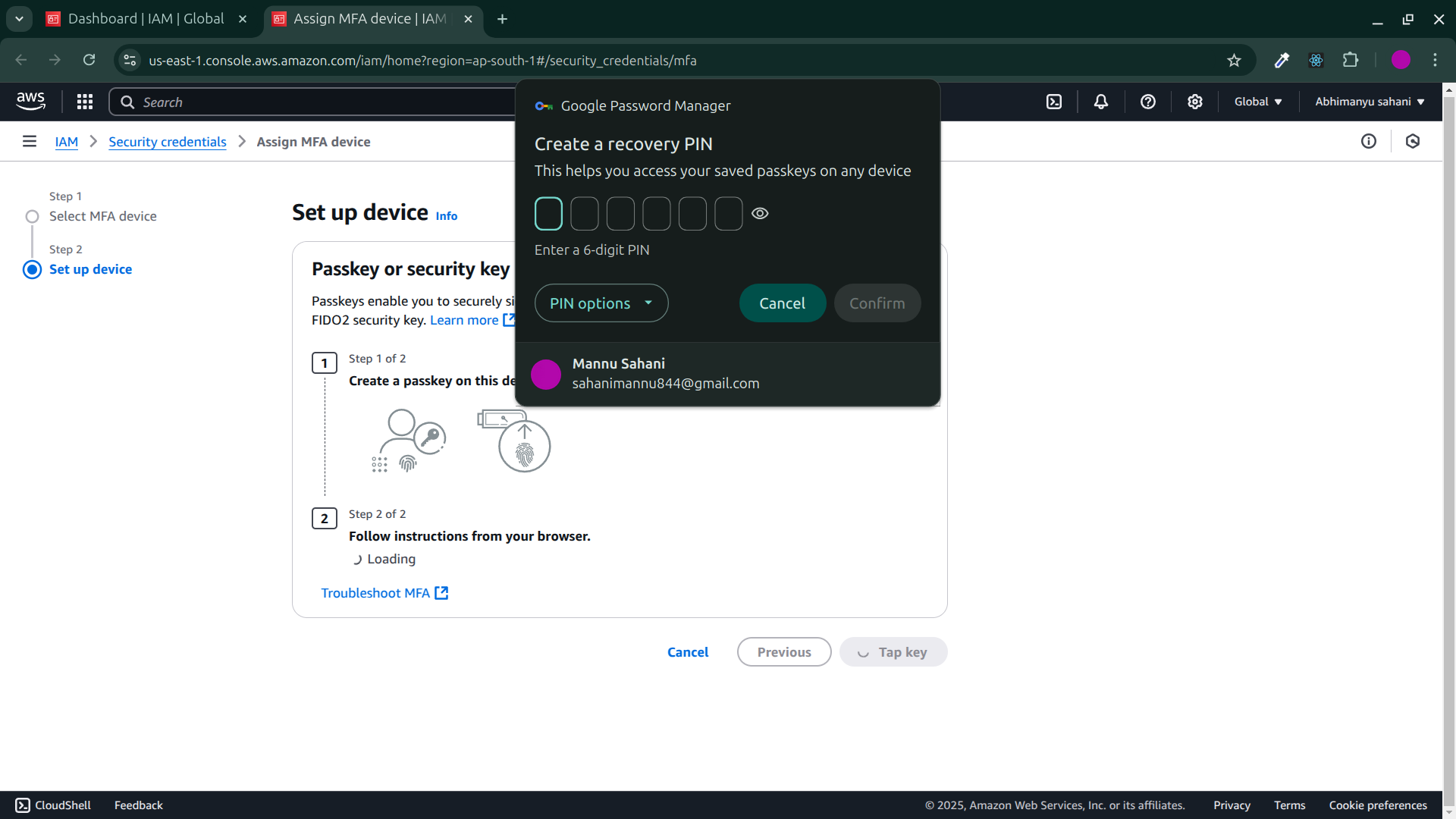
Create a recovery pin and click on confirm.
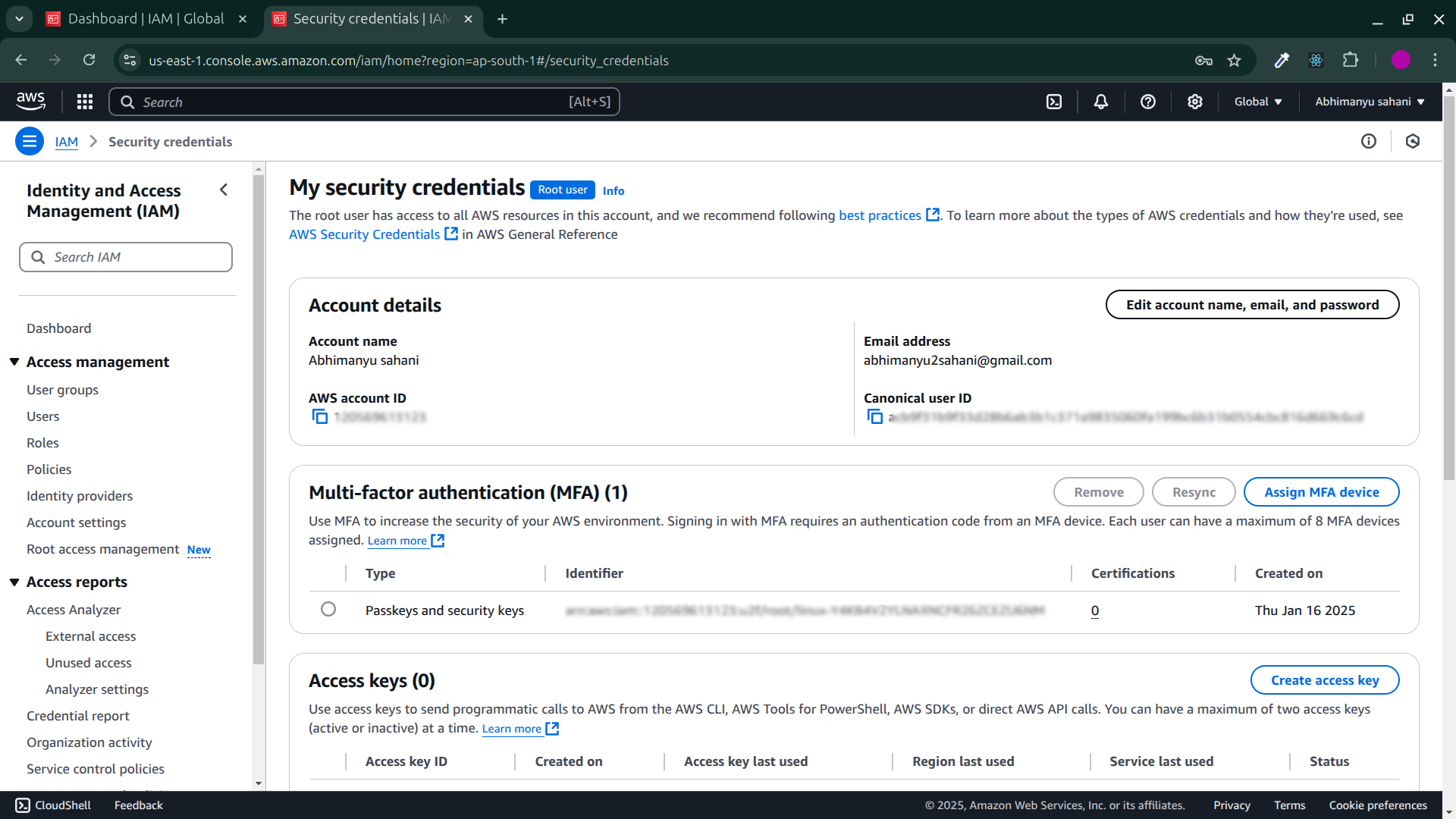
Now you can accounts details.
Account Name
Email Address
AWS account id
Canonical user ID, etc...
How to create IAM User?
Step 1: Sign In to AWS Management Console
Step 2: Search IAM
Step 3: Click on users
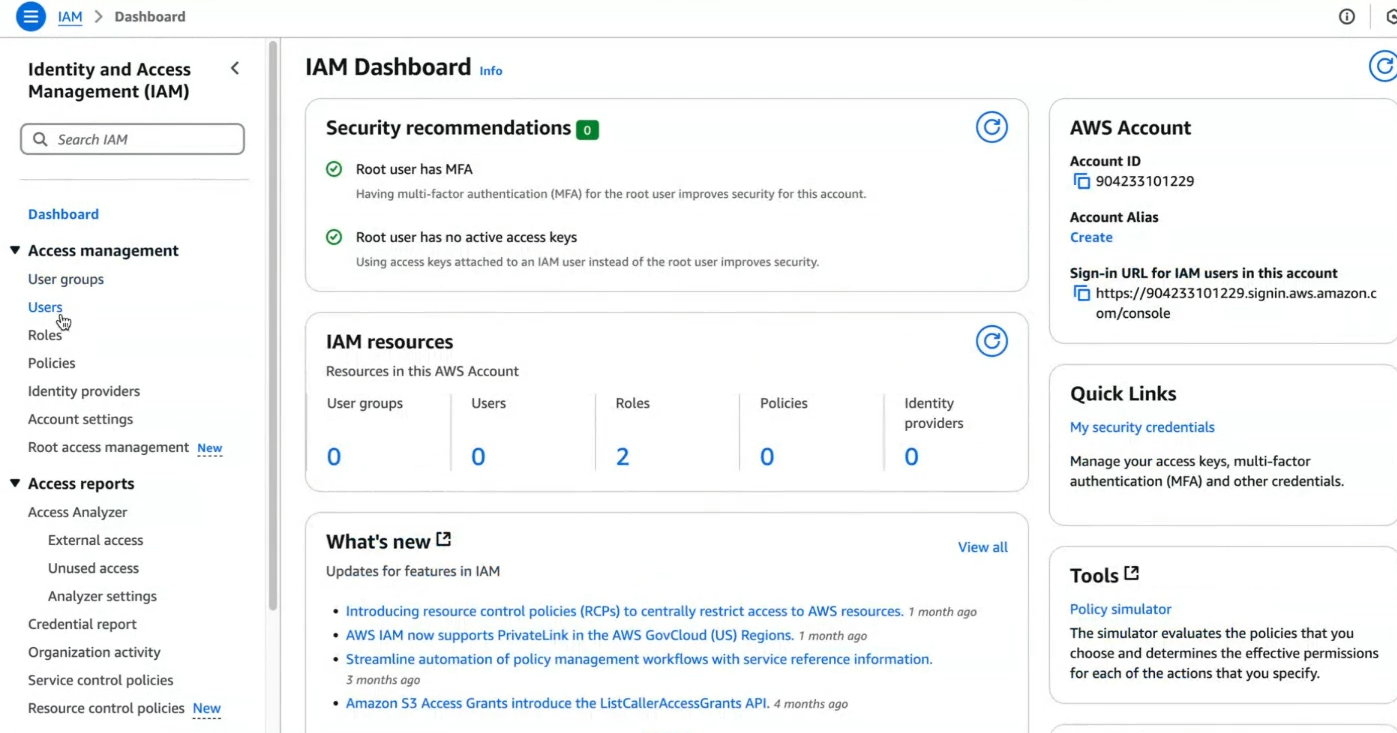
Step 4: Click on create users
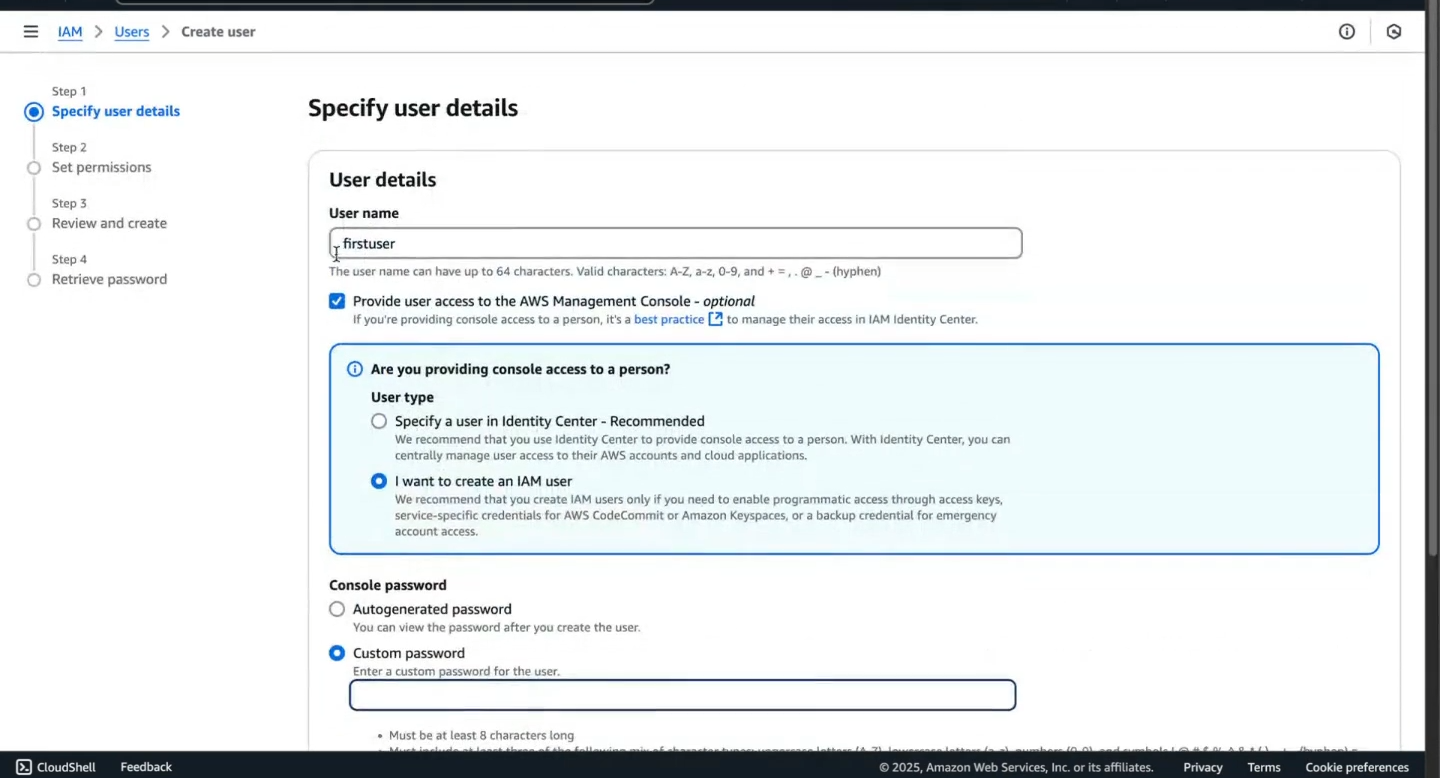
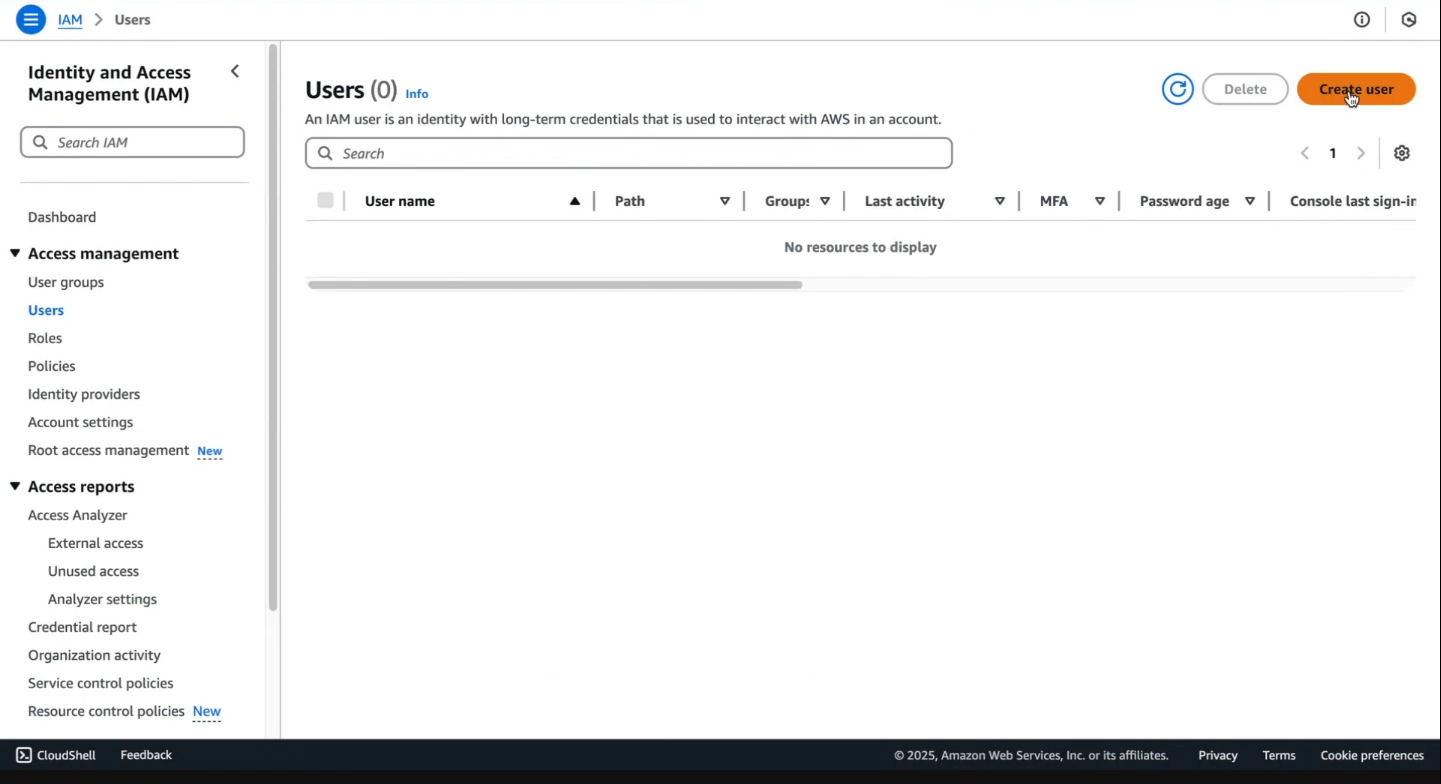 ### Step 5: Specify User Details
### Step 5: Specify User Details1.Enter a user name
2.Select i want to create IAM user
3.Set Password
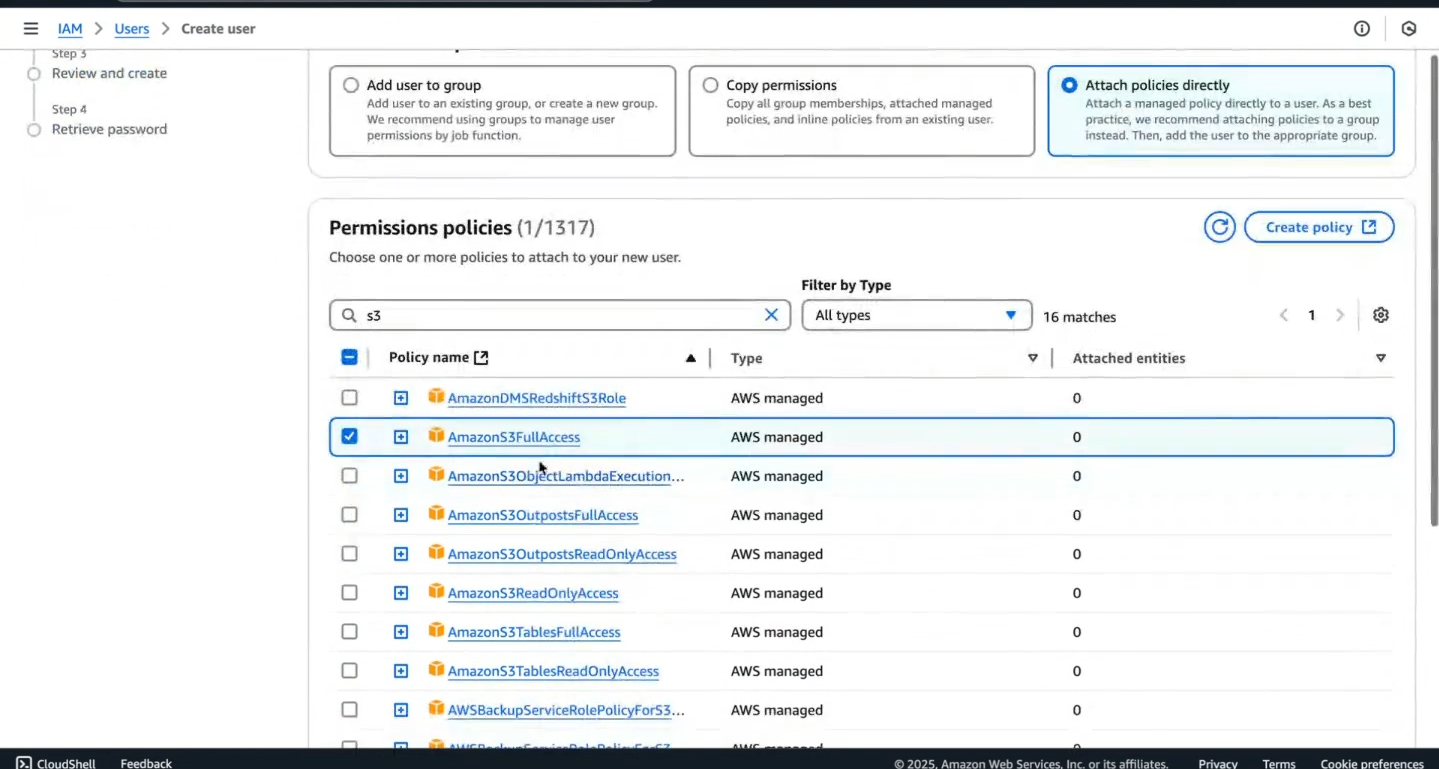
Step 6: Attach policies to user and click next button
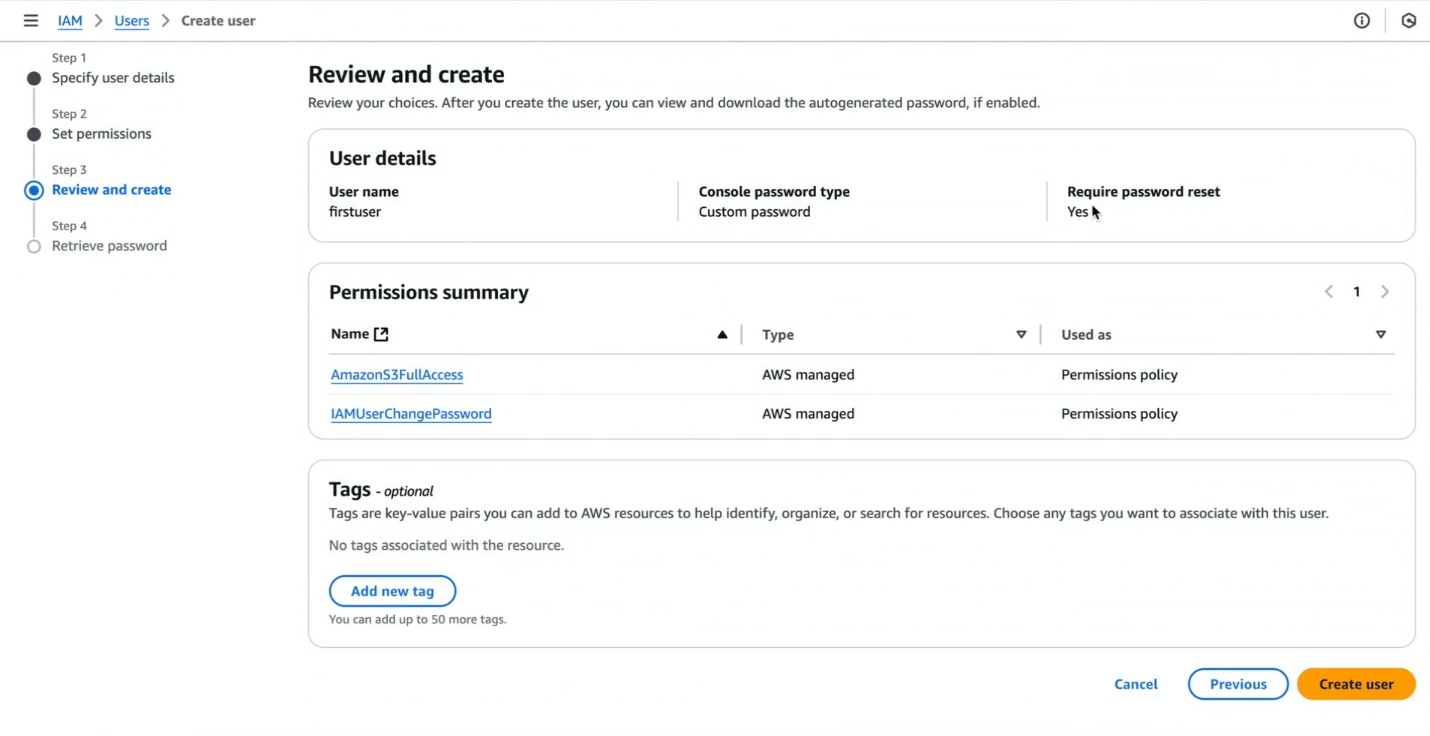
Step 7: Review the details of the user and permissions.
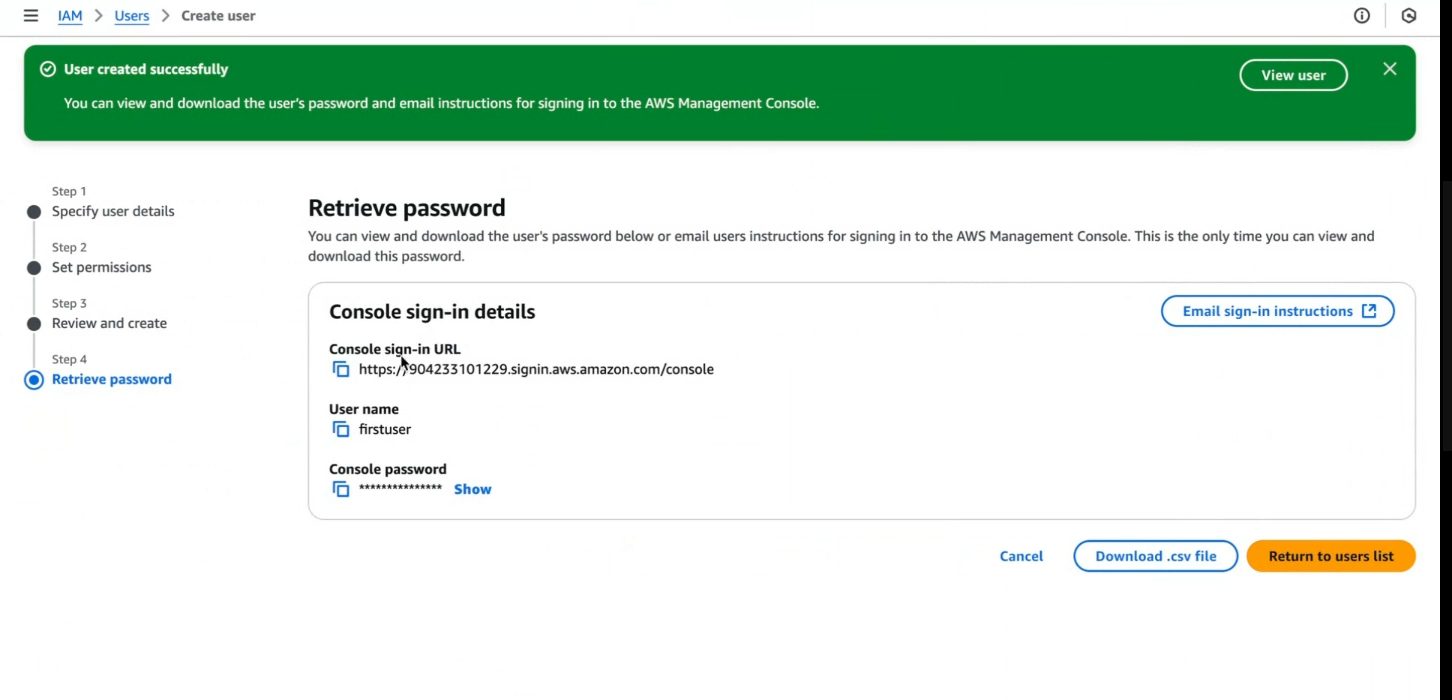
Step 8: Save IAM Credentials.
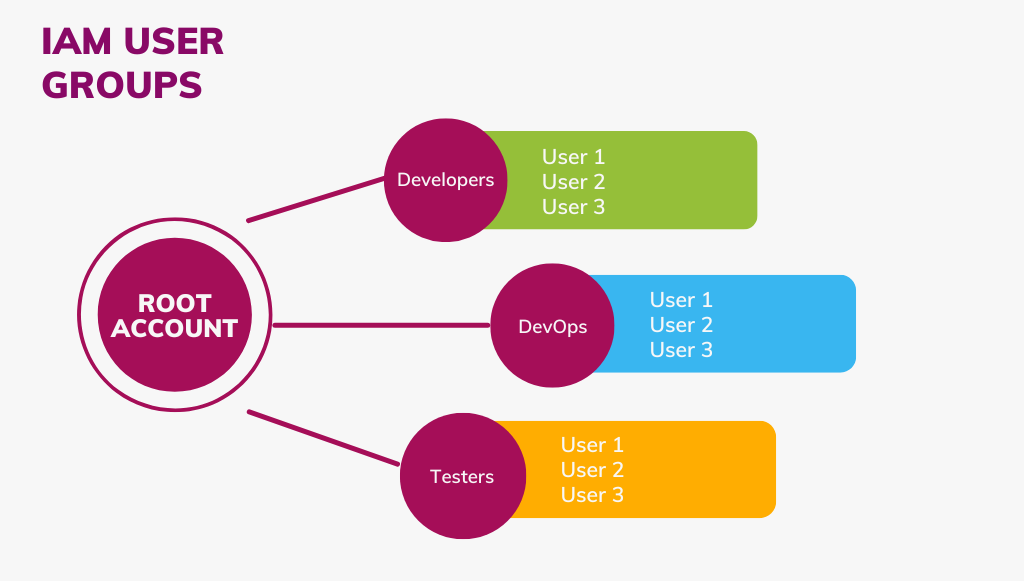
IAM User Groups
The User group is a collection of IAM users. It let you to assign permissions for multiple users, which can make it easier to manage the permissions for those users. So, the users that require the same permissions can be grouped together. A user group can contain many users, and these users can also belong to multiple user groups. Changes made to a group are reflected to all users within that group.
Let's learn how to create IAM user groups and how to add users to groups.
Step 1: Go to the AWS Website
Open your favorite browser and navigate to AWS Login Page
Then enter in your password and click submit. You have now successfully signed in to the AWS Management Console.
Step 2: Search for IAM
In the search bar type IAM and click on IAM(Manage access to AWS resources) to navigate to IAM Dashboard.
Step 3: Start creating user groups
On the left side of the page, you should see an option called Users groups.
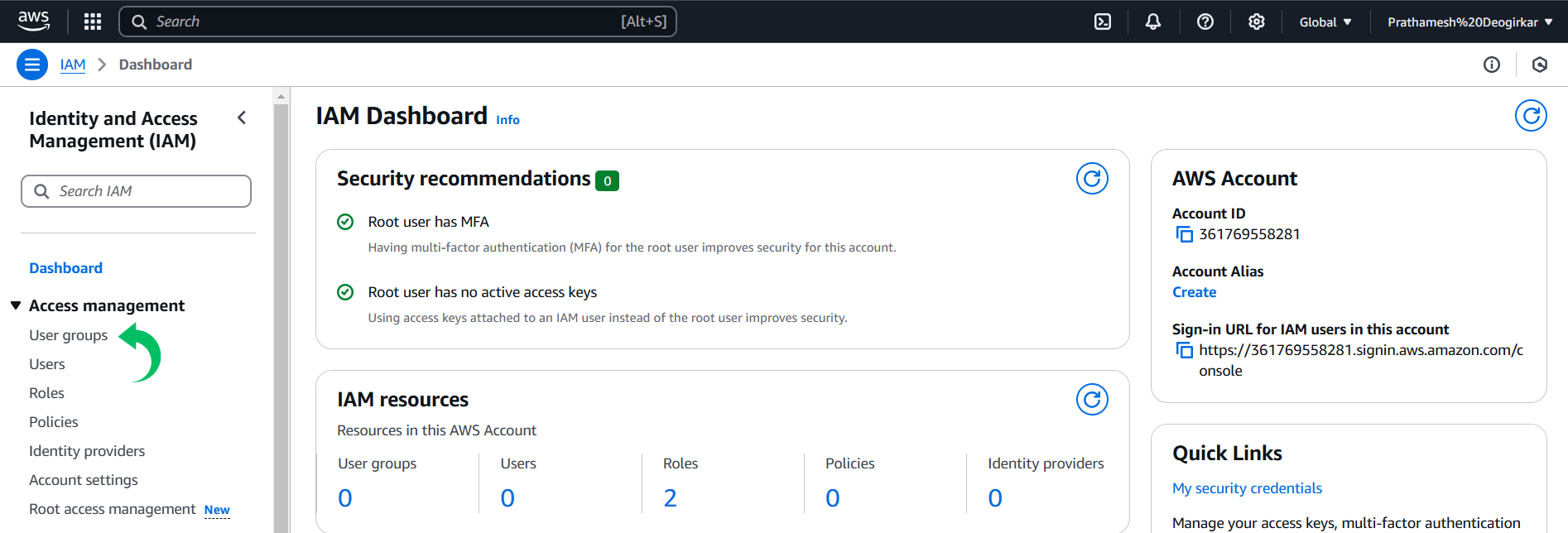
- Click on that option, and you will be taken to the Users groups Page
Step 4: Navigating
Click on create group button to create a user
Step 5: Providing name and permissions
- Provide a Group name
- Select the Users who needed to be a part of the group.
- Provide any permissions from existing policies

- Scroll down and click on Create group button.
Congratulations you have created an IAM User group🤩🤩
Policies in AWS
In simple terms, a Policy is a document that explains what permissions are allowed or denied for a user, group, or role. Policies control access to AWS resources, and they are written in JSON format.
Policies are rules that says what user and groups can do or can't do in AWS
There are three main types of policies in AWS:
Managed Policies:
- These are pre-made policies created and managed by AWS.
- They handle common use cases, like giving read-only access to a storage service.
- You can attach these policies to multiple users, groups, or roles.
- You cannot edit Managed Policies, but you can copy them and make your own custom version.
Customer Policies:
- These are policies created and managed by you (the user).
- They can be attached to multiple users, groups, or roles within your AWS account.
- Customer Policies give you full control over permissions.
Inline Policies:
- These are policies directly linked to a single user, group, or role.
- If the entity (user, group, or role) is deleted, the policy is also deleted.
- Inline Policies are useful for specific, one-off permissions.
So how do we create a Policy?
- We’ll start from the AWS console, search up IAM and then select Policies. After that we’ll select Create Policy.
- There are two ways to create policies in the console.
- policies are essentially JSON documents, so we can just write it up.
- Optionally we can use the console’s excellent policy maker:
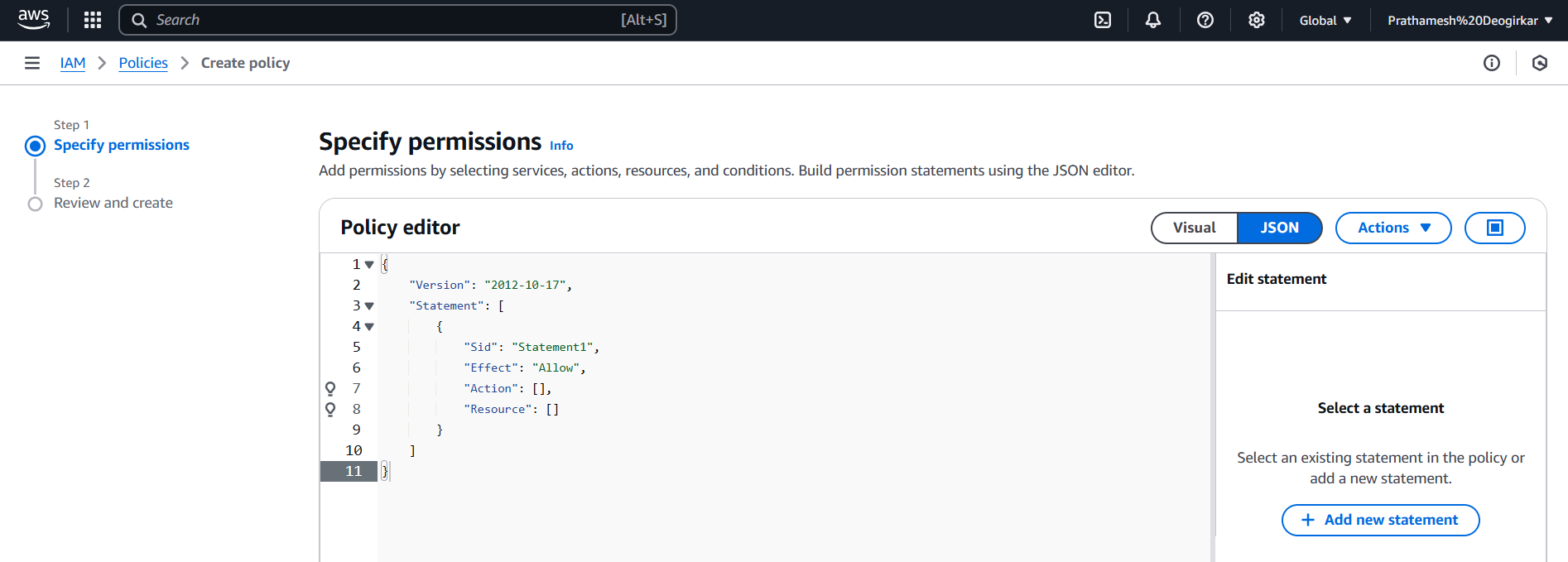
- After this step, we can add tags to make it easier to find our policy, and give it a name.
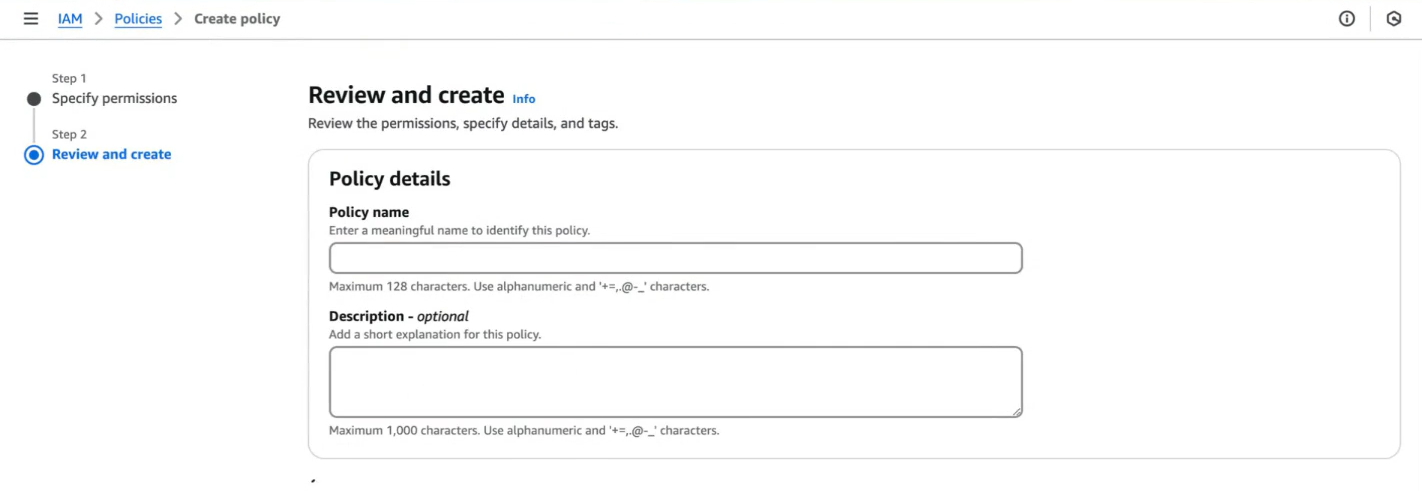
So we have our policy. Now we just need to attach it to an entity How do we do it?
We just need to select a user and Add Permission.
Click on create policy.
and here we done. 🥳
Examples of IAM Policies
Here are some examples of simple IAM policies for common use cases:
Allow read-only access to an S3 bucket
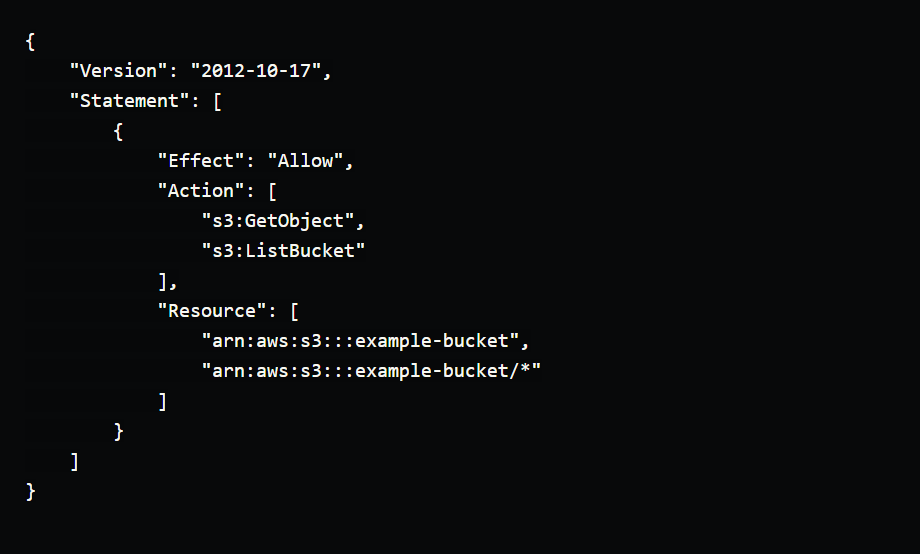
This policy allows a user to read objects from the example-bucket S3 bucket and list the contents of the bucket, but does not allow them to upload or modify objects.
Allow read-only access to an RDS instance
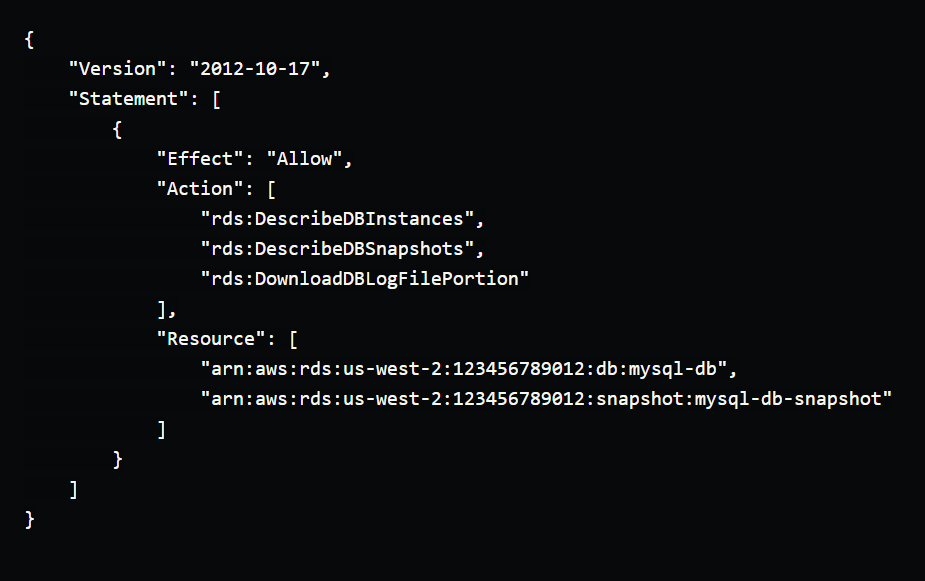
This policy allows a user to view information about the mysql-db RDS instance and download log files, but does not allow them to perform any modifications.
Allow full access to an EC2 instance
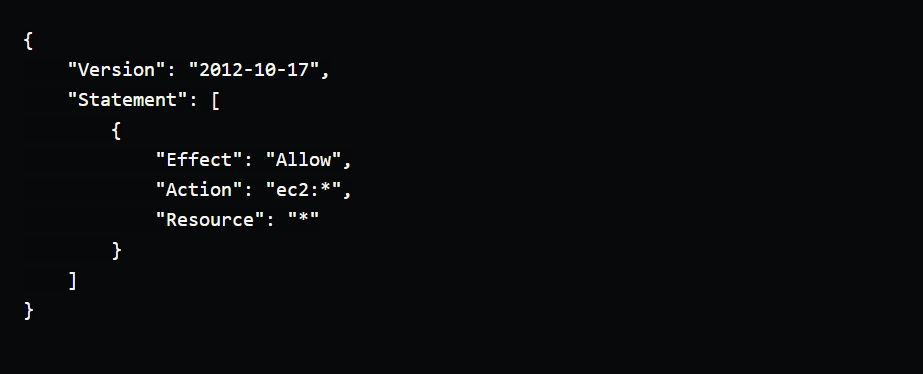
This policy allows a user to perform any action on any EC2 instance in the account.
Role in AWS
What is an IAM Role in AWS?
A role is a set of permissions that defines what actions can be perform on AWS resources.
IAM roles are similar to IAM users, but with some important differences.
IAM roles are not associated with a specific user or group. Instead, they are intended to be assumed by anyone who needs the permissions associated with the role.
IAM roles are a way to delegate access to AWS resources without the need to create and manage long-term AWS credentials.
For example, you might create an IAM role that grants access to an S3 bucket, and then allow a Lambda function to assume that role when it needs to access the bucket.
This way, you don't need to manage access keys for the Lambda function, and you can maintain tighter control over who has access to the S3 bucket.
Main Elements of an IAM Role

Understanding AWS IAM Role Assumption
Assuming an AWS IAM Role means temporarily using the permissions and policies linked to that role. This is done through the AWS Security Token Service (STS) API, which provides temporary security credentials. These credentials include:
- Access Key
- Secret Access Key
- Security Token
Who Can Assume a Role? For a user to assume a role, they must have permission, which is granted by the role's Trust Policy. This trust policy defines which users or services are allowed to assume the role.
Ways to Assume an IAM Role There are different methods to assume a role in AWS:
- AWS Management Console
- AWS CLI (Command Line Interface)
- AWS SDKs
- AssumeRole API
How Long Can You Use the Temporary Credentials?
- The temporary credentials are valid for a limited time, known as the session duration.
- By default, this duration is set to 1 hour but can be extended to a maximum of 12 hours, depending on the role's session duration policy.
Key Points to Remember
- Always check the Trust Policy to confirm who can assume a role.
- Use the temporary credentials to access resources only during the valid session duration.
- Choose the right method (Console, CLI, SDK, or API) based on your requirement.
This process is useful for managing permissions and securely accessing resources in AWS.